Hereditas(Beijing) ›› 2024, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (4): 279-289.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.23-307
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
The roles and mechanisms of histone variant H2A.Z in transcriptional regulation
- School of Basic Medical Sciences, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Medical Epigenetics, Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300070, China
-
Received:2023-12-13Revised:2024-02-27Online:2024-04-20Published:2024-02-29 -
Contact:Xudong Wu E-mail:591162534@qq.com;wuxudong@tmu.edu.cn -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(31870725);National Natural Science Foundation of China(32071204)
Cite this article
Zhaoran Sun, Xudong Wu. The roles and mechanisms of histone variant H2A.Z in transcriptional regulation[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2024, 46(4): 279-289.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] |
Chen P, Zhao JC, Li GH. Histone variants in development and diseases. J Genet Genomics, 2013, 40(7): 355-365.
doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2013.05.001 pmid: 23876776 |
| [2] | Buschbeck M, Hake SB. Variants of core histones and their roles in cell fate decisions, development and cancer. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2017, 18(5): 299-314. |
| [3] | Talbert PB, Henikoff S. Histone variants on the move: substrates for chromatin dynamics. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2017, 18(2): 115-126. |
| [4] |
Doenecke D, Albig W, Bode C, Drabent B, Franke K, Gavenis K, Witt O. Histones: genetic diversity and tissue-specific gene expression. Histochem Cell Biol, 1997, 107(1): 1-10.
pmid: 9049636 |
| [5] |
Albig W, Doenecke D. The human histone gene cluster at the D6S105 locus. Hum Genet, 1997, 101(3): 284-294.
doi: 10.1007/s004390050630 pmid: 9439656 |
| [6] |
Venkatesh S, Workman JL. Histone exchange, chromatin structure and the regulation of transcription. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2015, 16(3): 178-189.
doi: 10.1038/nrm3941 |
| [7] |
Chakravarthy S, Luger K. The histone variant macro-H2A preferentially forms "hybrid nucleosomes". J Biol Chem, 2006, 281(35): 25522-25531.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M602258200 pmid: 16803903 |
| [8] |
Thakar A, Gupta P, Ishibashi T, Finn R, Silva-Moreno B, Uchiyama S, Fukui K, Tomschik M, Ausio J, Zlatanova J. H2A.Z and H3.3 histone variants affect nucleosome structure: biochemical and biophysical studies. Biochemistry, 2009, 48(46): 10852-10857.
doi: 10.1021/bi901129e pmid: 19856965 |
| [9] |
West MH, Bonner WM. Histone 2A, a heteromorphous family of eight protein species. Biochemistry, 1980, 19(14): 3238-3245.
pmid: 7407044 |
| [10] |
Suto RK, Clarkson MJ, Tremethick DJ, Luger K. Crystal structure of a nucleosome core particle containing the variant histone H2A.Z. Nat Struct Biol, 2000, 7(12): 1121-1124.
pmid: 11101893 |
| [11] |
Kreienbaum C, Paasche LW, Hake SB. H2A.Z's 'social' network: functional partners of an enigmatic histone variant. Trends Biochem Sci, 2022, 47(11): 909-920.
doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2022.04.014 |
| [12] |
Colino-Sanguino Y, Clark SJ, Valdes-Mora F. The H2A.Z-nuclesome code in mammals: emerging functions. Trends Genet, 2022, 38(3): 273-289.
doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2021.10.003 |
| [13] |
Fuda NJ, Ardehali MB, Lis JT. Defining mechanisms that regulate RNA polymerase II transcription in vivo. Nature, 2009, 461(7261): 186-192.
doi: 10.1038/nature08449 |
| [14] |
Lorch Y, Kornberg RD. Chromatin-remodeling for transcription. Q Rev Biophys, 2017, 50: e5.
doi: 10.1017/S003358351700004X |
| [15] |
Lorch Y, LaPointe JW, Kornberg RD. Nucleosomes inhibit the initiation of transcription but allow chain elongation with the displacement of histones. Cell, 1987, 49(2): 203-210.
pmid: 3568125 |
| [16] |
Coon JJ, Ueberheide B, Syka JEP, Dryhurst DD, Ausio J, Shabanowitz J, Hunt DF. Protein identification using sequential ion/ion reactions and tandem mass spectrometry. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2005, 102(27): 9463-9468.
pmid: 15983376 |
| [17] |
Talbert PB, Ahmad K, Almouzni G, Ausió J, Berger F, Bhalla PL, Bonner WM, Cande WZ, Chadwick BP, Chan SWL, Cross GAM, Cui LW, Dimitrov SI, Doenecke D, Eirin-López JM, Gorovsky MA, Hake SB, Hamkalo BA, Holec S, Jacobsen SE, Kamieniarz K, Khochbin S, Ladurner AG, Landsman D, Latham JA, Loppin B, Malik HS, Marzluff WF, Pehrson JR, Postberg J, Schneider R, Singh MB, Smith MM, Thompson E, Torres-Padilla ME, Tremethick DJ, Turner BM, Waterborg JH, Wollmann H, Yelagandula R, Zhu B, Henikoff S. A unified phylogeny-based nomenclature for histone variants. Epigenetics Chromatin, 2012, 5: 7.
doi: 10.1186/1756-8935-5-7 pmid: 22650316 |
| [18] |
Matsuda R, Hori T, Kitamura H, Takeuchi K, Fukagawa T, Harata M. Identification and characterization of the two isoforms of the vertebrate H2A.Z histone variant. Nucleic Acids Res, 2010, 38(13): 4263-4273.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq171 pmid: 20299344 |
| [19] |
Draker R, Ng MK, Sarcinella E, Ignatchenko V, Kislinger T, Cheung P. A combination of H2A.Z and H4 acetylation recruits Brd2 to chromatin during transcriptional activation. PLoS Genet, 2012, 8(11): e1003047.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003047 |
| [20] |
Vardabasso C, Gaspar-Maia A, Hasson D, Pünzeler S, Valle-Garcia D, Straub T, Keilhauer EC, Strub T, Dong J, Panda T, Chung CY, Yao JL, Singh R, Segura MF, Fontanals-Cirera B, Verma A, Mann M, Hernando E, Hake SB, Bernstein E. Histone Variant H2A.Z.2 mediates proliferation and drug sensitivity of malignant melanoma. Mol Cell, 2015, 59(1): 75-88.
doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.05.009 pmid: 26051178 |
| [21] |
Zhao B, Chen Y, Jiang N, Yang L, Sun SF, Zhang Y, Wen ZQ, Ray L, Liu H, Hou GL, Lin XH. Znhit 1 controls intestinal stem cell maintenance by regulating H2A.Z incorporation. Nat Commun, 2019, 10(1): 1071.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09060-w |
| [22] |
Creyghton MP, Markoulaki S, Levine SS, Hanna J, Lodato MA, Sha K, Young RA, Jaenisch R, Boyer LA. H2AZ is enriched at polycomb complex target genes in ES cells and is necessary for lineage commitment. Cell, 2008, 135(4): 649-661.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.09.056 pmid: 18992931 |
| [23] |
Rudnizky S, Bavly A, Malik O, Pnueli L, Melamed P, Kaplan A. H2A.Z controls the stability and mobility of nucleosomes to regulate expression of the LH genes. Nat Commun, 2016, 7: 12958.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms12958 pmid: 27653784 |
| [24] |
Su LB, Xia WL, Shen TJ, Liang QL, Wang WW, Li H, Jiao JW. H2A.Z.1 crosstalk with H3K56-acetylation controls gliogenesis through the transcription of folate receptor. Nucleic Acids Res, 2018, 46(17): 8817-8831.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gky585 pmid: 29982651 |
| [25] |
Li ZQ, Li YX, Jiao JW. Neural progenitor cells mediated by H2A.Z.2 regulate microglial development via Cxcl14 in the embryonic brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2019, 116(48): 24122-24132.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1913978116 pmid: 31712428 |
| [26] |
Wratting D, Thistlethwaite A, Harris M, Zeef LAH, Millar CB. A conserved function for the H2A.Z C terminus. J Biol Chem, 2012, 287(23): 19148-19157.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.317990 pmid: 22493515 |
| [27] |
Bönisch C, Schneider K, Pünzeler S, Wiedemann SM, Bielmeier C, Bocola M, Eberl HC, Kuegel W, Neumann J, Kremmer E, Leonhardt H, Mann M, Michaelis J, Schermelleh L, Hake SB. H2A.Z.2.2 is an alternatively spliced histone H2A.Z variant that causes severe nucleosome destabilization. Nucleic Acids Res, 2012, 40(13): 5951-5964.
pmid: 22467210 |
| [28] |
Giaimo BD, Ferrante F, Herchenröther A, Hake SB, Borggrefe T. The histone variant H2A.Z in gene regulation. Epigenetics Chromatin, 2019, 12(1): 37.
doi: 10.1186/s13072-019-0274-9 pmid: 31200754 |
| [29] |
Bönisch C, Hake SB. Histone H2A variants in nucleosomes and chromatin: more or less stable? Nucleic Acids Res, 2012, 40(21): 10719-10741.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gks865 pmid: 23002134 |
| [30] |
Eickbush TH, Godfrey JE, Elia MC, Moudrianakis EN. H2a-specific proteolysis as a unique probe in the analysis of the histone octamer. J Biol Chem, 1988, 263(35): 18972-18978.
pmid: 3058692 |
| [31] |
Adam M, Robert F, Larochelle M, Gaudreau L. H2A.Z is required for global chromatin integrity and for recruitment of RNA polymerase II under specific conditions. Mol Cell Biol, 2001, 21(18): 6270-6279.
doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.18.6270-6279.2001 pmid: 11509669 |
| [32] |
Horikoshi N, Sato K, Shimada K, Arimura Y, Osakabe A, Tachiwana H, Hayashi-Takanaka Y, Iwasaki W, Kagawa W, Harata M, Kimura H, Kurumizaka H.Structural polymorphism in the L1 loop regions of human H2A.Z.1 and H2A.Z.2. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr, 2013, 69(Pt 12): 2431-2439.
doi: 10.1107/S090744491302252X |
| [33] |
Greenberg RS, Long HK, Swigut T, Wysocka J. Single amino acid change underlies distinct roles of H2A.Z subtypes in Human Syndrome. Cell, 2019, 178(6): 1421-1436.e24.
doi: S0092-8674(19)30890-6 pmid: 31491386 |
| [34] |
Lamaa A, Humbert J, Aguirrebengoa M, Cheng X, Nicolas E, Côté J, Trouche D. Integrated analysis of H2A.Z isoforms function reveals a complex interplay in gene regulation. eLife, 2020, 9: e53375.
doi: 10.7554/eLife.53375 |
| [35] |
Strahl BD, Allis CD. The language of covalent histone modifications. Nature, 2000, 403(6765): 41-45.
doi: 10.1038/47412 |
| [36] |
Kouzarides T. Chromatin modifications and their function. Cell, 2007, 128(4): 693-705.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.02.005 pmid: 17320507 |
| [37] |
Vavra KJ, Allis CD, Gorovsky MA. Regulation of histone acetylation in Tetrahymena macro- and micronuclei. J Biol Chem, 1982, 257(5): 2591-2598.
pmid: 7061439 |
| [38] |
Dryhurst D, Ishibashi T, Rose KL, Eirín-López JM, McDonald D, Silva-Moreno B, Veldhoen N, Helbing CC, Hendzel MJ, Shabanowitz J, Hunt DF, Ausió J. Characterization of the histone H2A.Z-1 and H2A.Z-2 isoforms in vertebrates. BMC Biol, 2009, 7: 86.
doi: 10.1186/1741-7007-7-86 pmid: 20003410 |
| [39] |
Bruce K, Myers FA, Mantouvalou E, Lefevre P, Greaves I, Bonifer C, Tremethick DJ, Thorne AW, Crane-Robinson C. The replacement histone H2A. Z in a hyperacetylated form is a feature of active genes in the chicken. Nucleic Acids Res, 2005, 33(17): 5633-5639.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gki874 |
| [40] |
Santisteban MS, Kalashnikova T, Smith MM. Histone H2A.Z regulats transcription and is partially redundant with nucleosome remodeling complexes. Cell, 2000, 103(3): 411-422.
pmid: 11081628 |
| [41] |
Bellucci L, Dalvai M, Kocanova S, Moutahir F, Bystricky K. Activation of p21 by HDAC inhibitors requires acetylation of H2A.Z. PLoS One, 2013, 8(1): e54102.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054102 |
| [42] |
Dalvai M, Fleury L, Bellucci L, Kocanova S, Bystricky K. TIP48/Reptin and H2A.Z requirement for initiating chromatin remodeling in estrogen-activated transcription. PLoS Genet, 2013, 9(4): e1003387.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003387 |
| [43] |
Valdés-Mora F, Song JZ, Statham AL, Strbenac D, Robinson MD, Nair SS, Patterson KI, Tremethick DJ, Stirzaker C, Clark SJ. Acetylation of H2A.Z is a key epigenetic modification associated with gene deregulation and epigenetic remodeling in cancer. Genome Res, 2012, 22(2): 307-321.
doi: 10.1101/gr.118919.110 pmid: 21788347 |
| [44] |
Ku M, Jaffe JD, Koche RP, Rheinbay E, Endoh M, Koseki H, Carr SA, Bernstein BE. H2A.Z landscapes and dual modifications in pluripotent and multipotent stem cells underlie complex genome regulatory functions. Genome Biol, 2012, 13(10): R85.
doi: 10.1186/gb-2012-13-10-r85 |
| [45] |
Hu GQ, Cui KR, Northrup D, Liu CY, Wang CC, Tang QS, Ge K, Levens D, Crane-Robinson C, Zhao KJ. H2A.Z facilitates access of active and repressive complexes to chromatin in embryonic stem cell self-renewal and differentiation. Cell Stem Cell, 2013, 12(2): 180-192.
doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2012.11.003 pmid: 23260488 |
| [46] |
Giaimo BD, Ferrante F, Vallejo DM, Hein K, Gutierrez-Perez I, Nist A, Stiewe T, Mittler G, Herold S, Zimmermann T, Bartkuhn M, Schwarz P, Oswald F, Dominguez M, Borggrefe T. Histone variant H2A.Z deposition and acetylation directs the canonical Notch signaling response. Nucleic Acids Res, 2018, 46(16): 8197-8215.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gky551 pmid: 29986055 |
| [47] |
Valdés-Mora F, Gould CM, Colino-Sanguino Y, Qu WJ, Song JZ, Taylor KM, Buske FA, Statham AL, Nair SS, Armstrong NJ, Kench JG, Lee KML, Horvath LG, Qiu MR, Ilinykh A, Yeo-Teh NS, Gallego-Ortega D, Stirzaker C, Clark SJ. Acetylated histone variant H2A.Z is involved in the activation of neo-enhancers in prostate cancer. Nat Commun, 2017, 8(1): 1346.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-01393-8 pmid: 29116202 |
| [48] |
Babiarz JE, Halley JE, Rine J. Telomeric heterochromatin boundaries require NuA4-dependent acetylation of histone variant H2A. Z in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genes Dev, 2006, 20(6): 700-710.
doi: 10.1101/gad.1386306 |
| [49] |
Kim HS, Vanoosthuyse V, Fillingham J, Roguev A, Watt S, Kislinger T, Treyer A, Carpenter LR, Bennett CS, Emili A, Greenblatt JF, Hardwick KG, Krogan NJ, Bähler J, Keogh MC. An acetylated form of histone H2A.Z regulates chromosome architecture in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Nat Struct Mol Biol, 2009, 16(12): 1286-1293.
doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1688 |
| [50] |
Dalvai M, Bellucci L, Fleury L, Lavigne AC, Moutahir F, Bystricky K. H2A.Z-dependent crosstalk between enhancer and promoter regulates cyclin D1 expression. Oncogene, 2013, 32(36): 4243-4251.
doi: 10.1038/onc.2012.442 pmid: 23108396 |
| [51] |
Krogan NJ, Keogh MC, Datta N, Sawa C, Ryan OW, Ding HM, Haw RA, Pootoolal J, Tong A, Canadien V, Richards DP, Wu XR, Emili A, Hughes TR, Buratowski S, Greenblatt JF. A Snf2 family ATPase complex required for recruitment of the histone H2A variant Htz1. Mol Cell, 2003, 12(6): 1565-1576.
pmid: 14690608 |
| [52] |
Link S, Spitzer RMM, Sana M, Torrado M, Völker-Albert MC, Keilhauer EC, Burgold T, Pünzeler S, Low JKK, Lindström I, Nist A, Regnard C, Stiewe T, Hendrich B, Imhof A, Mann M, Mackay JP, Bartkuhn M, Hake SB. PWWP2A binds distinct chromatin moieties and interacts with an MTA1-specific core NuRD complex. Nat Commun, 2018, 9(1): 4300.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06665-5 pmid: 30327463 |
| [53] |
Draker R, Sarcinella E, Cheung P. USP10 deubiquitylates the histone variant H2A.Z and both are required for androgen receptor-mediated gene activation. Nucleic Acids Res, 2011, 39(9): 3529-3542.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq1352 pmid: 21245042 |
| [54] |
Sarcinella E, Zuzarte PC, Lau PNI, Draker R, Cheung P. Monoubiquitylation of H2A.Z distinguishes its association with euchromatin or facultative heterochromatin. Mol Cell Biol, 2007, 27(18): 6457-6468.
pmid: 17636032 |
| [55] |
Surface LE, Fields PA, Subramanian V, Behmer R, Udeshi N, Peach SE, Carr SA, Jaffe JD, Boyer LA. H2A.Z.1 monoubiquitylation antagonizes BRD2 to maintain poised chromatin in ESCs. Cell Rep, 2016, 14(5): 1142-1155.
doi: S2211-1247(15)01556-9 pmid: 26804911 |
| [56] |
Sarangi P, Zhao XL. SUMO-mediated regulation of DNA damage repair and responses. Trends Biochem Sci, 2015, 40(4): 233-242.
doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2015.02.006 pmid: 25778614 |
| [57] |
Hay RT. SUMO: a history of modification. Mol Cell, 2005, 18(1): 1-12.
doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2005.03.012 pmid: 15808504 |
| [58] |
Kalocsay M, Hiller NJ, Jentsch S. Chromosome-wide Rad 51 Spreading and SUMO-H2A.Z-dependent chromosome fixation in response to a persistent DNA double- strand break. Mol Cell, 2009, 33(3): 335-343.
doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.01.016 pmid: 19217407 |
| [59] |
Fukuto A, Ikura M, Ikura T, Sun JY, Horikoshi Y, Shima H, Igarashi K, Kusakabe M, Harata M, Horikoshi N, Kurumizaka H, Kiuchi Y, Tashiro S. SUMO modification system facilitates the exchange of histone variant H2A.Z-2 at DNA damage sites. Nucleus, 2018, 9(1): 87-94.
doi: 10.1080/19491034.2017.1395543 pmid: 29095668 |
| [60] |
Binda O, Sevilla A, LeRoy G, Lemischka IR, Garcia BA, Richard S. SETD6 monomethylates H2AZ on lysine 7 and is required for the maintenance of embryonic stem cell self-renewal. Epigenetics, 2013, 8(2): 177-183.
doi: 10.4161/epi.23416 pmid: 23324626 |
| [61] |
Tsai CH, Chen YJ, Yu CJ, Tzeng SR, Wu IC, Kuo WH, Lin MC, Chan NL, Wu KJ, Teng SC. SMYD3-mediated H2A.Z.1 methylation promotes cell cycle and cancer proliferation. Cancer Res, 2016, 76(20): 6043-6053.
doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-0500 |
| [62] |
Li B, Pattenden SG, Lee D, Gutiérrez J, Chen J, Seidel C, Gerton J, Workman JL. Preferential occupancy of histone variant H2AZ at inactive promoters influences local histone modifications and chromatin remodeling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2005, 102(51): 18385-18390.
pmid: 16344463 |
| [63] |
Raisner RM, Hartley PD, Meneghini MD, Bao MZ, Liu CL, Schreiber SL, Rando OJ, Madhani HD. Histone variant H2A.Z marks the 5′ ends of both active and inactive genes in euchromatin. Cell, 2005, 123(2): 233-248.
pmid: 16239142 |
| [64] |
Farris SD, Rubio ED, Moon JJ, Gombert WM, Nelson BH, Krumm A. Transcription-induced chromatin remodeling at the c-myc gene involves the local exchange of histone H2A.Z. J Biol Chem, 2005, 280(26): 25298-25303.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M501784200 |
| [65] |
Sutcliffe EL, Parish IA, He YQ, Juelich T, Tierney ML, Rangasamy D, Milburn PJ, Parish CR, Tremethick DJ, Rao S. Dynamic histone variant exchange accompanies gene induction in T cells. Mol Cell Biol, 2009, 29(7): 1972-1986.
doi: 10.1128/MCB.01590-08 pmid: 19158270 |
| [66] |
Hardy S, Jacques PE, Gévry N, Forest A, Fortin ME, Laflamme L, Gaudreau L, Robert F. The euchromatic and heterochromatic landscapes are shaped by antagonizing effects of transcription on H2A.Z deposition. PLoS Genet, 2009, 5(10): e1000687.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000687 |
| [67] |
Day DS, Zhang B, Stevens SM, Ferrari F, Larschan EN, Park PJ, Pu WT. Comprehensive analysis of promoter- proximal RNA polymerase II pausing across mammalian cell types. Genome Biol, 2016, 17(1): 120.
doi: 10.1186/s13059-016-0984-2 |
| [68] |
Mylonas C, Lee C, Auld AL, Cisse II, Boyer LA. A dual role for H2A.Z.1 in modulating the dynamics of RNA polymerase II initiation and elongation. Nat Struct Mol Biol, 2021, 28(5): 435-442.
doi: 10.1038/s41594-021-00589-3 pmid: 33972784 |
| [69] |
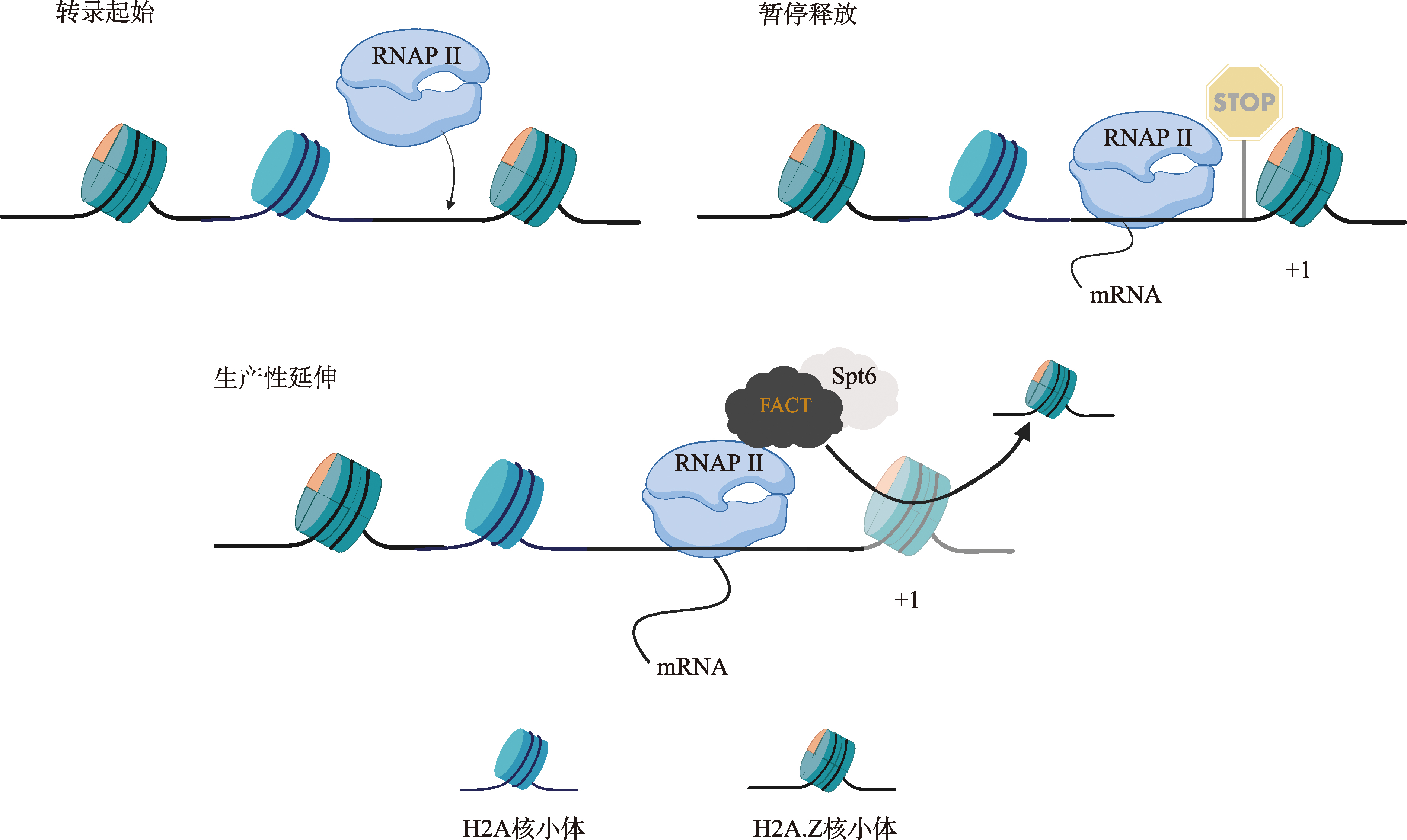
Jeronimo C, Watanabe S, Kaplan CD, Peterson CL, Robert F. The histone chaperones FACT and Spt6 restrict H2A.Z from Intragenic Locations. Mol Cell, 2015, 58(6): 1113-1123.
doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.03.030 pmid: 25959393 |
| [70] |
Rudnizky S, Bavly A, Malik O, Pnueli L, Melamed P, Kaplan A. H2A.Z controls the stability and mobility of nucleosomes to regulate expression of the LH genes. Nat Commun, 2016, 7: 12958.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms12958 pmid: 27653784 |
| [71] |
Jin CY, Zang CZ, Wei G, Cui KR, Peng WQ, Zhao KJ, Felsenfeld G. H3.3/H2A.Z double variant-containing nucleosomes mark 'nucleosome-free regions' of active promoters and other regulatory regions. Nat Genet, 2009, 41(8): 941-945.
doi: 10.1038/ng.409 pmid: 19633671 |
| [72] |
Brunelle M, Nordell Markovits A, Rodrigue S, Lupien M, Jacques PÉ, Gévry N. The histone variant H2A.Z is an important regulator of enhancer activity. Nucleic Acids Res, 2015, 43(20): 9742-9756.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv825 pmid: 26319018 |
| [73] |
Colino-Sanguino Y, Cornett EM, Moulder D, Smith GC, Hrit J, Cordeiro-Spinetti E, Vaughan RM, Krajewski K, Rothbart SB, Clark SJ, Valdés-Mora F. A read/write mechanism connects p300 bromodomain function to H2A.Z acetylation. iScience, 2019, 21: 773-788.
doi: S2589-0042(19)30434-1 pmid: 31727574 |
| [74] |
Yang Y, Dai ZM, Dai XH. Insights into active intragenic enhancers. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2019, 515(3): 423-428.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.05.160 |
| [75] | Liu X, Zhang JJ, Zhou JL, Bu GW, Zhu W, He HN, Sun QR, Yu ZS, Xiong WJ, Wang LY, Wu DY, Dou CL, Yu LT, Zhou K, Wang SK, Fan ZG, Wang TT, Hu RF, Hu TT, Zhang X, Miao YL. Hierarchical accumulation of histone variant H2A.Z regulates transcriptional states and histone modifications in early mammalian embryos. Adv Sci (Weinh), 2022, 9(23): e2200057. |
| [76] |
Kobor MS, Venkatasubrahmanyam S, Meneghini MD, Gin JW, Jennings JL, Link AJ, Madhani HD, Rine J. A protein complex containing the conserved Swi2/Snf2- related ATPase Swr1p deposits histone variant H2A.Z into euchromatin. PLoS Biol, 2004, 2(5): E131.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0020131 |
| [77] |
Krogan NJ, Dover J, Wood A, Schneider J, Heidt J, Boateng MA, Dean K, Ryan OW, Golshani A, Johnston M, Greenblatt JF, Shilatifard A. The Paf 1 complex is required for histone H3 methylation by COMPASS and Dot1p: linking transcriptional elongation to histone methylation. Mol Cell, 2003, 11(3): 721-729.
pmid: 12667454 |
| [78] |
Mizuguchi G, Shen XT, Landry J, Wu WH, Sen S, Wu C. ATP-driven exchange of histone H2AZ variant catalyzed by SWR1 chromatin remodeling complex. Science, 2004, 303(5656): 343-348.
pmid: 14645854 |
| [79] |
Ladurner AG, Inouye C, Jain R, Tjian R. Bromodomains mediate an acetyl-histone encoded antisilencing function at heterochromatin boundaries. Mol Cell, 2003, 11(2): 365-376.
pmid: 12620225 |
| [80] |
Matangkasombut O, Buratowski S. Different sensitivities of bromodomain factors 1 and 2 to histone H4 acetylation. Mol Cell, 2003, 11(2): 353-363.
pmid: 12620224 |
| [81] |
Gévry N, Chan H, Laflamme L, Livingston DM, Gaudreau L. p21 transcription is regulated by differential localization of histone H2A.Z. Genes Dev, 2007, 21(15): 1869-1881.
doi: 10.1101/gad.1545707 |
| [82] |
Ruhl DD, Jin JJ, Cai Y, Swanson S, Florens L, Washburn MP, Conaway RC, Conaway JW, Chrivia JC. Purification of a human SRCAP complex that remodels chromatin by incorporating the histone variant H2A.Z into nucleosomes. Biochemistry, 2006, 45(17): 5671-5677.
doi: 10.1021/bi060043d |
| [83] |
Choi J, Heo K, An W. Cooperative action of TIP48 and TIP49 in H2A.Z exchange catalyzed by acetylation of nucleosomal H2A. Nucleic Acids Res, 2009, 37(18): 5993-6007.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp660 pmid: 19696079 |
| [84] |
Cai Y, Jin JJ, Tomomori-Sato C, Sato S, Sorokina I, Parmely TJ, Conaway RC, Conaway JW. Identification of new subunits of the multiprotein mammalian TRRAP/ TIP60-containing histone acetyltransferase complex. J Biol Chem, 2003, 278(44): 42733-42736.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.C300389200 |
| [85] |
Doyon Y, Selleck W, Lane WS, Tan S, Côté J.Structural and functional conservation of the NuA4 histone acetyltransferase complex from yeast to humans. Mol Cell Biol, 2004, 24(5): 1884-1896.
doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.5.1884-1896.2004 |
| [86] |
Yang Y, Zhang LW, Xiong CY, Chen J, Wang L, Wen ZQ, Yu J, Chen P, Xu YH, Jin JJ, Cai Y, Li GH. HIRA complex presets transcriptional potential through coordinating depositions of the histone variants H3.3 and H2A.Z on the poised genes in mESCs. Nucleic Acids Res, 2022, 50(1): 191-206.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab1221 |
| [87] |
Greenberg RS, Long HK, Swigut T, Wysocka J. Single amino acid change underlies distinct roles of H2A.Z subtypes in Human Syndrome. Cell, 2019, 178(6): 1421-1436.e24.
doi: S0092-8674(19)30890-6 pmid: 31491386 |
| [88] |
Chen CW, Zhang LD, Dutta R, Niroula A, Miller PG, Gibson CJ, Bick AG, Reyes JM, Lee YT, Tovy A, Gu TP, Waldvogel S, Chen YH, Venters BJ, Estève PO, Pradhan S, Keogh MC, Natarajan P, Takahashi K, Sperling AS, Goodell MA. SRCAP mutations drive clonal hematopoiesis through epigenetic and DNA repair dysregulation. Cell Stem Cell, 2023, 30(11): 1503-1519.e8.
doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2023.09.011 |
| [89] |
Berta DG, Kuisma H, Välimäki N, Räisänen M, Jäntti M, Pasanen A, Karhu A, Kaukomaa J, Taira A, Cajuso T, Nieminen S, Penttinen RM, Ahonen S, Lehtonen R, Mehine M, Vahteristo P, Jalkanen J, Sahu B, Ravantti J, Mäkinen N, Rajamäki K, Palin K, Taipale J, Heikinheimo O, Bützow R, Kaasinen E, Aaltonen LA. Deficient H2A.Z deposition is associated with genesis of uterine leiomyoma. Nature, 2021, 596(7872): 398-403.
doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03747-1 |
| [90] |
Luk E, Vu ND, Patteson K, Mizuguchi G, Wu WH, Ranjan A, Backus J, Sen S, Lewis M, Bai YW, Wu C. Chz1, a nuclear chaperone for histone H2AZ. Mol Cell, 2007, 25(3): 357-368.
pmid: 17289584 |
| [91] |
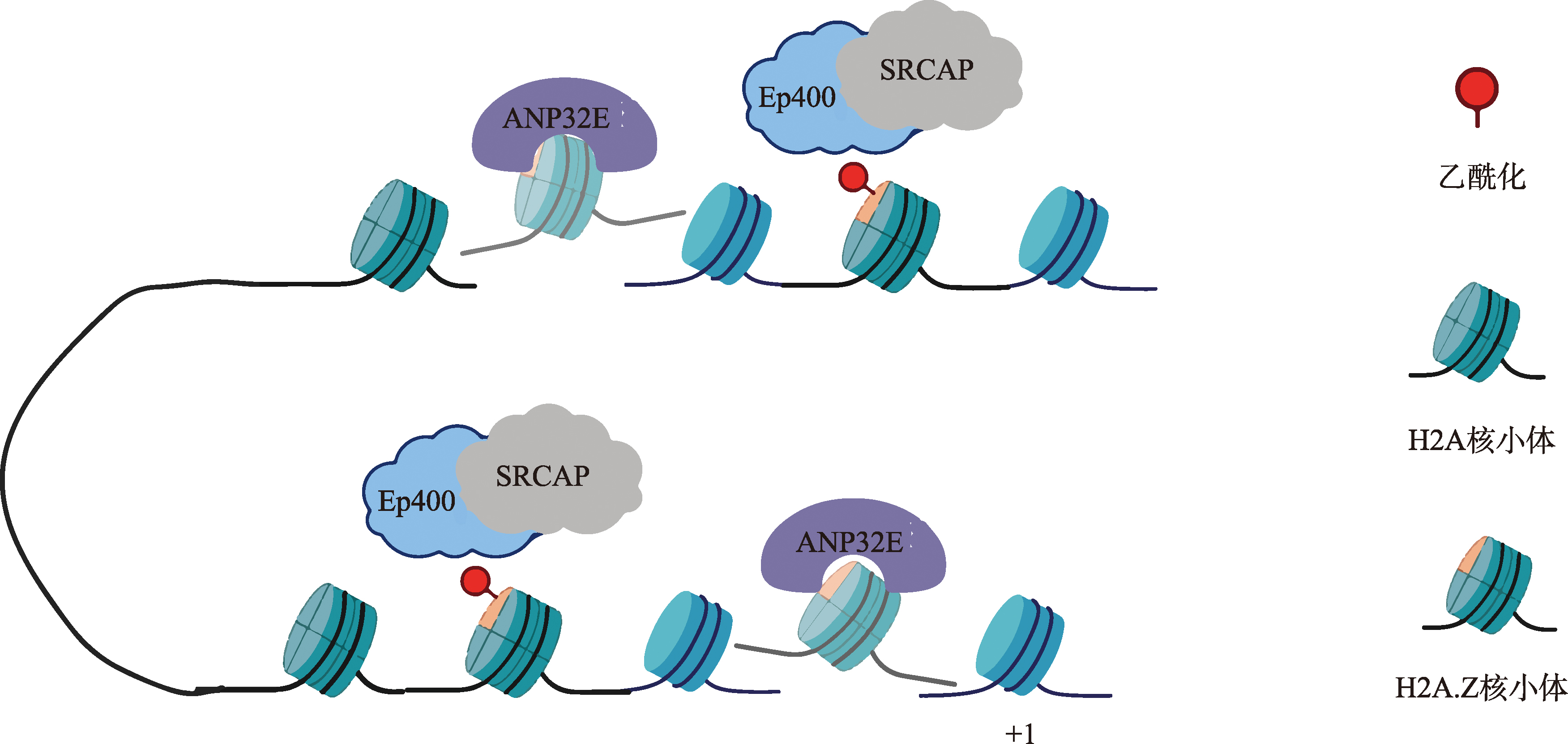
Obri A, Ouararhni K, Papin C, Diebold ML, Padmanabhan K, Marek M, Stoll I, Roy L, Reilly PT, Mak TW, Dimitrov S, Romier C, Hamiche A. ANP32E is a histone chaperone that removes H2A.Z from chromatin. Nature, 2014, 505(7485): 648-653.
doi: 10.1038/nature12922 |
| [92] |
Mao Z, Pan L, Wang WX, Sun J, Shan S, Dong Q, Liang XP, Dai LC, Ding XJ, Chen S, Zhang ZQ, Zhu B, Zhou Z. Anp32e, a higher eukaryotic histone chaperone directs preferential recognition for H2A.Z. Cell Res, 2014, 24(4): 389-399.
doi: 10.1038/cr.2014.30 pmid: 24613878 |
| [93] |
Watanabe S, Peterson CL. The INO 80 family of chromatin-remodeling enzymes: regulators of histone variant dynamics. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol, 2010, 75: 35-42.
doi: 10.1101/sqb.2010.75.063 pmid: 21502417 |
| [94] |
Papamichos-Chronakis M, Watanabe S, Rando OJ, Peterson CL. Global regulation of H2A.Z localization by the INO80 chromatin-remodeling enzyme is essential for genome integrity. Cell, 2011, 144(2): 200-213.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.12.021 pmid: 21241891 |
| [95] |
Alatwi HE, Downs JA. Removal of H2A.Z by INO80 promotes homologous recombination. EMBO Rep, 2015, 16(8): 986-994.
doi: 10.15252/embr.201540330 pmid: 26142279 |
| [1] | Yan Zhao, Chenxin Wang, Tianming Yang, Chunshuang Li, Lihong Zhang, Dongni Du, Ruoxi Wang, Jing Wang, Min Wei, Xueqing Ba. Linking oxidative DNA lesion 8-OxoG to tumor development and progression [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(6): 466-477. |
| [2] | Haoliang Cui, Peihua Shi, Jinchun Gao, Xinbo Zhang, Shunran Zhao, Chenyu Tao. Progress on the study of nucleosome reorganization during cellular reprogramming [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(3): 208-215. |
| [3] | Jiangping He, Jiekai Chen. Epigenetic control of transposable elements and cell fate decision [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2021, 43(9): 822-834. |
| [4] | Weihang Deng, Xinhui Li. Resolving nucleosomal positioning and occupancy with MNase-seq [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2020, 42(12): 1143-1155. |
| [5] | Jingwen Zhang,Qian Xu,Guoliang Li. Epigenetics in the genesis and development of cancers [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2019, 41(7): 567-581. |
| [6] | Chunyou Ning,Mengnan He,Qianzi Tang,Qing Zhu,Mingzhou Li,Diyan Li. Advances in mammalian three-dimensional genome by using Hi-C technology approach [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2019, 41(3): 215-233. |
| [7] | Xiangrong Cheng,Xinglin Hu,Qi Jiang,Xingwei Huang,Nan Wang,Lei Lei. The epigenetic regulation of ribosomal DNA and tumorigenesis [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2019, 41(3): 185-192. |
| [8] | Xingwei Huang, Xiangrong Cheng, Nan Wang, Yuwei Zhang, Chen Liao, Lianhong Jin, Lei. Histone variant H3.3 and its functions in reprogramming [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2018, 40(3): 186-196. |
| [9] | Jian Wang, Kaixiang Zhang, Guozhen Lu, Xianghui Zhao. Research progress on 5hmC and TET dioxygenases in neurodevelopment and neurological diseases [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2017, 39(12): 1138-1149. |
| [10] | Tingting Cui, Tianyu Xing, Yankan Chu, Hui Li, Ning Wang. Genetic and epigenetic regulation of PPARγ during adipogenesis [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2017, 39(11): 1066-1077. |
| [11] | Lili Yu,Wanru Dong,Minghui Chen,Xiangyang Kong. Progress in the molecular genetic mechanism of gonadoblastoma [J]. HEREDITAS(Beijing), 2015, 37(11): 1105-1115. |
| [12] | Xuefeng Pan, Nan Jiang, Xifang Chen, Xiaohong Zhou, Liang Ding, Fei Duan. R-loop structure: the formation and the effects on genomic stability [J]. HEREDITAS(Beijing), 2014, 36(12): 1185-1194. |
| [13] | ZHANG Jun-Fang ZHU Hua-Bin ZHANG Liu-Guang HAO Hai-Sheng ZHAO Xue-Ming QIN Tong LU Yong-Qiang WANG Dong. Advance on research of gene expression during spermiogenesis at transcription level [J]. HEREDITAS, 2013, 35(5): 587-594. |
| [14] | LIANG Xin-Quan, DU Yi-Peng, WANG Dong-Lai, YANG Yang. The biological functions of lysine methyltransferase PR-SET7 [J]. HEREDITAS, 2013, 35(3): 241-254. |
| [15] | GE Shao-Qin, LI Jian-Zhong, ZHANG Xiao-Jing. Methylation and acetylation of histones during spermatogenesis [J]. HEREDITAS, 2011, 33(9): 939-946. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||