遗传 ›› 2020, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (8): 775-787.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.20-139
收稿日期:2020-05-18
修回日期:2020-07-10
出版日期:2020-08-20
发布日期:2020-07-10
通讯作者:
曹鹏博,周钢桥
E-mail:birchcpb@163.com;zhougq114@126.com
作者简介:骆红波,硕士研究生,专业方向:肝癌转录组学。E-mail: 基金资助:
Hongbo Luo1, Pengbo Cao2( ), Gangqiao Zhou1,2(
), Gangqiao Zhou1,2( )
)
Received:2020-05-18
Revised:2020-07-10
Online:2020-08-20
Published:2020-07-10
Contact:
Cao Pengbo,Zhou Gangqiao
E-mail:birchcpb@163.com;zhougq114@126.com
Supported by:摘要:
肝细胞癌(hepatocellular carcinoma,简称肝癌)是最常见的恶性肿瘤之一。DNA甲基化的异常是恶性肿瘤的特征之一,并被发现在肝癌等肿瘤的发生发展中发挥重要作用。为了能为肝癌患者提供新的临床预后预测标志物,本研究首先采用整合组学分析策略在全基因组范围内鉴定与肝癌患者预后相关的DNA甲基化驱动的差异表达基因;然后,采用LASSO (least absolute shrinkage and selection operator)分析建立了10个最优基因组合的预后预测模型。Cox比例风险回归分析显示,在校正临床特征参数后,此预测模型高风险评分与患者不良预后显著相关,表明该模型具有潜在的独立预后价值。受试者工作特征(receiver operating characteristic, ROC)曲线分析显示该风险评分模型在预测患者短期和长期预后方面优于其他已被报道的肝癌预后预测模型。基因集富集分析(gene set enrichment analysis, GSEA)表明,高风险评分与细胞周期和DNA损伤修复通路相关。以上结果表明,本研究构建了一个基于10个DNA甲基化驱动基因的预后风险评分模型,该模型可作为肝癌患者的潜在预后生物标志物,有助于肝癌患者的生存预后评估和治疗策略的指导。
骆红波, 曹鹏博, 周钢桥. DNA甲基化驱动的转录表达特征作为肝癌预后预测标志物的价值[J]. 遗传, 2020, 42(8): 775-787.
Hongbo Luo, Pengbo Cao, Gangqiao Zhou. Prognostic and predictive value of a DNA methylation-driven transcriptional signature in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2020, 42(8): 775-787.
表1
本研究中涉及的所有肝癌队列"
| 研究队列 | 数据集 | 样本量 | 数据类型 | 数据来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 发掘队列 | SRP069212 | 20例配对的癌和癌旁组织 | mRNA表达 | GEO |
| SRP118972 | 12例癌组织样本和8例癌旁组织 | mRNA表达 | GEO | |
| GSE89852 | 33例配对的癌和癌旁组织 | DNA甲基化 | GEO | |
| GSE54503 | 66例配对的癌和癌旁组织 | DNA甲基化 | GEO | |
| 模型训练队列 | TCGA-LIHC | 371例癌组织和50例癌旁组织 | mRNA表达和DNA甲基化 | TCGA |
| ICGC-LIRI-JP | 203例癌组织 | mRNA表达 | ICGC | |
| 模型验证队列 | GSE76427 | 115例癌组织 | 基因表达 | GEO |
| GSE84005 | 37例癌组织 | 基因表达 | GEO |
图1
肝癌中DNA甲基化驱动的差异表达基因的鉴定 A:研究技术路线图。主要包括候选DNA甲基化驱动的差异表达基因的发掘阶段、模型训练阶段和模型验证和评估阶段。B:在发掘队列中鉴定出的DNA甲基化驱动的差异表达基因数量。上图为鉴定出的“低甲基化-高表达”基因数量,下图为鉴定出“高甲基化-低表达”基因数量。C:在发掘队列和模型训练队列中DNA甲基化驱动的差异表达基因的热图。左图为基因DNA甲基化水平热图(平均甲基化水平),右图为基因表达热图(平均表达水平)。ICGC-LIRI-JP:国际癌症基因组联盟日本肝癌项目(international cancer genome consortium liver cancer-RIKEN of JP project);N:肝癌癌旁组织数量;T:肝癌组织数量;TCGA-LIHC:癌症基因组图谱-肝细胞癌项目(the cancer genome atlas-liver hepatocellular carcinoma);β:基因的DNA甲基化水平。"
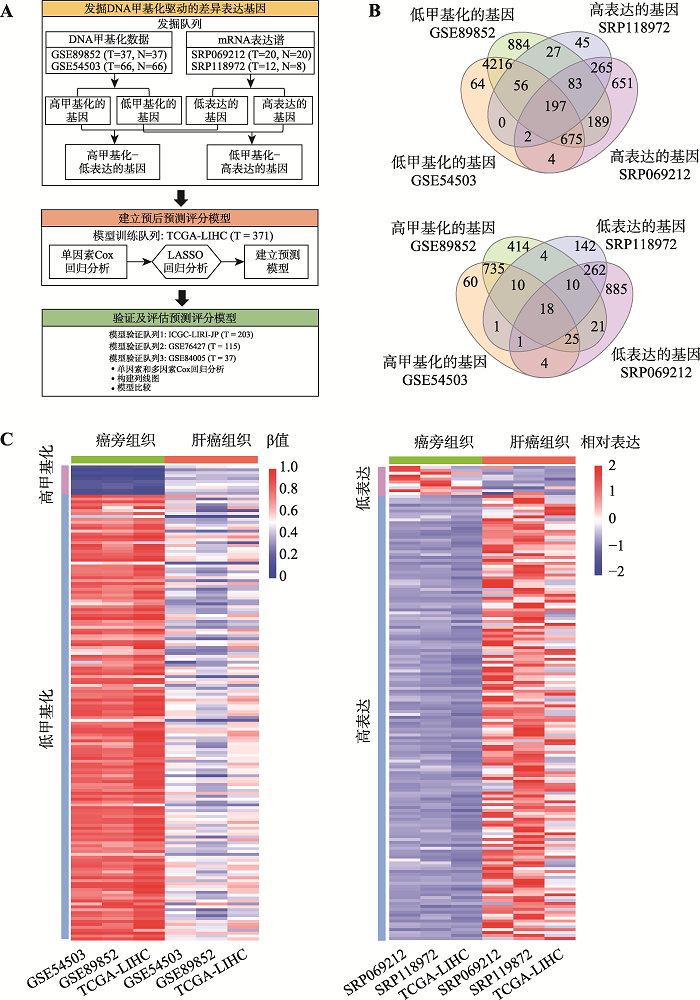
表2
10个最优基因的Cox比例风险回归分析结果、LASSO回归系数和基因组变异频率"
| 基因 | HR (95% CI) | P值 | LASSO系数 | 基因组变异频率(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CDCA8 | 2.21 (1.54~3.01) | <0.0001 | 0.1194 | 0.0 |
| PRC1 | 1.85 (1.29~2.54) | 0.0005 | 0.08869 | 0.3 |
| MAPT | 1.72 (1.21~2.46) | 0.0021 | 0.2597 | 1.7 |
| SFN | 1.72 (1.21~2.45) | 0.0021 | 0.001652 | 0.3 |
| STC2 | 1.73 (1.22~2.43) | 0.0021 | 0.03600 | 0.8 |
| MYO18B | 1.69 (1.19~2.37) | 0.0031 | 0.1932 | 4.0 |
| PBK | 1.67 (1.17~2.35) | 0.0036 | 0.06524 | 6.0 |
| MAEL | 1.55 (1.09~2.17) | 0.013 | -0.1766 | 10.0 |
| TTC39A | 1.55 (1.09~2.17) | 0.013 | -0.01347 | 1.4 |
| LPL | 1.55 (1.10~2.18) | 0.014 | 0.003126 | 7.0 |
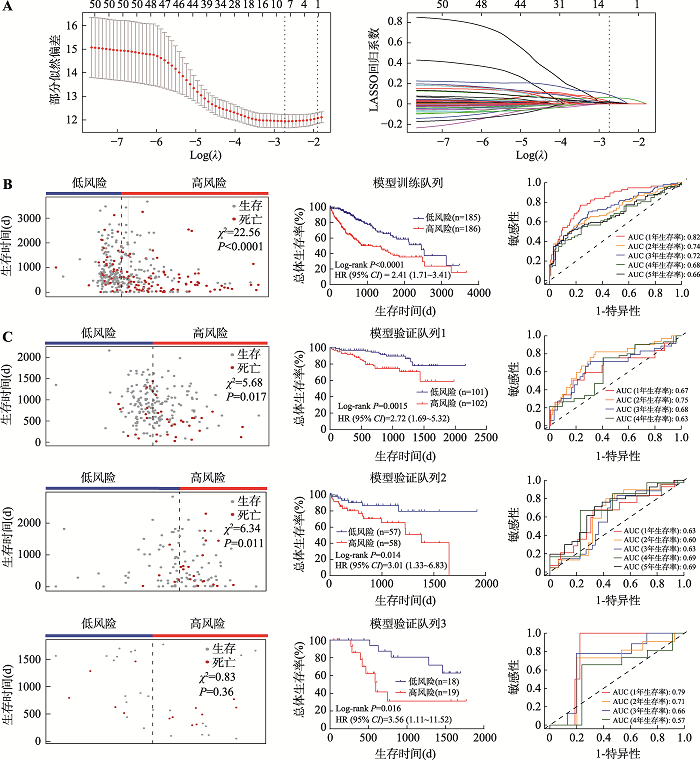
图2
建立和验证10个基因的预后评分模型 A:使用LASSO回归分析和10倍交叉验证构建预后预测评分模型。左图为基于最小原则(minimum criteria)采用10倍交叉验证对LASSO模型进行调参,通过LASSO回归交叉验证计算的部分似然偏差(partial likelihood deviance)被绘制为log(λ)的函数。y轴表示部分似然偏差,x轴表示log(λ),沿x轴上方的数字表示预测变量的平均数量,红点表示具有给定λ的每个模型的平均偏差值,穿过红点的竖线表示偏差的上限值和下限值,垂直虚线分别表示最小误差的λ值和最大λ值。右图为51个预后基因的LASSO系数分布,垂直虚线表示采用10倍交叉验证选取的基因数,当基因数为10时,部分似然偏差为最小值,对应最小λ值。B:基于LASSO系数和基因表达在模型训练队列建立预后模型。左图为模型训练队列中肝癌患者的风险评分及生存时间的散点图,中间图为模型训练队列中不同风险评分组(中位数分组)患者的生存曲线图,右图为采用ROC曲线分析评估预测模型对训练队列中患者生存率的预测性能。C:在模型验证队列中验证预后模型。左图为模型验证队列中肝癌患者的风险评分及生存时间的散点图,中间图为模型验证队列中不同风险评分组(中位数分组)患者的生存曲线图,右图为ROC曲线分析评估预测模型对验证队列中患者生存率的预测性能。由于验证队列1和3中患者达到5年生存的数量较少,所以并未对患者5年生存率进行ROC分析。卡方检验(χ2)用于评价组间患者生存分布差异;组间生存差异采用Log-rank方法进行比较;ROC分析用于评估模型预测性能。AUC:曲线下面积(area under curve);CI:置信区间(confidence interval);HR:风险比例(hazard ratios);LASSO:最小绝对值收敛和选择算子(least absolute shrinkage and selection operator);ROC:受试者工作特征曲线(receiver operating characteristic curve)。"
| [1] |
Villanueva A . Hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med, 2019,380(15):1450-1462.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1713263 pmid: 30970190 |
| [2] |
Samonakis DN, Kouroumalis EA . Systemic treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma: still unmet expectations. World J Hepatol, 2017,9(2):80-90.
doi: 10.4254/wjh.v9.i2.80 pmid: 28144389 |
| [3] |
Zhang JW, Xu Q, Li GL . Epigenetics in the genesis and development of cancers. Hereditas(Beijing), 2019,41(7):567-581.
doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.19-077 pmid: 31307967 |
|
张競文, 续倩, 李国亮 . 癌症发生发展中的表观遗传学研究. 遗传, 2019,41(7):567-581.
doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.19-077 pmid: 31307967 |
|
| [4] |
Sun LY, Li XY, Sun ZW . Progress of epigenetics and its therapeutic application in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hereditas(Beijing), 2015,37(6):517-527.
doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.14-443 pmid: 26351047 |
|
孙凌云, 李星逾, 孙志为 . 原发性肝癌的表观遗传学及其治疗. 遗传, 2015,37(06):517-527.
doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.14-443 pmid: 26351047 |
|
| [5] |
Tan AC, Jimeno A, Lin SH, Wheelhouse J, Chan F, Solomon A, Rajeshkumar NV, Rubio-Viqueira B, Hidalgo M . Characterizing DNA methylation patterns in pancreatic cancer genome. Mol Oncol, 2009,3(5-6):425-438.
doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2009.03.004 pmid: 19497796 |
| [6] |
Dobin A, Davis CA, Schlesinger F, Drenkow J, Zaleski C, Jha S, Batut P, Chaisson M, Gingeras TR . STAR: ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics, 2013,29(1):15-21.
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts635 |
| [7] |
Kim D, Langmead B, Salzberg SL . HISAT: a fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat Methods, 2015,12(4):357-360.
doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3317 pmid: 25751142 |
| [8] |
Love MI, Huber W, Anders S . Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol, 2014,15(12):550.
doi: 10.1186/s13059-014-0550-8 pmid: 25516281 |
| [9] |
Morris TJ, Butcher LM, Feber A, Teschendorff AE, Chakravarthy AR, Wojdacz TK, Beck S . ChAMP: 450k chip analysis methylation pipeline. Bioinformatics, 2014,30(3):428-430.
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btt684 |
| [10] |
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu YF, Law CW, Shi W, Smyth GK . Limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res, 2015,43(7):e47.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv007 pmid: 25605792 |
| [11] |
Mah WC, Thurnherr T, Chow PKH, Chung AYF, Ooi LLPJ, Toh HC, Teh BT, Saunthararajah Y, Lee CGL . Methylation profiles reveal distinct subgroup of hepatocellular carcinoma patients with poor prognosis. PLoS One, 2014,9(8):e104158.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0104158 pmid: 25093504 |
| [12] | Friedman J, Hastie T, Tibshirani R . Regularization paths for generalized linear models via coordinate descent. J Stat Softw, 2010,33(1):1-22. |
| [13] |
Blanche P, Dartigues JF, Jacqmin-Gadda H . Estimating and comparing time-dependent areas under receiver operating characteristic curves for censored event times with competing risks. Stat Med, 2013,32(30):5381-5397.
doi: 10.1002/sim.5958 pmid: 24027076 |
| [14] |
Steyerberg EWS, Vergouwe Y . Towards better clinical prediction models: seven steps for development and an ABCD for validation. Eur Heart J, 2014,35(29):1925-1931.
doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehu207 |
| [15] | Zheng YJ, Liu YL, Zhao SF, Zheng ZT, Shen CY, An L, Yuan YL . Large-scale analysis reveals a novel risk score to predict overall survival in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Manag Res, 2018, ( 10):6079-6096. |
| [16] |
Yang Y, Lu Q, Shao XJ, Mo BH, Nie XQ, Liu W, Chen XH, Tang Y, Deng YC, Yan J . Development of a three-gene prognostic signature for hepatitis b virus associated heaptocellular carcinoma based on integrated transcriptomic analysis. J Cancer, 2018,9(11):1989-2002.
doi: 10.7150/jca.23762 pmid: 29896284 |
| [17] |
Long JY, Chen PP, Lin JZ, Bai Y, Yang X, Bian J, Lin Y, Wang DX, Yang XB, Zheng YC, Sang XT, Zhao HT . DNA methylation-driven genes for constructing diagnostic, prognostic, and recurrence models for hepatocellular carcinoma. Theranostics, 2019,9(24):7251-7267.
doi: 10.7150/thno.31155 pmid: 31695766 |
| [18] |
Torgovnick A, Schumacher B . DNA repair mechanisms in cancer development and therapy. Front Genet, 2015,6:157.
doi: 10.3389/fgene.2015.00157 pmid: 25954303 |
| [19] |
Feitelson MA . Parallel epigenetic and genetic changes in the pathogenesis of hepatitis virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett, 2006,239(1):10-20.
doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2005.07.009 pmid: 16154256 |
| [20] |
Liu LL, Dai YD, Chen JN, Zeng TT, Li Y, Chen LL, Zhu YH, Li JC, Li Y, Ma S, Xie D, Yuan YF, Guan XY . Maelstrom promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition by way of Akt/GSK-3β/Snail signaling. Hepatology, 2014,59(2):531-543.
doi: 10.1002/hep.26677 |
| [21] |
Zhang ZY, Zhu JF, Huang YS, Li WB, Cheng HQ . MYO18B promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by activating PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Diagn Pathol, 2018,13(1):85.
doi: 10.1186/s13000-018-0763-3 pmid: 30390677 |
| [22] |
Cao D, Song XH, Che L, Li XL, Pilo MG, Vidili G, Porcu A, Solinas A, Cigliano A, Pes GM, Ribback S, Dombrowski F, Chen X, Li L, Calvisi DF . Both de novo synthetized and exogenous fatty acids support the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Liver Int, 2017,37(1):80-89.
doi: 10.1111/liv.13183 pmid: 27264722 |
| [23] |
Liu P, Atkinson SJ, Akbareian SE, Zhou ZG, Munsterberg A, Robinson SD, Bao YP . Sulforaphane exerts anti-angiogenesis effects against hepatocellular carcinoma through inhibition of STAT3/HIF-1α/VEGF signalling. Sci Rep, 2017,7(1):12651.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-12855-w pmid: 28978924 |
| [24] | Wang HX, Wu KJ, Sun Y, Li YD, Wu MY, Qiao Q, Wei YJ, Han ZG, Cai B . STC2 is upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes cell proliferation and migration in vitro. BMB Rep, 2012,45(11):629-634. |
| [25] |
Chen JX, Rajasekaran M, Xia HP, Zhang XQ, Kong SN, Sekar K, Seshachalam VP, Deivasigamani A, Goh BKP, Ooi LL, Hong WJ, Hui KM . The microtubule-associated protein PRC1 promotes early recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma in association with the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway. Gut, 2016,65(9):1522-1534.
doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2015-310625 pmid: 26941395 |
| [26] |
Desai A, Mitchison TJ . Microtubule polymerization dynamics. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol, 1997,13:83-117.
doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.13.1.83 pmid: 9442869 |
| [27] | Safran M, Dalah I, Alexander J, Rosen N, Stein TI, Shmoish M, Nativ N, Bahir I, Doniger T, Krug H, Sirota-Madi A, Olender T, Golan Y, Stelzer G, Harel A, Lancet D . GeneCards Version 3: the human gene integrator. Database (Oxford), 2010, 2010: baq020. |
| [1] | 时文睿, 渠鸿竹, 方向东. 痛风的多组学研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2023, 45(8): 643-657. |
| [2] | 韩熙, 罗富成. 单细胞转录组测序在少突胶质谱系细胞异质性与神经系统疾病中的应用[J]. 遗传, 2023, 45(3): 198-211. |
| [3] | 许梦萱, 周明. 植物RNA聚合酶IV调控DNA甲基化和发育的研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2022, 44(7): 567-580. |
| [4] | 郭彦, 杨乐乐, 戚华宇. 小鼠雄性生殖干细胞转录组分析揭示成熟精原干细胞特征[J]. 遗传, 2022, 44(7): 591-608. |
| [5] | 程敏, 张静, 曹鹏博, 周钢桥. 缺氧相关长链非编码RNA作为肝癌预后预测标志物的潜在价值[J]. 遗传, 2022, 44(2): 153-167. |
| [6] | 雷常贵, 贾学渊, 孙文靖. 基于癌症基因组图谱计划多组学数据构建胶质母细胞瘤六基因预后模型[J]. 遗传, 2021, 43(7): 665-679. |
| [7] | 石田培,张莉. 全转录组学在畜牧业中的应用[J]. 遗传, 2019, 41(3): 193-205. |
| [8] | 张高华, 于树涛, 王鹤, 王旭达. 高油酸花生发芽期低温胁迫转录组及差异表达基因分析[J]. 遗传, 2019, 41(11): 1050-1059. |
| [9] | 任岚,肖茹丹,张倩,娄晓敏,张昭军,方向东. KLF1和KLF9对K562细胞红系分化的协同调控作用[J]. 遗传, 2018, 40(11): 998-1006. |
| [10] | 杨莹,陈宇晟,孙宝发,杨运桂. RNA甲基化修饰调控和规律[J]. 遗传, 2018, 40(11): 964-976. |
| [11] | 刘亚军,张峰,刘宏德,孙啸. 下一代测序技术在干细胞转录调控研究中的应用[J]. 遗传, 2017, 39(8): 717-725. |
| [12] | 李玉席, 李俊宏, 周大旺. Hippo信号通路与肝脏稳态调控及疾病发生[J]. 遗传, 2017, 39(7): 607-616. |
| [13] | 叶仲杰,刘启鹏,岑山,李晓宇. LINE-1编码的逆转录酶在肿瘤形成过程中的作用[J]. 遗传, 2017, 39(5): 368-376. |
| [14] | 魏凯,马磊. 高通量测序时代下持家基因定义的发展[J]. 遗传, 2017, 39(2): 127-134. |
| [15] | 李光奇, 孙从佼, 吴桂琴, 石凤英, 刘爱巧, 孙皓, 杨宁. 利用转录组测序筛选鸡蛋褐壳性状相关基因[J]. 遗传, 2017, 39(11): 1102-1111. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||

www.chinagene.cn
备案号:京ICP备09063187号-4
总访问:,今日访问:,当前在线:
