Hereditas(Beijing) ›› 2024, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (4): 290-305.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.23-291
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Progress on the relationship between tumor suppressor PDCD4 and diseases based on the analysis of structural characteristics
- 1. Chongqing College of Electronic Engineering, Smart Health College, Chongqing 401331, China
2. The Third Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 510150, China
3. Division of Basic Research, Guangzhou National Laboratory, Guangzhou 510005, China
-
Received:2023-11-23Revised:2024-01-22Online:2024-04-20Published:2024-02-01 -
Contact:Hui Li, Guangming Wu E-mail:huili19@163.com;wu_guangming@gzlab.ac.cn -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(31801181);Chongqing Natural Science Foundation General Project(cstc2020jcyj-msxmX0903);Scientific Research Project of Chongqing College of Electronic Engineering(22XJDXWT35)
Cite this article
Hui Li, Guangming Wu. Progress on the relationship between tumor suppressor PDCD4 and diseases based on the analysis of structural characteristics[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2024, 46(4): 290-305.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Table 1
Important structural components and functions of PDCD4"
| 结构域或序列或位点 | 个数 | 位置 | 功能 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
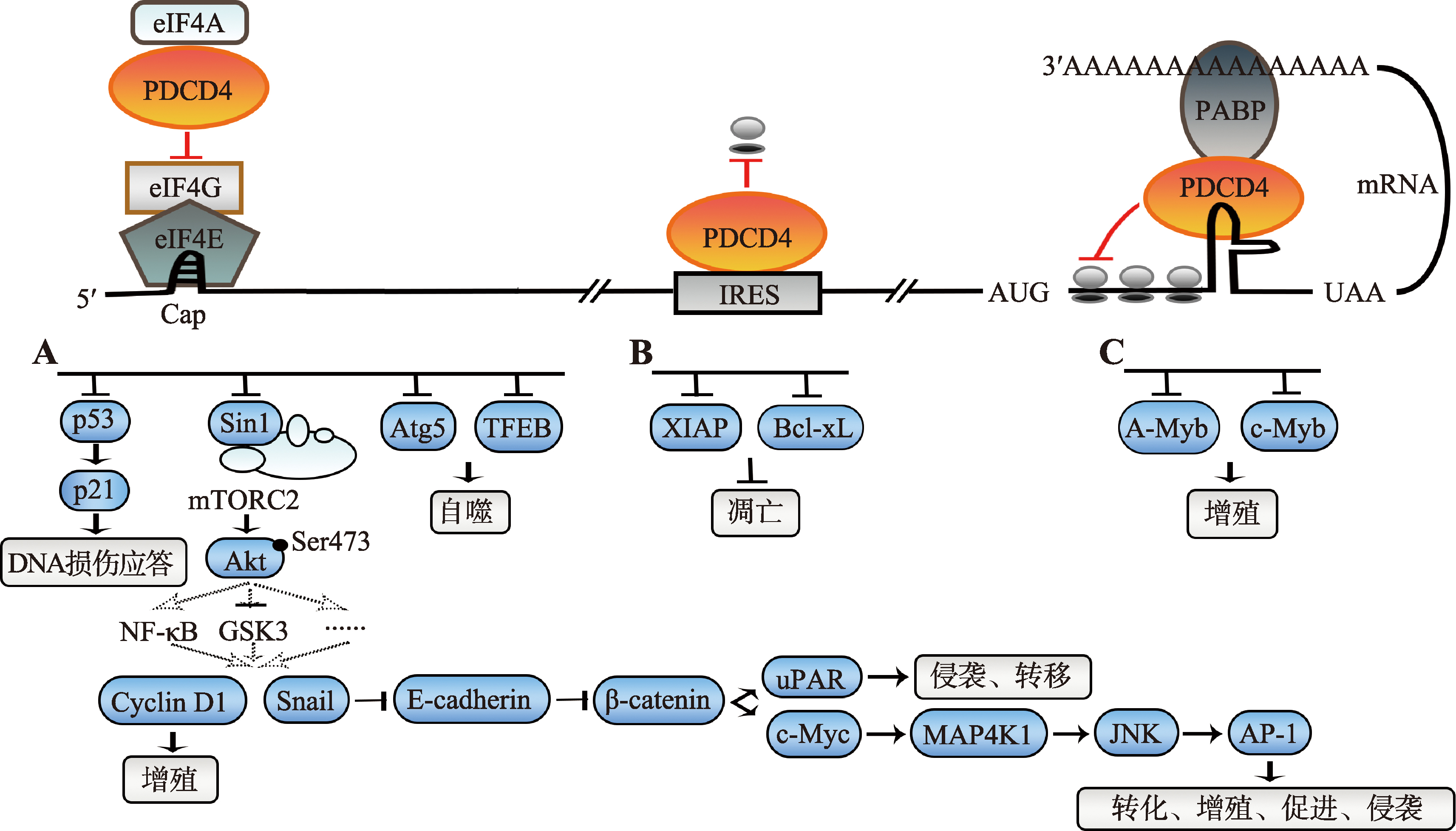
| MA3结构域 | 2 | 157~302 aa, 319~449 aa | 与eIF4A结合,阻碍正常的蛋白翻译起始复合物形成,从而抑制帽依赖性蛋白从头翻译。其中重要的氨基酸为E249、D253、D414、D418。 | [ |
| 核定位信号(NLSs) | 2 | 58~64 aa, 448~454 aa | PDCD4在大部分正常组织中主要表达于细胞核内。 | [ |
| 出核信号 (NESs) | 2 | 182~192 aa, 241~251 aa | PDCD4受细胞外信号影响可出核,表达于细胞质。 | [ |
| RNA结合碱性氨基酸簇(RBM) | 2 | 58~66 aa, 100~107aa | RNA结合域中与RNA结合序列,调节RNA代谢。 | [ |
| PABP结合簇 | 1 | RNA结合域的后端 | 与PABP结合,影响与RNA结合的稳定性和核糖体的招募,起关键作用的氨基酸为K114K115和V123W124。 | [ |
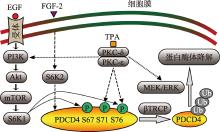
| 磷酸化位点 | 4 | Ser67 | 被Akt或S6K磷酸化,进一步促进71和76位点的磷酸化。 | [ |
| Ser71, Ser76 | 磷酸化后与βTRCP结合,使PDCD4泛素化后至蛋白酶体降解。 | [ | ||
| Ser457 | 被Akt磷酸化,促进出核。 | [ | ||
| 甲基化位点 | 1 | Arg110 | 在营养缺乏期间促进肿瘤的生存能力。 | [ |
| [1] |
Shibahara K, Asano M, Ishida Y, Aoki T, Koike T, Honjo T. Isolation of a novel mouse gene MA-3 that is induced upon programmed cell death. Gene, 1995, 166(2): 297-301.
pmid: 8543179 |
| [2] |
Onishi Y, Kizaki H. Molecular cloning of the genes suppressed in RVC lymphoma cells by topoisomerase inhibitors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 1996, 228(1): 7-13.
doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1996.1609 |
| [3] |
Onishi Y, Hashimoto S, Kizaki H. Cloning of the TIS gene suppressed by topoisomerase inhibitors. Gene, 1998, 215(2): 453-459.
pmid: 9714845 |
| [4] |
Azzoni L, Zatsepina O, Abebe B, Bennett IM, Kanakaraj P, Perussia B. Differential transcriptional regulation of CD161 and a novel gene, 197/15a, by IL-2, IL-15, and IL-12 in NK and T cells. J Immunol, 1998, 161(7): 3493-3500.
pmid: 9759869 |
| [5] |
Schlichter U, Burk O, Worpenberg S, Klempnauer KH. The chicken Pdcd4 gene is regulated by v-Myb. Oncogene, 2001, 20(2): 231-239.
pmid: 11313950 |
| [6] |
Göke A, Göke R, Knolle A, Trusheim H, Schmidt H, Wilmen A, Carmody R, Göke B, Chen YH. DUG is a novel homologue of translation initiation factor 4G that binds eIF4A. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2002, 297(1): 78-82.
doi: 10.1016/S0006-291X(02)02129-0 |
| [7] |
Wedeken L, Ohnheiser J, Hirschi B, Wethkamp N, Klempnauer KH. Association of tumor suppressor protein Pdcd4 with ribosomes is mediated by protein-protein and protein-RNA interactions. Genes Cancer, 2010, 1(3): 293-301.
doi: 10.1177/1947601910364227 pmid: 21779451 |
| [8] |
Bitomsky N, Böhm M, Klempnauer KH. Transformation suppressor protein Pdcd4 interferes with JNK-mediated phosphorylation of c-Jun and recruitment of the coactivator p300 by c-Jun. Oncogene, 2004, 23(45): 7484-7493.
pmid: 15334056 |
| [9] |
Waters LC, Veverka V, Böhm M, Schmedt T, Choong PT, Muskett FW, Klempnauer KH, Carr MD. Structure of the C-terminal MA-3 domain of the tumour suppressor protein Pdcd4 and characterization of its interaction with eIF4A. Oncogene, 2007, 26(34): 4941-4950.
pmid: 17310995 |
| [10] |
Suzuki C, Garces RG, Edmonds KA, Hiller S, Hyberts SG, Marintchev A, Wagner G. PDCD4 inhibits translation initiation by binding to eIF4A using both its MA3 domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2008, 105(9): 3274-3279.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0712235105 pmid: 18296639 |
| [11] |
Loh PG, Yang HS, Walsh MA, Wang Q, Wang XX, Cheng ZH, Liu DX, Song HW.Structural basis for translational inhibition by the tumour suppressor Pdcd4. EMBO J, 2009, 28(3): 274-285.
doi: 10.1038/emboj.2008.278 pmid: 19153607 |
| [12] |
Böhm M, Sawicka K, Siebrasse JP, Brehmer-Fastnacht A, Peters R, Klempnauer KH. The transformation suppressor protein Pdcd4 shuttles between nucleus and cytoplasm and binds RNA. Oncogene, 2003, 22(31): 4905-4910.
pmid: 12894233 |
| [13] |
Palamarchuk A, Efanov A, Maximov V, Aqeilan RI, Croce CM, Pekarsky Y. Akt phosphorylates and regulates Pdcd4 tumor suppressor protein. Cancer Res, 2005, 65(24): 11282-11286.
pmid: 16357133 |
| [14] |
Dorrello NV, Peschiaroli A, Guardavaccaro D, Colburn NH, Sherman NE, Pagano M. S6K1- and βTRCP- mediated degradation of PDCD4 promotes protein translation and cell growth. Science, 2006, 314(5798): 467-471.
doi: 10.1126/science.1130276 pmid: 17053147 |
| [15] |
Powers MA, Fay MM, Factor RE, Welm AL, Ullman KS. Protein arginine methyltransferase 5 accelerates tumor growth by arginine methylation of the tumor suppressor programmed cell death 4. Cancer Res, 2011, 71(16): 5579-5587.
doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-0458 pmid: 21700716 |
| [16] |
Zheng CX, Ma XF, Zhang YH, Li HJ, Zhang GF. Research progress in the mechanism of translation initiation of eukaryotic mRNAs. Hereditas(Beijing), 2018, 40(8): 607-619.
doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.17-393 pmid: 30117417 |
| 郑超星, 马小凤, 张永华, 李洪杰, 张根发. 真核生物mRNA翻译起始机制研究进展. 遗传, 2018, 40(8): 607-619. | |
| [17] |
Waters LC, Strong SL, Ferlemann E, Oka O, Muskett FW, Veverka V, Banerjee S, Schmedt T, Henry AJ, Klempnauer KH, Carr MD. Structure of the tandem MA-3 region of Pdcd4 protein and characterization of its interactions with eIF4A and eIF4G: molecular mechanisms of a tumor suppressor. J Biol Chem, 2011, 286(19): 17270-17280.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.166157 pmid: 21454508 |
| [18] |
Yang HS, Cho MH, Zakowicz H, Hegamyer G, Sonenberg N, Colburn NH. A novel function of the MA-3 domains in transformation and translation suppressor Pdcd4 is essential for its binding to eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4A. Mol Cell Biol, 2004, 24(9): 3894-3906.
doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.9.3894-3906.2004 |
| [19] |
Chang JH, Cho YH, Sohn SY, Choi JM, Kim A, Kim YC, Jang SK, Cho Y. Crystal structure of the eIF4A- PDCD4 complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2009, 106(9): 3148-3153.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0808275106 |
| [20] |
Wedeken L, Singh P, Klempnauer KH. Tumor suppressor protein Pdcd4 inhibits translation of p53 mRNA. J Biol Chem, 2011, 286(50): 42855-42862.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.269456 pmid: 22033922 |
| [21] |
Wang Q, Zhu J, Wang YW, Dai Y, Wang YL, Wang C, Liu J, Baker A, Colburn NH, Yang HS. Tumor suppressor Pdcd4 attenuates Sin1 translation to inhibit invasion in colon carcinoma. Oncogene, 2017, 36(45): 6225-6234.
doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.228 pmid: 28692058 |
| [22] |
Song XG, Zhang X, Wang XY, Zhu FL, Guo C, Wang Q, Shi YY, Wang JN, Chen YH, Zhang LN. Tumor suppressor gene PDCD4 negatively regulates autophagy by inhibiting the expression of autophagy-related gene ATG5. Autophagy, 2013, 9(5): 743-755.
doi: 10.4161/auto.24069 |
| [23] |
Chen XT, Guan YT, Zhang Y, Jia YF, Li W, Guo C, Li Y, Wang XY, Shi YY, Wang Q, Zhu FL, Li Y, Zhang LN. Programmed cell death 4 modulates lysosomal function by inhibiting TFEB translation. Cell Death Differ, 2021, 28(4): 1237-1250.
doi: 10.1038/s41418-020-00646-2 pmid: 33100324 |
| [24] | Wang Q, Yang HS. The role of Pdcd4 in tumour suppression and protein translation. Biol Cell, 2018. |
| [25] |
Zhao TL, Zhang S, Qian WF. Cis-regulatory mechanisms and biological effects of translation elongation. Hereditas(Beijing), 2020, 42(7): 613-631.
doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.20-074 pmid: 32694102 |
| 肇涛澜, 张硕, 钱文峰. 翻译延伸的顺式调控机理与生物学效应. 遗传, 2020, 42(7): 613-631. | |
| [26] |
Singh P, Wedeken L, Waters LC, Carr MD, Klempnauer KH. Pdcd4 directly binds the coding region of c-myb mRNA and suppresses its translation. Oncogene, 2011, 30(49): 4864-4873.
doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.202 pmid: 21643008 |
| [27] |
Biyanee A, Ohnheiser J, Singh P, Klempnauer KH. A novel mechanism for the control of translation of specific mRNAs by tumor suppressor protein Pdcd4: inhibition of translation elongation. Oncogene, 2015, 34(11): 1384-1392.
doi: 10.1038/onc.2014.83 pmid: 24681950 |
| [28] |
Eto K, Goto S, Nakashima W, Ura Y, Abe SI. Loss of programmed cell death 4 induces apoptosis by promoting the translation of procaspase-3 mRNA. Cell Death Differ, 2012, 19(4): 573-581.
doi: 10.1038/cdd.2011.126 pmid: 21959934 |
| [29] |
Haas A, Nilges BS, Leidel SA, Klempnauer KH. PDCD4 controls the G1/S-phase transition in a telomerase-immortalized epithelial cell line and affects the expression level and translation of multiple mRNAs. Sci Rep, 2020, 10(1): 2758.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-59678-w pmid: 32066800 |
| [30] | Liwak U, Thakor N, Jordan LE, Roy R, Lewis SM, Pardo OE, Seckl M, Holcik M.Tumor suppressor PDCD4 represses internal ribosome entry site-mediated translation of antiapoptotic proteins and is regulated by S 6 kinase 2. Mol Cell Biol, 2012, 32(10): 1818-1829. |
| [31] |
Fehler O, Singh P, Haas A, Ulrich D, Müller JP, Ohnheiser J, Klempnauer KH.An evolutionarily conserved interaction of tumor suppressor protein Pdcd4 with the poly(A)-binding protein contributes to translation suppression by Pdcd4. Nucleic Acids Res, 2014, 42(17): 11107-11118.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gku800 pmid: 25190455 |
| [32] |
Shuvalova E, Egorova T, Ivanov A, Shuvalov A, Biziaev N, Mukba S, Pustogarov N, Terenin I, Alkalaeva E. Discovery of a novel role of tumor suppressor PDCD4 in stimulation of translation termination. J Biol Chem, 2021, 297(5): 101269.
doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.101269 |
| [33] |
Matsuhashi S, Hamajima H, Xia JH, Zhang H, Mizuta T, Anzai K, Ozaki I. Control of a tumor suppressor PDCD4: Degradation mechanisms of the protein in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cell Signal, 2014, 26(3): 603-610.
doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.11.038 pmid: 24334270 |
| [34] |
Schmid T, Jansen AP, Baker AR, Hegamyer G, Hagan JP, Colburn NH. Translation inhibitor Pdcd4 is targeted for degradation during tumor promotion. Cancer Res, 2008, 68(5): 1254-1260.
doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-1719 pmid: 18296647 |
| [35] |
Matsuhashi S, Manirujjaman M, Hamajima H, Ozaki I. Control mechanisms of the tumor suppressor PDCD4: expression and functions. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(9): 2304.
doi: 10.3390/ijms20092304 |
| [36] |
Long JL, Yin YT, Guo HN, Li SL, Sun YQ, Zeng C, Zhu W. The mechanisms and clinical significance of PDCD4 in colorectal cancer. Gene, 2019, 680: 59-64.
doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.09.034 |
| [37] |
Cai Q, Yang HS, Li YC, Zhu J. Dissecting the roles of PDCD4 in breast cancer. Front Oncol, 2022, 12: 855807.
doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.855807 |
| [38] |
Fay MM, Clegg JM, Uchida KA, Powers MA, Ullman KS. Enhanced arginine methylation of programmed cell death 4 protein during nutrient deprivation promotes tumor cell viability. J Biol Chem, 2014, 289(25): 17541-17552.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.541300 pmid: 24764298 |
| [39] |
Cheng Y, Xiang GX, Meng YB, Dong RZ.MiRNA-183-5p promotes cell proliferation and inhibits apoptosis in human breast cancer by targeting the PDCD4. Reprod Biol, 2016, 16(3): 225-233.
doi: S1642-431X(16)30027-4 pmid: 27476679 |
| [40] |
Li ZY, Zhou Y, Zhang LY, Jia KW, Wang SY, Wang M, Li N, Yu YZ, Cao XT, Hou J.microRNA-199a-3p inhibits hepatic apoptosis and hepatocarcinogenesis by targeting PDCD4. Oncogenesis, 2020, 9(10): 95.
doi: 10.1038/s41389-020-00282-y pmid: 33099584 |
| [41] |
Ma QQ, Huang JT, Xiong YG, Yang XY, Han R, Zhu WW. MicroRNA-96 regulates apoptosis by targeting PDCD4 in human glioma cells. Technol Cancer Res Treat, 2017, 16(1): 92-98.
doi: 10.1177/1533034616629260 |
| [42] |
Wang WQ, Zhao JJ, Wang HB, Sun YG, Peng ZH, Zhou G, Fan LL, Wang XW, Yang SM, Wang RQ, Fang DC. Programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) mediates the sensitivity of gastric cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis by down-regulation of FLIP expression. Exp Cell Res, 2010, 316(15): 2456-2464.
doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2010.05.027 pmid: 20595005 |
| [43] |
Liu CF, Tong Z, Tan JY, Xin ZX, Wang ZY, Tian LM. MicroRNA-21-5p targeting PDCD4 suppresses apoptosis via regulating the PI3K/AKT/FOXO1 signaling pathway in tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Exp Ther Med, 2019, 18(5): 3543-3551.
doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.7970 pmid: 31602231 |
| [44] |
Wan JJ, Yang J, Huang YS, Deng LH.MicroRNA-150 inhibitors enhance cell apoptosis of melanoma by targeting PDCD4. Oncol Lett, 2018, 15(2): 1475-1482.
doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.7445 pmid: 29434838 |
| [45] |
Sun YH, Wang FC, Wang L, Jiao ZD, Fang J, Li JM. MicroRNA-433 regulates apoptosis by targeting PDCD4 in human osteosarcoma cells. Oncol Lett, 2017, 14(2): 2353-2358.
doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.6441 pmid: 28781674 |
| [46] |
Bitomsky N, Wethkamp N, Marikkannu R, Klempnauer KH. siRNA-mediated knockdown of Pdcd4 expression causes upregulation of p21(Waf1/Cip1) expression. Oncogene, 2008, 27(35): 4820-4829.
doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.115 pmid: 18427550 |
| [47] |
Feng MG, Liu CF, Chen L, Feng WB, Liu M, Hai H, Lu JM. MiR-21 attenuates apoptosis-triggered by amyloid-β via modulating PDCD4/PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β pathway in SH-SY5Y cells. Biomed Pharmacother, 2018, 101: 1003-1007.
doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.02.043 |
| [48] |
Burmi RS, Maginn EN, Gabra H, Stronach EA, Wasan HS. Combined inhibition of the PI3K/mTOR/MEK pathway induces Bim/Mcl-1-regulated apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Biol Ther, 2019, 20(1): 21-30.
doi: 10.1080/15384047.2018.1504718 pmid: 30261145 |
| [49] |
Allgayer H. Pdcd4, a colon cancer prognostic that is regulated by a microRNA. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol, 2010, 73(3): 185-191.
doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2009.09.001 pmid: 19836969 |
| [50] |
Ferris WF. The Role and Interactions of Programmed Cell Death 4 and its Regulation by microRNA in Transformed Cells of the Gastrointestinal Tract. Front Oncol, 2022, 12: 903374.
doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.903374 |
| [51] |
Lu Z, Liu M, Stribinskis V, Klinge CM, Ramos KS, Colburn NH, Li Y. MicroRNA-21 promotes cell transformation by targeting the programmed cell death 4 gene. Oncogene, 2008, 27(31): 4373-4379.
doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.72 pmid: 18372920 |
| [52] |
Fu XF, He YL, Wang XF, Peng DX, Chen XY, Li XR, Wan Q. MicroRNA-16 promotes ovarian granulosa cell proliferation and suppresses apoptosis through targeting PDCD4 in polycystic ovarian syndrome. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2018, 48(2): 670-682.
doi: 10.1159/000491894 pmid: 30025387 |
| [53] |
Yang HS, Matthews CP, Clair T, Wang Q, Baker AR, Li CCH, Tan TH, Colburn NH. Tumorigenesis suppressor Pdcd4 down-regulates mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase kinase 1 expression to suppress colon carcinoma cell invasion. Mol Cell Biol, 2006, 26(4): 1297-1306.
doi: 10.1128/MCB.26.4.1297-1306.2006 |
| [54] | Zhou J, Li H, Li N, Li XP, Zhang HB, Song QB, Peng M.MicroRNA-641 inhibits lung cancer cells proliferation, metastasis but promotes apoptosis in cells by targeting PDCD4. Int J Clin Exp Pathol, 2017, 10(8): 8211-8221. |
| [55] |
Wu P, Wang JO, Mao XY, Xu HM, Zhu Z. PDCD4 regulates apoptosis in human peritoneal mesothelial cells and promotes gastric cancer peritoneal metastasis. Histol Histopathol, 2021, 36(4): 447-457.
doi: 10.14670/HH-18-305 pmid: 33442866 |
| [56] | Guo LM, Ding GF, Xu WC, Ge H, Jiang Y, Lu YF. Anti-PD-L1 antibody enhances T cell immune responses and reduces resistance of breast cancer cells to radiotherapy. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2022, 2022: 5938688. |
| [57] |
Zhang X, Wang XY, Song XG, Liu CM, Shi YY, Wang YK, Afonja O, Ma CH, Chen YH, Zhang LN. Programmed cell death 4 enhances chemosensitivity of ovarian cancer cells by activating death receptor pathway in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Sci, 2010, 101(10): 2163-2170.
doi: 10.1111/cas.2010.101.issue-10 |
| [58] |
Lu P, Sun HF, Zhang LX, Hou HL, Zhang L, Zhao FY, Ge C, Yao M, Wang TP, Li JJ. Isocorydine targets the drug-resistant cellular side population through PDCD4- related apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Med, 2012, 18(1): 1136-1146.
doi: 10.2119/molmed.2012.00055 |
| [59] |
Tang HE, Chen Y, Zhang N, Deng JC, Zhou K. Higher expression of programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) in acute myeloid leukemia is associated with better prognosis after chemotherapy. Ann Hematol, 2023, 102(12): 3401-3412.
doi: 10.1007/s00277-023-05516-8 |
| [60] |
Zarezadeh R, Abbasi K, Aboutalebi Vand Beilankouhi E, Navali N, Hakimi P, Fattahi A, Farzadi L. Programmed cell death 4: a novel player in the pathogenesis of polycystic ovary syndrome. Cell Biochem Funct, 2023, 42(1): e3905.
doi: 10.1002/cbf.v42.1 |
| [61] |
Wang Y, Gao CY, Zhou K, Liu WL, Zhang YL, Zhao Y. MicroRNA-532-5p-programmed cell death protein 4 (PDCD4) axis regulates angiotensin II-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cell apoptosis and proliferation. Microvasc Res, 2021, 138: 104195.
doi: 10.1016/j.mvr.2021.104195 |
| [62] |
Zhang YJ, Xiao YY, Ma Y, Liang NJ, Liang YH, Lu C, Xiao F.ROS-mediated miR-21-5p regulates the proliferation and apoptosis of Cr(VI)-exposed L02 hepatocytes via targeting PDCD4. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf, 2020, 191: 110160.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.110160 |
| [63] |
Shan WF, Ge HF, Chen BQ, Huang LG, Zhu SJ, Zhou YF.Upregulation of miR-499a-5p decreases cerebral ischemia/ reperfusion injury by targeting PDCD4. Cell Mol Neurobiol, 2022, 42(7): 2157-2170.
doi: 10.1007/s10571-021-01085-4 |
| [64] |
Li JW, Wei L, Han ZJ, Chen Z. Mesenchymal stromal cells-derived exosomes alleviate ischemia/reperfusion injury in mouse lung by transporting anti-apoptotic miR-21-5p. Eur J Pharmacol, 2019, 852: 68-76.
doi: S0014-2999(19)30055-X pmid: 30682335 |
| [65] |
Wang JW, Wang JL, Wang Y, Ma RY, Zhang SC, Zheng J, Xue WJ, Ding XM.Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived miR-21-5p protects grafted islets against apoptosis by targeting PDCD4. Stem Cells, 2023, 41(2): 169-183.
doi: 10.1093/stmcls/sxac085 |
| [66] |
Yang HS, Knies JL, Stark C, Colburn NH. Pdcd4 suppresses tumor phenotype in JB6 cells by inhibiting AP-1 transactivation. Oncogene, 2003, 22(24): 3712-3720.
doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206433 |
| [67] |
Yang HS, Jansen AP, Nair R, Shibahara K, Verma AK, Cmarik JL, Colburn NH. A novel transformation suppressor, Pdcd4, inhibits AP-1 transactivation but not NF-κB or ODC transactivation. Oncogene, 2001, 20(6): 669-676.
pmid: 11314000 |
| [68] |
Jansen AP, Camalier CE, Colburn NH. Epidermal expression of the translation inhibitor programmed cell death 4 suppresses tumorigenesis. Cancer Res, 2005, 65(14): 6034-6041.
pmid: 16024603 |
| [69] |
Guo XL, Li WJ, Wang Q, Yang HS. AKT activation by Pdcd4 knockdown up-regulates cyclin D1 expression and promotes cell proliferation. Genes Cancer, 2011, 2(8): 818-828.
doi: 10.1177/1947601911431082 pmid: 22393466 |
| [70] |
Wang Q, Sun Z, Yang HS. Downregulation of tumor suppressor Pdcd4 promotes invasion and activates both β-catenin/Tcf and AP-1-dependent transcription in colon carcinoma cells. Oncogene, 2008, 27(11): 1527-1535.
pmid: 17828298 |
| [71] |
Wang Q, Sun ZX, Allgayer H, Yang HS. Downregulation of E-cadherin is an essential event in activating β-catenin/Tcf-dependent transcription and expression of its target genes in Pdcd4 knockdown cells. Oncogene, 2010, 29(1): 128-138.
doi: 10.1038/onc.2009.302 pmid: 19784072 |
| [72] |
Wang Q, Zhu J, Zhang Y, Sun ZX, Guo XL, Wang X, Lee E, Bakthavatchalu V, Yang QF, Yang HS. Down-regulation of programmed cell death 4 leads to epithelial to mesenchymal transition and promotes metastasis in mice. Eur J Cancer, 2013, 49(7): 1761-1770.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2012.12.014 pmid: 23312883 |
| [73] |
Wang Q, Zhang Y, Yang HS. Pdcd4 knockdown up-regulates MAP4K1 expression and activation of AP-1 dependent transcription through c-Myc. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2012, 1823(10): 1807-1814.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2012.07.004 pmid: 22801218 |
| [74] |
Talotta F, Cimmino A, Matarazzo MR, Casalino L, De Vita G, D'Esposito M, Di Lauro R, Verde P. An autoregulatory loop mediated by miR-21 and PDCD4 controls the AP-1 activity in RAS transformation. Oncogene, 2009, 28(1): 73-84.
doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.370 pmid: 18850008 |
| [75] |
Jiang B, Liu Q, Gai JD, Guan JQ, Li QC. LncRNA SLC16A1-AS1 regulates the miR-182/PDCD4 axis and inhibits the triple-negative breast cancer cell cycle. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol, 2022, 44(4): 534-540.
doi: 10.1080/08923973.2022.2056482 |
| [76] |
Lv L, Du JH, Wang DR, Yan ZQ. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0026344 suppresses gastric cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion via the miR-590-5p/PDCD4 axis. J Pharm Pharmacol, 2022, 74(8): 1193-1204.
doi: 10.1093/jpp/rgac032 |
| [77] |
Zhou H, Shi PF, Jia XF, Xue QF. Long non-coding RNA LINC 01018 inhibits the progression of acute myeloid leukemia by targeting miR-499a-5p to regulate PDCD4. Oncol Lett, 2021, 22(1): 541.
doi: 10.3892/ol |
| [78] | Ji CL, Hu JS, Wang XH, Zheng WF, Deng XC, Song HM, Yu YH, Luo QF, Hua KY, Zhou XQ, Fang L. Hsa_circ_0053063 inhibits breast cancer cell proliferation via hsa_circ_0053063/hsa-miR-330-3p/PDCD4 axis. Aging (Albany NY), 2021, 13(7): 9627-9645. |
| [79] |
Li RN, Liu YW, Zhou FY, Yang HJ, Li JK, Dai NT, Sun W, Kong JY, Gao SG. Clinical significance of porphyromonas gingivalis enriching cancer stem cells by inhibiting programmed cell death factor 4 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. ACS Infect Dis, 2023, 9(10): 1846-1857.
doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.3c00182 |
| [80] | Zhu YD, Ba H, Chen J, Zhang M, Li P. Celastrus orbiculatus extract reduces stemness of gastric cancer stem cells by targeting PDCD4 and EIF3H. Integr Cancer Ther, 2021, 20: 15347354211058168. |
| [81] |
Li Y, Wang XY, Wang XS, Wan L, Liu YP, Shi YY, Zhang LN, Fang ZH, Wei ZT. PDCD4 suppresses proliferation, migration, and invasion of endometrial cells by inhibiting autophagy and NF-κB/MMP2/MMP9 signal pathway. Biol Reprod, 2018, 99(2): 360-372.
doi: 10.1093/biolre/ioy052 pmid: 29912279 |
| [82] |
Chen ML, Fan L, Huang GR, Sun ZF. Knockdown of miR-150-5p reduces hypoxia-induced autophagy and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of endometriotic cells via regulating the PDCD4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Cytokine, 2023, 162: 156086.
doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2022.156086 |
| [83] |
Wang L, Ye N, Lian XY, Peng F, Zhang HX, Gong H. MiR-208a-3p aggravates autophagy through the PDCD4- ATG5 pathway in Ang II-induced H9c2 cardiomyoblasts. Biomed Pharmacother, 2018, 98: 1-8.
doi: S0753-3322(17)34936-3 pmid: 29241069 |
| [84] |
Osoro EK, Du XJ, Liang D, Lan X, Farooq R, Huang FM, Zhu WH, Ren JJ, Sadiq M, Tian LF, Yang XD, Li DM, Lu SM.Induction of PDCD4 by albumin in proximal tubule epithelial cells potentiates proteinuria-induced dysfunctional autophagy by negatively targeting Atg5. Biochem Cell Biol, 2021, 99(5): 617-628.
doi: 10.1139/bcb-2021-0028 |
| [85] |
Wang L, Jiang Y, Song X, Guo C, Zhu F, Wang X, Wang Q, Shi Y, Wang J, Gao F, Zhao W, Chen YH, Zhang L. Pdcd4 deficiency enhances macrophage lipoautophagy and attenuates foam cell formation and atherosclerosis in mice. Cell Death Dis, 2016, 7(1): e2055.
doi: 10.1038/cddis.2015.416 |
| [86] |
Li S, Gao GD, Wu FY, Liu D, Zhao HY, Ke J, Liu Y, Li F, Li J, Chen ZY, Tang ZM, Bai L, Zhang JX, Zheng W, Chen X. Programmed cell death protein 4 deficiency suppresses foam cell formation by activating autophagy in advanced glycation end-product low-density lipoprotein- induced macrophages. J Cell Biochem, 2019, 120(5): 7689-7700.
doi: 10.1002/jcb.v120.5 |
| [87] |
Hilliard A, Hilliard B, Zheng SJ, Sun HH, Miwa T, Song WC, Göke R, Chen YH.Translational regulation of autoimmune inflammation and lymphoma genesis by programmed cell death 4. J Immunol, 2006, 177(11): 8095-8102.
pmid: 17114484 |
| [88] |
Chen Q, Lu HJ, Duan CW, Zhu XY, Zhang Y, Li MM, Zhang DM. PDCD4 simultaneously promotes microglia activation via PDCD4-MAPK-NF-κB positive loop and facilitates neuron apoptosis during neuroinflammation. Inflammation, 2022, 45(1): 234-252.
doi: 10.1007/s10753-021-01541-9 |
| [89] |
Fei XH, Cen XJ, Zhao RC, Wang J, Cui HB. PRMT5 knockdown enhances cell viability and suppresses cell apoptosis, oxidative stress, inflammation and endothelial dysfunction in ox-LDL-induced vascular endothelial cells via interacting with PDCD4. Int Immunopharmacol, 2023, 122: 110529.
doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110529 |
| [90] | Lin HY, Gao D, Wang SJ, Wang ZC, Guan HW, Wang YW, Zhou Y. Inhibition of circ_0000231 suppresses oxidized low density lipoprotein-induced apoptosis, autophagy and inflammation in human umbilical vein endothelial cells by regulating miR-590-5p/PDCD4 axis. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc, 2023. |
| [91] |
Liu HF, Sun JZ, Gao L, Fan LL, Chen DM, Wu LF. MicroRNA-421 attenuates macrophage-mediated inflammation by inhibiting PDCD4 in vitro. Mol Med Rep, 2021, 24(1): 527.
doi: 10.3892/mmr |
| [92] |
Zhong B, Yang XD, Sun QZ, Liu L, Lan X, Tian J, He QR, Hou W, Liu HY, Jiang CS, Gao N, Lu SM. Pdcd4 modulates markers of macrophage alternative activation and airway remodeling in antigen-induced pulmonary inflammation. J Leukoc Biol, 2014, 96(6): 1065-1075.
doi: 10.1189/jlb.3A0313-136RRR |
| [93] |
Schmid T, Bajer MM, Blees JS, Eifler LK, Milke L, Rübsamen D, Schulz K, Weigert A, Baker AR, Colburn NH, Brüne B. Inflammation-induced loss of Pdcd4 is mediated by phosphorylation-dependent degradation. Carcinogenesis, 2011, 32(10): 1427-1433.
doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgr131 pmid: 21771721 |
| [94] |
Vadivel Gnanasundram S, Bonczek O, Wang LX, Chen S, Fahraeus R. p53 mRNA metabolism links with the DNA damage response. Genes (Basel), 2021, 12(9): 1446.
doi: 10.3390/genes12091446 |
| [95] |
Singh P, Marikkannu R, Bitomsky N, Klempnauer KH. Disruption of the Pdcd4 tumor suppressor gene in chicken DT40 cells reveals its role in the DNA-damage response. Oncogene, 2009, 28(42): 3758-3764.
doi: 10.1038/onc.2009.239 pmid: 19684621 |
| [96] |
Kumar N, Wethkamp N, Waters LC, Carr MD, Klempnauer KH.Tumor suppressor protein Pdcd4 interacts with Daxx and modulates the stability of Daxx and the Hipk2-dependent phosphorylation of p 53 at serine 46. Oncogenesis, 2013, 2(1): e37.
doi: 10.1038/oncsis.2012.37 |
| [97] |
Yang WH, George AP, Wang CM, Yang RH, Duncan AM, Patel D, Neil ZD, Yang WH. Tumor suppressor p53 down-regulates programmed cell death protein 4 (PDCD4) expression. Curr Oncol, 2023, 30(2): 1614-1625.
doi: 10.3390/curroncol30020124 pmid: 36826085 |
| [1] | Qingyu Sun, Yang Zhou, Lijuan Du, Mengke Zhang, Jiale Wang, Yuanyuan Ren, Fang Liu. Analysis between macrophage-related genes with prognosis and tumor microenvironment in non-small cell lung cancer [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2023, 45(8): 684-699. |
| [2] | Chenghao Yan, Weiyu Bai, Zhimeng Zhang, Junling Shen, Youjun Wang, Jianwei Sun. The roles and mechanism of STIM1 in tumorigenesis and metastasis [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2023, 45(5): 395-408. |
| [3] | Chunhui Ma, Haixu Hu, Lijuan Zhang, Yi Liu, Tianyi Liu. Establishment and verification of a digital PCR assay for the detection of CK19 expression in quantitative analysis of circulating tumor cell [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2023, 45(3): 250-260. |
| [4] | Dong Chang, Xiangxiang Liu, Rui Liu, Jianwei Sun. The role and regulatory mechanism of FSCN1 in breast tumorigenesis and progression [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2023, 45(2): 115-127. |
| [5] | Qinggang Hao, Fenggui Sun, Chenghao Yan, Jianwei Sun. Progress on the role and mechanism of MT1-MMP in tumor metastasis [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(9): 745-755. |
| [6] | Mingliang Jiang, Hong Lang, Xiaonan Li, Ye Zu, Jing Zhao, Shenling Peng, Zhen Liu, Zongxiang Zhan, Zhongyun Piao. Progress on plant orphan genes [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(8): 682-694. |
| [7] | Yan Zhao, Chenxin Wang, Tianming Yang, Chunshuang Li, Lihong Zhang, Dongni Du, Ruoxi Wang, Jing Wang, Min Wei, Xueqing Ba. Linking oxidative DNA lesion 8-OxoG to tumor development and progression [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(6): 466-477. |
| [8] | Yanni Kou, Shan Cen, Xiaoyu Li. Research and application on LINE-1 in diagnosis and treatment of tumorigenesis [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2021, 43(6): 571-579. |
| [9] |
Zhuo Wang, Xiaohan Shen, Qihui Shi.
|
| [10] | Linan Zhao, Na Wang, Guoliang Yang, Xianbin Su, Zeguang Han. A method for reliable detection of genomic point mutations based on single-cell target-sequencing [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2020, 42(7): 703-712. |
| [11] | Shumin Chen, Ling Ma, Shan Cen. Progress of SLFN family proteins in tumor and virus infection [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2020, 42(5): 444-451. |
| [12] | Qiang Zhang, Mingliang Gu. Single-cell sequencing and its application in breast cancer [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2020, 42(3): 250-268. |
| [13] | Huanzi Lu,Dikan Wang,Zhi Wang. Correlation analysis of the prognosis of HPV positive oropharyngeal cancer patients with T cell infiltration and neoantigen load [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2019, 41(8): 725-735. |
| [14] | Xiangrong Cheng,Xinglin Hu,Qi Jiang,Xingwei Huang,Nan Wang,Lei Lei. The epigenetic regulation of ribosomal DNA and tumorigenesis [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2019, 41(3): 185-192. |
| [15] | Baojun Wu,Zhuo Wang,Yu Dong,Yuliang Deng,Qihui Shi. Identification and single-cell sequencing analysis of rare tumor cells in malignant pleural effusion of lung cancer patients [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2019, 41(2): 175-184. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||