遗传 ›› 2025, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (7): 768-785.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.25-007
程芙蓉1,2( ), 宋文煜2, 曹鹏博2, 周钢桥1,2(
), 宋文煜2, 曹鹏博2, 周钢桥1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2025-01-06
修回日期:2025-03-17
出版日期:2025-03-26
发布日期:2025-03-26
通讯作者:
周钢桥,博士,研究员,研究方向:医学遗传与基因组学。E-mail: zhougq114@126.com作者简介:程芙蓉,硕士研究生,专业方向:生物学。E-mail: 1578877852@qq.com
基金资助:
Furong Cheng1,2( ), Wenyu Song2, Pengbo Cao2, Gangqiao Zhou1,2(
), Wenyu Song2, Pengbo Cao2, Gangqiao Zhou1,2( )
)
Received:2025-01-06
Revised:2025-03-17
Published:2025-03-26
Online:2025-03-26
Supported by:摘要:
抵抗失巢凋亡(anoikis)进而促进癌细胞存活是许多癌症发生、发展的关键特征。肝细胞癌(hepatocellular carcinoma,HCC)是一种复发率高、转移性强的恶性肿瘤,但其失巢凋亡相关研究仍然较少。因此,基于失巢凋亡相关基因(anoikis-related gene,ARG)预测HCC的预后及免疫微环境变化,可为基于失巢凋亡的治疗策略提供新的理论依据。本文基于癌症基因组图谱(The Cancer Genome Atlas,TCGA)HCC转录组数据,鉴定出74个在肝癌中显著差异表达的ARG。通过LASSO-Cox回归模型建立了包含其中9个特征基因的HCC预后风险评分模型。多因素Cox比例风险回归分析表明,该模型能准确预测患者总体生存率,是HCC新的独立预后指标。基于ARG建立的不同风险组在通路活性、免疫细胞浸润和HCC患者生存状态等多方面存在显著差异。与低风险组相比,高风险组中细胞增殖相关通路显著活化,免疫抑制性细胞的浸润比例显著增加,且与肝癌患者对PD-L1单抗治疗耐药相关。上述结果表明,本研究建立的ARG风险评分模型作为一种新的指标可以预测HCC患者的预后,并初步揭示了ARG在肝癌进展中的重要作用。
程芙蓉, 宋文煜, 曹鹏博, 周钢桥. 失巢凋亡相关转录特征预测肝癌预后和免疫微环境的潜在价值[J]. 遗传, 2025, 47(7): 768-785.
Furong Cheng, Wenyu Song, Pengbo Cao, Gangqiao Zhou. Potential value of anoikis transcriptional signatures in predicting prognosis and immune microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2025, 47(7): 768-785.
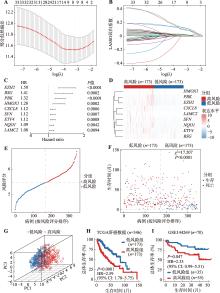
图2
肝癌相关ARG预后风险模型的构建及验证 A:通过10倍交叉验证确定LASSO回归模型最佳惩罚因子;B:33个ARG的LASSO回归系数曲线。不同的颜色代表不同的基因;C:森林图显示单因素Cox回归分析显示9个最佳预后ARG的HR和95% CI;D:热图展示了9个最佳预后ARG在TCGA肝癌患者(346例)中的表达水平;E:根据风险评分对肝癌患者进行排序;F:散点图展示了HCC患者生存时间与预后风险评分的相关性。使用χ2检验计算P值;G:三维散点PCA图展示了高风险和低风险评分的肝癌患者;H:根据ARG预后风险模型,分析TCGA肝癌队列中高风险组和低风险组的肝癌患者的Kaplan-Meier生存曲线;I:根据ARG预后风险模型,验证GSE144269队列中具有高风险和低风险评分的肝癌患者的Kaplan-Meier生存曲线。Cox回归分析计算风险比(HR)和95%置信区间(CI),log-rank检验计算P值。HR:风险比;CI:置信区间;PCA:主成分分析;TCGA:癌症基因组图谱。"
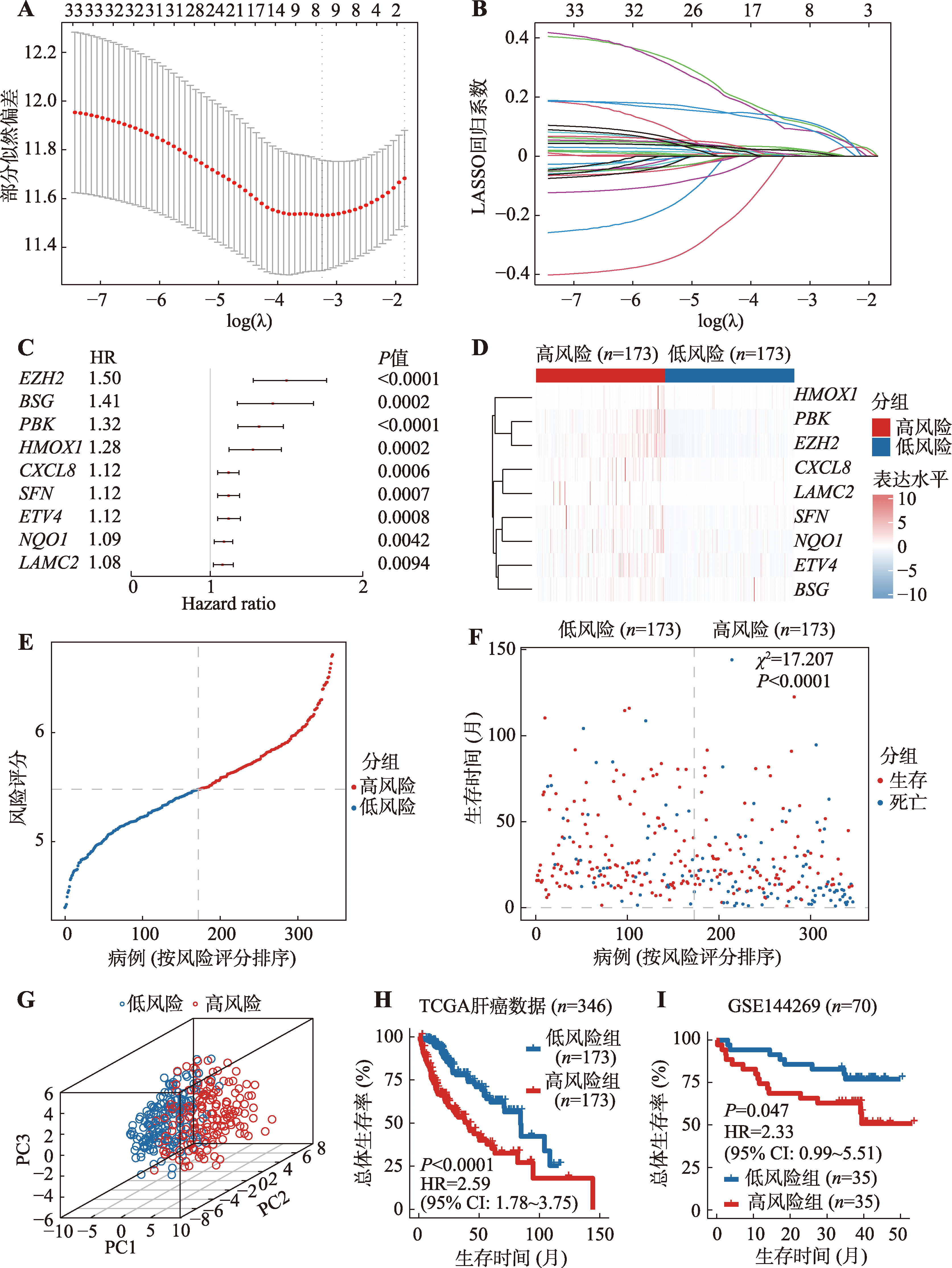

图6
失巢凋亡相关基因对免疫细胞浸润的影响 A:根据风险评分,通过CIBERSORT预测TCGA-LIHC肿瘤中22种免疫细胞比例的热图;B:免疫细胞比例和风险评分之间相关性的热图。运用Spearman相关性分析计算相关系数(Rho);C:高风险组和低风险组免疫细胞浸润情况。采用Kruskal-Wallis检验计算显著差异;D:高风险和低风险组中13种免疫功能特征打分情况;E:风险评分和免疫检查点表达水平的相关性热图。运用Spearman相关性分析计算相关系数(Rho);F:高风险和低风险组中免疫检查点的表达水平分析。采用Kruskal-Wallis检验计算显著差异。GSEA:基因集富集分析;TPM:转录本每百万读数;APC:抗原呈递细胞;CCR:C-C趋化因子受体;HLA:人类白细胞抗原;MHC:主要组织相容性复合体;IFN:干扰素。*:P<0.05,**:P< 0.01,***:P<0.001,****:P< 0.0001,ns表示不显著(non-significant)。"
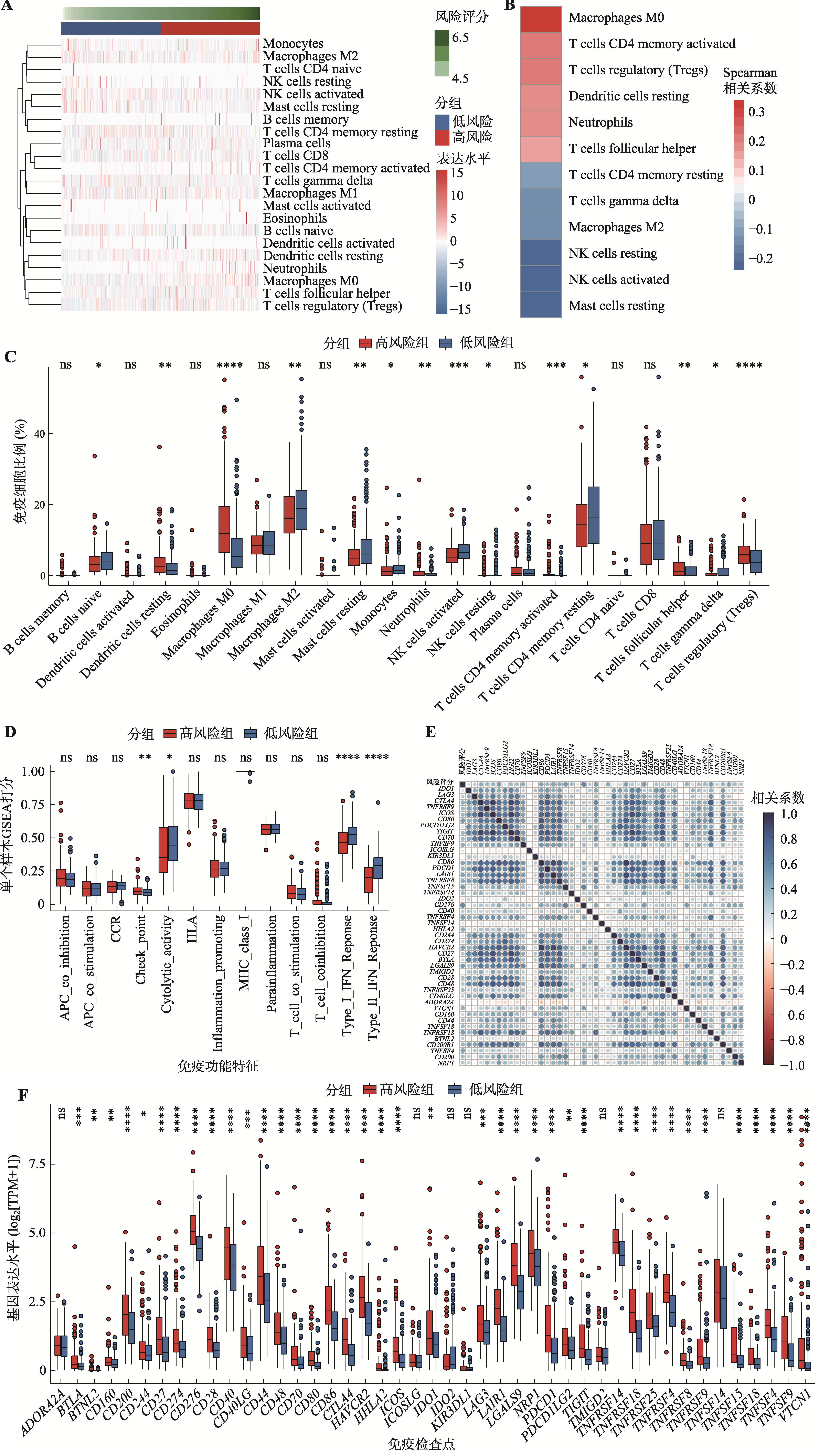
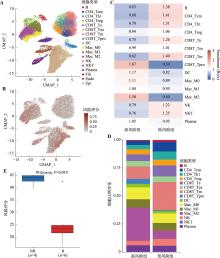
图7
ARG风险评分在肝癌微环境中各细胞类型中的分布及其与肝癌患者免疫治疗响应之间的关系 A:UMAP图展示了肝癌肿瘤微环境中主要细胞类型的分布情况。肝癌单细胞转录组数据来源于GSE149614(包括10例肝癌患者肿瘤样本的40,373个单细胞);B:ARG风险评分在肝癌微环境的各细胞类型中的活性;C:高风险组和低风险组中免疫细胞富集情况。采用Ro/e指数进行组间差异比较;D:高风险组和低风险组免疫细胞浸润比例变化;E:ARG风险评分在肝癌PD-L1单抗治疗队列中响应和未响应患者中的分布差异。此队列基因表达谱数据集来源于GSE279750(包括10例肝癌患者),采用秩和检验计算P值。NR:无响应患者;R:响应患者;Ro/e:观察到的细胞数与预期细胞数的比值;Tcm:中央记忆T细胞;Th1:辅助I型T细胞;Treg:调节T细胞;Te:效应T细胞;Tex:耗竭T细胞;Tm:记忆T细胞;Tpro:增殖T细胞;DC:树突状细胞;Mac:巨噬细胞;NK:自然杀伤性细胞;NKT:自然杀伤性T细胞;Fib:成纤维细胞;Endo:内皮细胞;Epi:上皮细胞。"
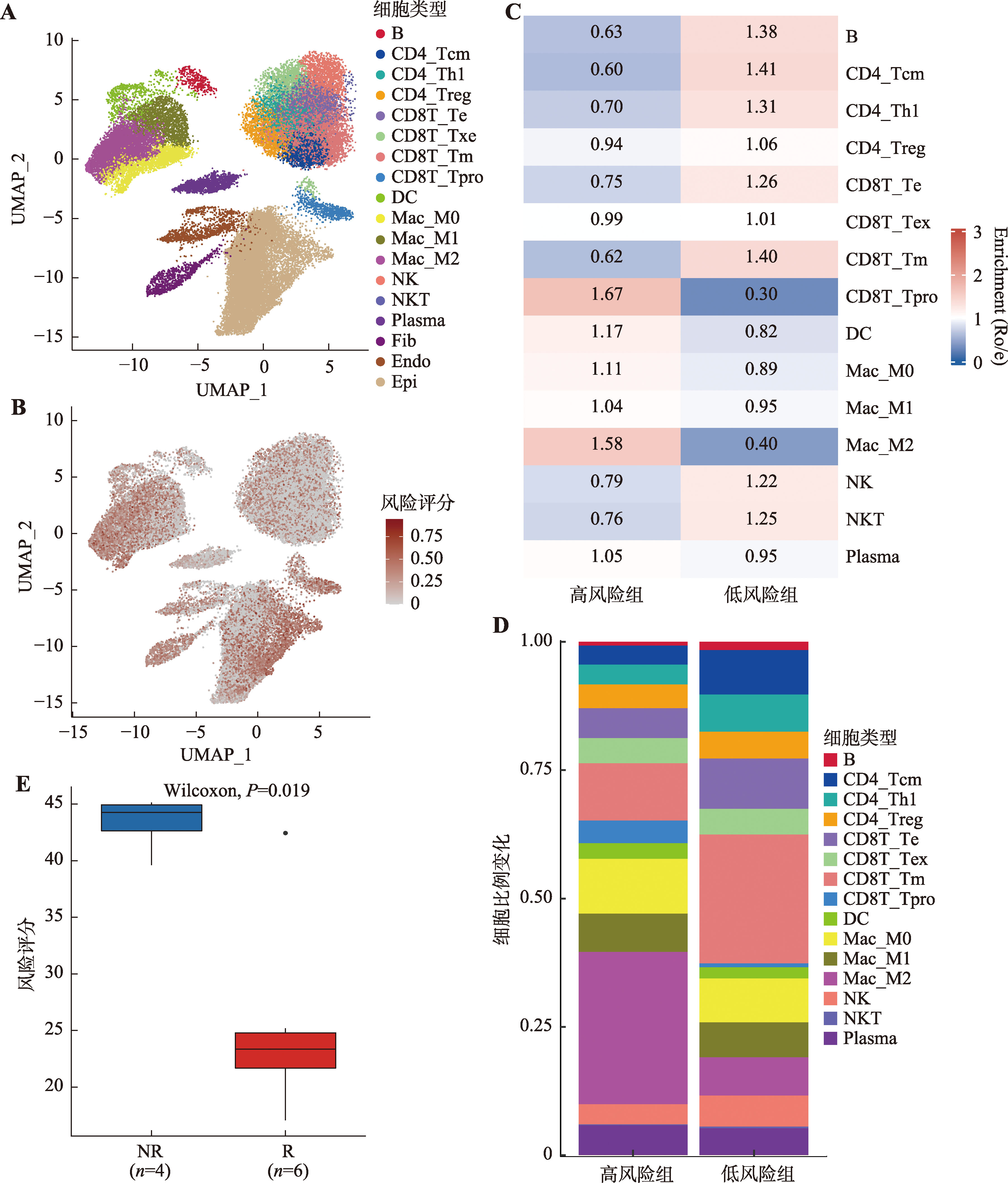
图8
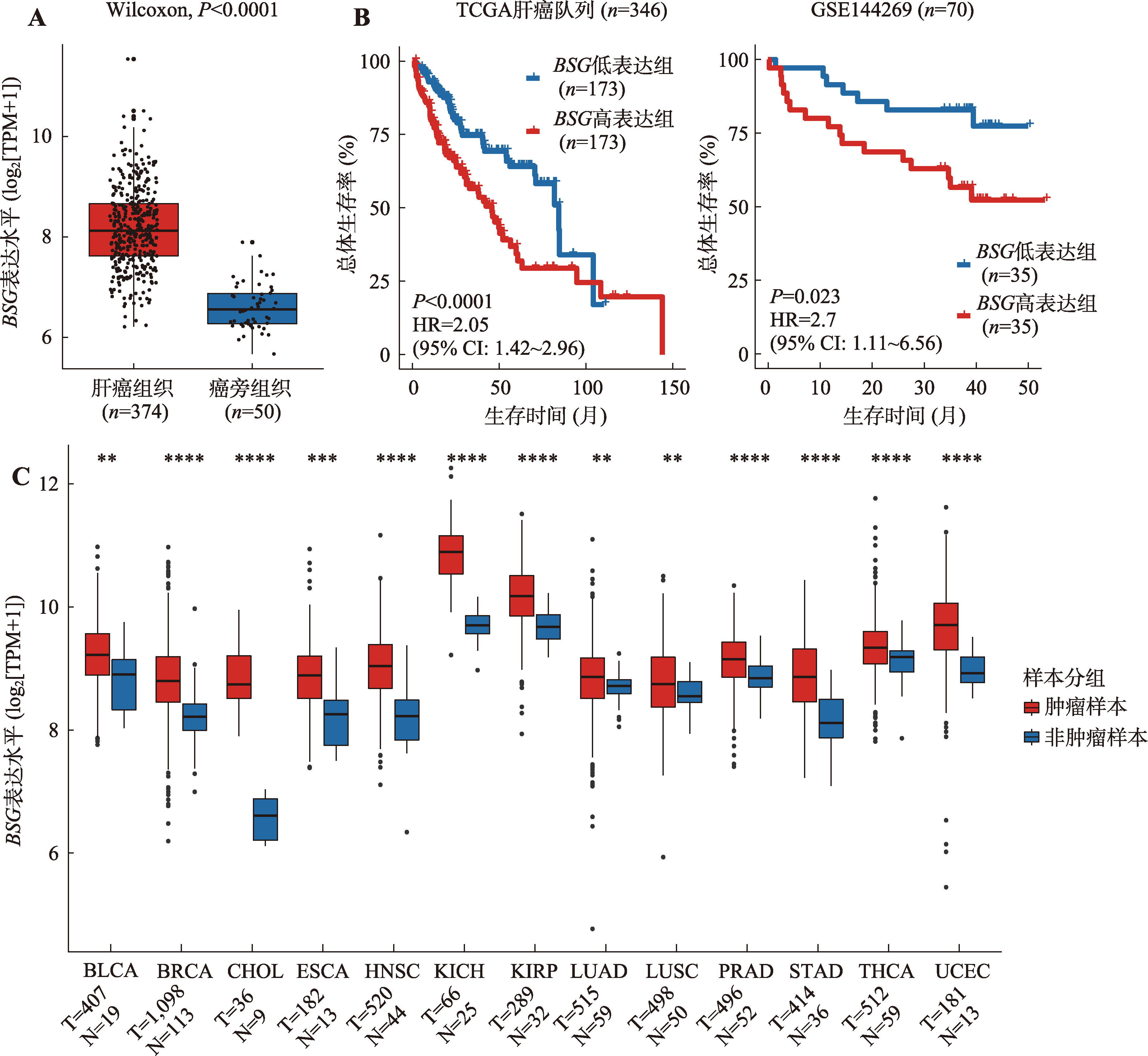
BSG在多种肿瘤中表达显著上调,且与肝癌的不良预后显著相关 A:BSG在肝癌与非肿瘤组织中的表达水平。运用秩和检验计算P值;B:BSG在肝癌中的表达与生存率之间的相关性分析。运用Kaplan-Meier生存分析绘制不同组别的生存曲线,Cox回归分析计算风险比(HR)和95%置信区间(CI),log-rank检验计算P值;C:BSG在13种肿瘤中的表达水平。HR:风险比;CI:置信区间;TCGA:癌症基因组图谱;TPM:转录本每百万读数;BLAC:膀胱尿路上皮癌;BRCA:乳腺浸润性癌;CHOL:胆管癌;ESCA:食管癌;HNSC:头颈部鳞状细胞癌;KICH:肾嫌色细胞癌;KIRC:肾透明细胞癌;LUAD:肺腺癌;LUSC:肺鳞状细胞癌;PRAD:前列腺腺癌;STAD:胃腺癌;THCA:甲状腺癌;UCEC:子宫内膜癌;T:肿瘤样本;N:非肿瘤样本。*:P<0.05,**:P< 0.01,***:P<0.001,ns表示不显著(non-significant)。"
| [1] |
Huang DQ, Mathurin P, Cortez-Pinto H, Loomba R. Global epidemiology of alcohol-associated cirrhosis and HCC: trends, projections and risk factors. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2023, 20(1): 37-49.
pmid: 36258033 |
| [2] |
Balitzer DJ, Greenland NY. The utility of next-generation sequencing in challenging liver FNA biopsies. Cancer Cytopathol, 2024, 132(11): 714-722.
pmid: 39097802 |
| [3] |
Watanabe T, Bertoletti A, Tanoto TA. PD-1/PD-L1 pathway and T-cell exhaustion in chronic hepatitis virus infection. J Viral Hepat, 2010, 17(7): 453-458.
pmid: 20487259 |
| [4] |
Ando S, Perkins CM, Sajiki Y, Chastain C, Valanparambil RM, Wieland A, Hudson WH, Hashimoto M, Ramalingam SS, Freeman GJ, Ahmed R, Araki K. mTOR regulates T cell exhaustion and PD-1-targeted immunotherapy response during chronic viral infection. J Clin Invest, 2023, 133(2): e160025.
pmid: 36378537 |
| [5] |
Chakraborty E, Sarkar D. Emerging therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Cancers (Basel), 2022, 14(11): 2798.
pmid: 35681776 |
| [6] |
Forner A, Reig M, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet, 2018, 391(10127): 1301-1314.
pmid: 29307467 |
| [7] |
Paoli P, Giannoni E, Chiarugi P. Anoikis molecular pathways and its role in cancer progression. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2013, 1833(12): 3481-3498.
pmid: 23830918 |
| [8] | Yang Y, Wang BS, Wang XM, Zhang Y, Wang MR, Jia XM. Screening and identification of anoikis-resistant gene UBCH7 in esophageal cancer cells. Hereditas (Beijing), 2012, 34(2): 190-197. |
| 杨扬, 王博石, 汪晓敏, 张钰, 王明荣, 贾雪梅. 食管癌细胞抗失巢凋亡基因UBCH7的发现与鉴定. 遗传, 2012, 34(2): 190-197. | |
| [9] |
de Sousa Mesquita AP, de Araújo Lopes S, Pernambuco Filho PCA, Nader HB, Lopes CC. Acquisition of anoikis resistance promotes alterations in the Ras/ERK and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways and matrix remodeling in endothelial cells. Apoptosis, 2017, 22(9): 1116-1137.
pmid: 28653224 |
| [10] |
Simpson CD, Anyiwe K, Schimmer AD. Anoikis resistance and tumor metastasis. Cancer Lett, 2008, 272(2): 177-185.
pmid: 18579285 |
| [11] |
Chiarugi P, Giannoni E. Anoikis: a necessary death program for anchorage-dependent cells. Biochem Pharmacol, 2008, 76(11): 1352-1364.
pmid: 18708031 |
| [12] |
Tajbakhsh A, Rivandi M, Abedini S, Pasdar A, Sahebkar A. Regulators and mechanisms of anoikis in triple- negative breast cancer (TNBC): a review. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol, 2019, 140: 17-27.
pmid: 31154235 |
| [13] |
Candia J, Bayarsaikhan E, Tandon M, Budhu A, Forgues M, Tovuu LO, Tudev U, Lack J, Chao A, Chinburen J, Wang XW. The genomic landscape of mongolian hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Commun, 2020, 11(1): 4383.
pmid: 32873799 |
| [14] |
Gui MH, Huang SL, Li SZ, Chen YY, Cheng FR, Liu YL, Wang JA, Wang YT, Guo R, Lu YM, Cao PB, Zhou GQ. Integrative single-cell transcriptomic analyses reveal the cellular ontological and functional heterogeneities of primary and metastatic liver tumors. J Transl Med, 2024, 22(1): 206.
pmid: 38414027 |
| [15] |
Xie PY, Guo L, Yu Q, Zhao YF, Yu MC, Wang H, Wu MY, Xu WX, Xu M, Zhu XD, Xu YF, Xiao YS, Huang C, Zhou J, Fan J, Hung MC, Sun HC, Ye QH, Zhang B, Li H. ACE2 enhances sensitivity to PD-L1 blockade by inhibiting macrophage-induced immunosuppression and angiogenesis. Cancer Res, 2025, 85(2): 299-313.
pmid: 39495239 |
| [16] |
Diao XY, Guo C, Li SQ. Identification of a novel anoikis-related gene signature to predict prognosis and tumor microenvironment in lung adenocarcinoma. Thorac Cancer, 2023, 14(3): 320-330.
pmid: 36507553 |
| [17] |
Chen YT, Huang WR, Ouyang J, Wang JX, Xie ZW. Identification of anoikis-related subgroups and prognosis model in liver hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(3): 2862.
pmid: 36769187 |
| [18] |
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu YF, Law CW, Shi W, Smyth GK. Limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res, 2015, 43(7): e47.
pmid: 25605792 |
| [19] | Friedman J, Hastie T, Tibshirani R. Regularization paths for generalized linear models via coordinate descent. J Stat Softw, 2010, 33(1): 1-22. [DOI] |
| [20] |
Peng T, Sun F, Yang JC, Cai MH, Huai MX, Pan JX, Zhang FY, Xu LM. Novel lactylation-related signature to predict prognosis for pancreatic adenocarcinoma. World J Gastroenterol, 2024, 30(19): 2575-2602.
pmid: 38817665 |
| [21] |
Steyerberg EW, Vergouwe Y. Towards better clinical prediction models: seven steps for development and an ABCD for validation. Eur Heart J, 2014, 35(29): 1925-1931.
pmid: 24898551 |
| [22] |
Blanche P, Dartigues JF, Jacqmin-Gadda H. Estimating and comparing time-dependent areas under receiver operating characteristic curves for censored event times with competing risks. Stat Med, 2013, 32(30): 5381-5397.
pmid: 24027076 |
| [23] |
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK, Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, Paulovich A, Pomeroy SL, Golub TR, Lander ES, Mesirov JP. Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2005, 102(43): 15545-15550.
pmid: 16199517 |
| [24] |
Newman AM, Liu CL, Green MR, Gentles AJ, Feng WG, Xu Y, Hoang CD, Diehn M, Alizadeh AA. Robust enumeration of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles. Nat Methods, 2015, 12(5): 453-457.
pmid: 25822800 |
| [25] |
Hänzelmann S, Castelo R, Guinney J. GSVA: gene set variation analysis for microarray and RNA-seq data. BMC Bioinformatics, 2013, 14: 7.
pmid: 23323831 |
| [26] |
He Y, Jiang ZH, Chen C, Wang XS. Classification of triple-negative breast cancers based on Immunogenomic profiling. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2018, 37(1): 327.
pmid: 30594216 |
| [27] |
Ma PJ, Amemiya HM, He LL, Gandhi SJ, Nicol R, Bhattacharyya RP, Smillie CS, Hung DT. Bacterial droplet- based single-cell RNA-seq reveals antibiotic-associated heterogeneous cellular states. Cell, 2023, 186(4): 877-891.
pmid: 36708705 |
| [28] |
Zhang L, Yu X, Zheng LT, Zhang YY, Li YS, Fang Q, Gao RR, Kang BX, Zhang QM, Huang JY, Konno H, Guo XY, Ye YJ, Gao SY, Wang S, Hu XD, Ren XW, Shen ZL, Ouyang WJ, Zhang ZM. Lineage tracking reveals dynamic relationships of T cells in colorectal cancer. Nature, 2018, 564(7735): 268-272.
pmid: 30479382 |
| [29] |
Wu TZ, Hu EQ, Xu SB, Chen MJ, Guo PF, Dai ZH, Feng TZ, Zhou L, Tang WL, Zhan L, Fu XC, Liu SS, Bo XC, Yu GC. ClusterProfiler 4.0: a universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data. Innovation (Camb), 2021, 2(3): 100141.
pmid: 34557778 |
| [30] |
Bian J, Xiong WJ, Yang ZG, Li MZ, Song DM, Zhang YL, Liu CY. Identification and prognostic biomarkers among ZDHHC4/12/18/24, and APT2 in lung adenocarcinoma. Sci Rep, 2024, 14(1): 522.
pmid: 38177255 |
| [31] |
Li L, Shao CY, Liu ZT, Wu XL, Yang JH, Wan HT. Comparative efficacy of Honghua class injections for treating acute ischemic stroke: a Bayesian network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front Pharmacol, 2022, 13: 1010533.
pmid: 36249799 |
| [32] |
Torgovnick A, Schumacher B. DNA repair mechanisms in cancer development and therapy. Front Genet, 2015, 6: 157.
pmid: 25954303 |
| [33] |
Xiao F, Liu XH, Chen Y, Dai HZ. Tumor-suppressing STF cDNA 3 overexpression suppresses renal fibrosis by alleviating anoikis resistance and inhibiting the PI3K/Akt pathway. Kidney Blood Press Res, 2021, 46(5): 588-600.
pmid: 34284400 |
| [34] |
Wang K, Jiang XL, Jiang Y, Liu J, Du YT, Zhang ZC, Li YL, Zhao XH, Li JP, Zhang R. EZH2-H3K27me3- mediated silencing of mir-139-5p inhibits cellular senescence in hepatocellular carcinoma by activating TOP2A. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2023, 42(1): 320.
pmid: 38008711 |
| [35] |
Li R, Yan XJ, Zhong WH, Zheng J, Li XJ, Liang JL, Hu ZY, Liu HY, Chen GH, Yang Y, Zhang JW, Qu EZ, Liu W. Stratifin promotes the malignant progression of HCC via binding and hyperactivating AKT signaling. Cancer Lett, 2024, 592: 216761.
pmid: 38490326 |
| [36] |
Trefts E, Gannon M, Wasserman DH. The liver. Curr Biol, 2017, 27(21): R1147-R1151.
pmid: 29112863 |
| [37] |
Badmus OO, Hillhouse SA, Anderson CD, Hinds TD, Stec DE. Molecular mechanisms of metabolic associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD): functional analysis of lipid metabolism pathways. Clin Sci (Lond), 2022, 136(18): 1347-1366.
pmid: 36148775 |
| [38] |
Herrera FG, Ronet C, Ochoa de Olza M, Barras D, Crespo I, Andreatta M, Corria-Osorio J, Spill A, Benedetti F, Genolet R, Orcurto A, Imbimbo M, Ghisoni E, Navarro Rodrigo B, Berthold DR, Sarivalasis A, Zaman K, Duran R, Dromain C, Prior J, Schaefer N, Bourhis J, Dimopoulou G, Tsourti Z, Messemaker M, Smith T, Warren SE, Foukas P, Rusakiewicz S, Pittet MJ, Zimmermann S, Sempoux C, Dafni U, Harari A, Kandalaft LE, Carmona SJ, Dangaj Laniti D, Irving M, Coukos G. Low-dose radiotherapy reverses tumor immune desertification and resistance to immunotherapy. Cancer Discov, 2022, 12(1): 108-133.
pmid: 34479871 |
| [39] |
Lei X, de Groot DC, Welters MJP, de Wit T, Schrama E, van Eenennaam H, Santegoets SJ, Oosenbrug T, van der Veen A, Vos JL, Zuur CL, Jacobs H, van der Burg SH, Borst J, Xiao YL. CD4+ T cells produce IFN-I to license cDC1s for induction of cytotoxic T-cell activity in human tumors. Cell Mol Immunol, 2024, 21(4): 374-392.
pmid: 38383773 |
| [40] |
Constant DA, Van Winkle JA, VanderHoek E, Dekker SE, Sofia MA, Regner E, Modiano N, Tsikitis VL, Nice TJ. Transcriptional and cytotoxic responses of human intestinal organoids to IFN types I, II, and III. Immunohorizons, 2022, 6(7): 416-429.
pmid: 35790340 |
| [41] |
Leblond MM, Tillé L, Nassiri S, Gilfillan CB, Imbratta C, Schmittnaegel M, Ries CH, Speiser DE, Verdeil G. CD40 agonist restores the antitumor efficacy of anti-PD1 therapy in muscle-invasive bladder cancer in an IFN I/II-mediated manner. Cancer Immunol Res, 2020, 8(9): 1180-1192.
pmid: 32661095 |
| [42] |
Xie M, Lin ZY, Ji XY, Luo XY, Zhang ZR, Sun MY, Chen XP, Zhang BX, Liang HF, Liu DF, Feng YY, Wang YJ, Li YW, Liu BF, Huang WJ, Xia LM. FGF19/FGFR4-mediated elevation of ETV4 facilitates hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis by upregulating PD-L1 and CCL2. J Hepatol, 2023, 79(1): 109-125.
pmid: 36907560 |
| [43] |
Han ZJ, Li YB, Yang LX, Cheng HJ, Liu X, Chen H. Roles of the CXCL8-CXCR1/2 axis in the tumor microenvironment and immunotherapy. Molecules, 2021, 27(1): 137.
pmid: 35011369 |
| [44] |
Nyalali AMK, Leonard AU, Xu YX, Li HY, Zhou JL, Zhang XR, Rugambwa TK, Shi XH, Li F. CD147: an integral and potential molecule to abrogate hallmarks of cancer. Front Oncol, 2023, 13: 1238051.
pmid: 38023152 |
| [45] |
Knutti N, Huber O, Friedrich K. CD147 (EMMPRIN) controls malignant properties of breast cancer cells by interdependent signaling of Wnt and JAK/STAT pathways. Mol Cell Biochem, 2019, 451(1-2): 197-209.
pmid: 30022447 |
| [46] |
Yang H, Chen BL. CD147 in ovarian and other cancers. Int J Gynecol Cancer, 2013, 23(1): 2-8.
pmid: 23221648 |
| [47] |
Raeisi M, Zehtabi M, Velaei K, Fayyazpour P, Aghaei N, Mehdizadeh A. Anoikis in cancer: the role of lipid signaling. Cell Biol Int, 2022, 46(11): 1717-1728.
pmid: 36030535 |
| [48] |
Yang QX, Zhong S, He L, Jia XJ, Tang H, Cheng ST, Ren JH, Yu HB, Zhou L, Zhou HZ, Ren F, Hu ZW, Gong R, Huang AL, Chen J. PBK overexpression promotes metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma via activating ETV4-uPAR signaling pathway. Cancer Lett, 2019, 452: 90-102.
pmid: 30914208 |
| [49] |
Peng XL, Ji MY, Yang ZR, Song J, Dong WG. Tumor suppressor function of ezrin-radixin-moesin-binding phosphoprotein-50 through β-catenin/E-cadherin pathway in human hepatocellular cancer. World J Gastroenterol, 2013, 19(8): 1306-1313.
pmid: 23483729 |
| [50] |
Yang Y, Zheng J, Wang MC, Zhang J, Tian T, Wang ZH, Yuan SX, Liu L, Zhu P, Gu FM, Fu SY, Shan YF, Pan ZY, Zhou WP. NQO1 promotes an aggressive phenotype in hepatocellular carcinoma via amplifying ERK-NRF2 signaling. Cancer Sci, 2021, 112(2): 641-654.
pmid: 33222332 |
| [51] |
Khan SU, Fatima K, Malik F. Understanding the cell survival mechanism of anoikis-resistant cancer cells during different steps of metastasis. Clin Exp Metastasis, 2022, 39(5): 715-726.
pmid: 35829806 |
| [52] |
Sattari Fard F, Jalilzadeh N, Mehdizadeh A, Sajjadian F, Velaei K. Understanding and targeting anoikis in metastasis for cancer therapies. Cell Biol Int, 2023, 47(4): 683-698.
pmid: 36453448 |
| [53] |
Yang JN, Zhang Y, Cheng SS, Xu YN, Wu MX, Gu SJ, Xu SL, Wu YS, Wang C, Wang Y. Anoikis-related signature predicts prognosis and characterizes immune landscape of ovarian cancer. Cancer Cell Int, 2024, 24(1): 53.
pmid: 38310291 |
| [54] |
Shi JX, Peng B, Zhou X, Wang CH, Xu R, Lu T, Chang XY, Shen ZP, Wang KY, Xu CY, Zhang LY. An anoikis- based gene signature for predicting prognosis in malignant pleural mesothelioma and revealing immune infiltration. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol, 2023, 149(13): 12089-12102.
pmid: 37421452 |
| [55] |
Chen J, Sun MJ, Chen CQ, Kang MY, Qian B, Sun J, Ma XP, Zhou JF, Huang L, Jiang B, Fang YJ. Construction of a novel anoikis-related prognostic model and analysis of its correlation with infiltration of immune cells in neuroblastoma. Front Immunol, 2023, 14: 1135617.
pmid: 37081871 |
| [56] |
Chen Y, Lin QX, Xu YT, Qian FJ, Lin CJ, Zhao WY, Huang JR, Tian L, Gu DN. An anoikis-related gene signature predicts prognosis and reveals immune infiltration in hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Oncol, 2023, 13: 1158605.
pmid: 37182175 |
| [57] |
Fang WZ, Chen Z. Identification of anoikis related subtypes and construction of prognostic model in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand), 2023, 69(9): 219-228.
pmid: 37807308 |
| [58] |
Savarese-Brenner B, Heugl M, Rath B, Schweizer C, Obermayr E, Stickler S, Hamilton G. MUC1 and CD147 are promising markers for the detection of circulating tumor cells in small cell lung cancer. Anticancer Res, 2022, 42(1): 429-439.
pmid: 34969753 |
| [59] |
Shigematsu Y, Kanda H, Takahashi Y, Takeuchi K, Inamura K. Relationships between tumor CD147 expression, tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, and oncostatin M in hepatocellular carcinoma. Virchows Arch, 2024, doi: 10.1007/s00428-024-03939-w.
pmid: 39395054 |
| [1] | 何锐, 郑秀娟, 王宁宁, 李旭颖, 李明其, 辇士晶, 王克维. 基于生物信息学识别肝细胞癌中的PANoptosis相关lncRNAs并构建预后模型[J]. 遗传, 2025, 47(4): 456-475. |
| [2] | 陈昱颖, 张倩, 桂梦会, 冯岚, 曹鹏博, 周钢桥. PTBP1通过调控FGFR2的可变剪接促进肝癌的发展[J]. 遗传, 2024, 46(1): 46-62. |
| [3] | 程敏, 张静, 曹鹏博, 周钢桥. 缺氧相关长链非编码RNA作为肝癌预后预测标志物的潜在价值[J]. 遗传, 2022, 44(2): 153-167. |
| [4] | 雷常贵, 贾学渊, 孙文靖. 基于癌症基因组图谱计划多组学数据构建胶质母细胞瘤六基因预后模型[J]. 遗传, 2021, 43(7): 665-679. |
| [5] | 骆红波, 曹鹏博, 周钢桥. DNA甲基化驱动的转录表达特征作为肝癌预后预测标志物的价值[J]. 遗传, 2020, 42(8): 775-787. |
| [6] | 苏红,司晓宇,唐文如,罗瑛. 失巢凋亡及其在肿瘤侵袭、转移中的调控[J]. 遗传, 2013, 35(1): 10-16. |
| [7] | 杨扬,王博石,汪晓敏,张钰,王明荣,贾雪梅. 食管癌细胞抗失巢凋亡基因UBCH7的发现与鉴定[J]. 遗传, 2012, 34(2): 190-197. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||

www.chinagene.cn
备案号:京ICP备09063187号-4
总访问:,今日访问:,当前在线:
