遗传 ›› 2023, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (5): 395-408.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.23-035
严程浩1( ), 白韦钰1(
), 白韦钰1( ), 张智猛1, 沈俊岭1, 王友军2(
), 张智猛1, 沈俊岭1, 王友军2( ), 孙建伟1(
), 孙建伟1( )
)
收稿日期:2023-02-18
修回日期:2023-04-03
出版日期:2023-05-20
发布日期:2023-04-17
作者简介:严程浩,在读硕士研究生,专业方向:肿瘤转移与发生机制。E-mail: 基金资助:
Chenghao Yan1( ), Weiyu Bai1(
), Weiyu Bai1( ), Zhimeng Zhang1, Junling Shen1, Youjun Wang2(
), Zhimeng Zhang1, Junling Shen1, Youjun Wang2( ), Jianwei Sun1(
), Jianwei Sun1( )
)
Received:2023-02-18
Revised:2023-04-03
Published:2023-05-20
Online:2023-04-17
Supported by:摘要:
基质互作分子1 (stromal interaction molecule 1,STIM1)是细胞钙库操纵性钙内流(store-operated calcium entry,SOCE)通路的关键成员,它定位在内质网膜上,并在多种肿瘤细胞中高表达。异常表达的STIM1能够通过影响侵袭伪足(invadopodia)形成、干扰血管生成、介导炎症反应、改变细胞骨架和细胞动力等方式促进肿瘤发生及转移,然而其具体的调控作用机制仍未完全阐明。本文综述了目前STIM1在不同肿瘤发生及转移中的最新研究进展,总结并探讨了其在肿瘤发生及转移中的调控机制,为将来在肿瘤领域对STIM1的深入研究提供借鉴和参考。
严程浩, 白韦钰, 张智猛, 沈俊岭, 王友军, 孙建伟. STIM1在肿瘤发生及转移中的研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2023, 45(5): 395-408.
Chenghao Yan, Weiyu Bai, Zhimeng Zhang, Junling Shen, Youjun Wang, Jianwei Sun. The roles and mechanism of STIM1 in tumorigenesis and metastasis[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2023, 45(5): 395-408.

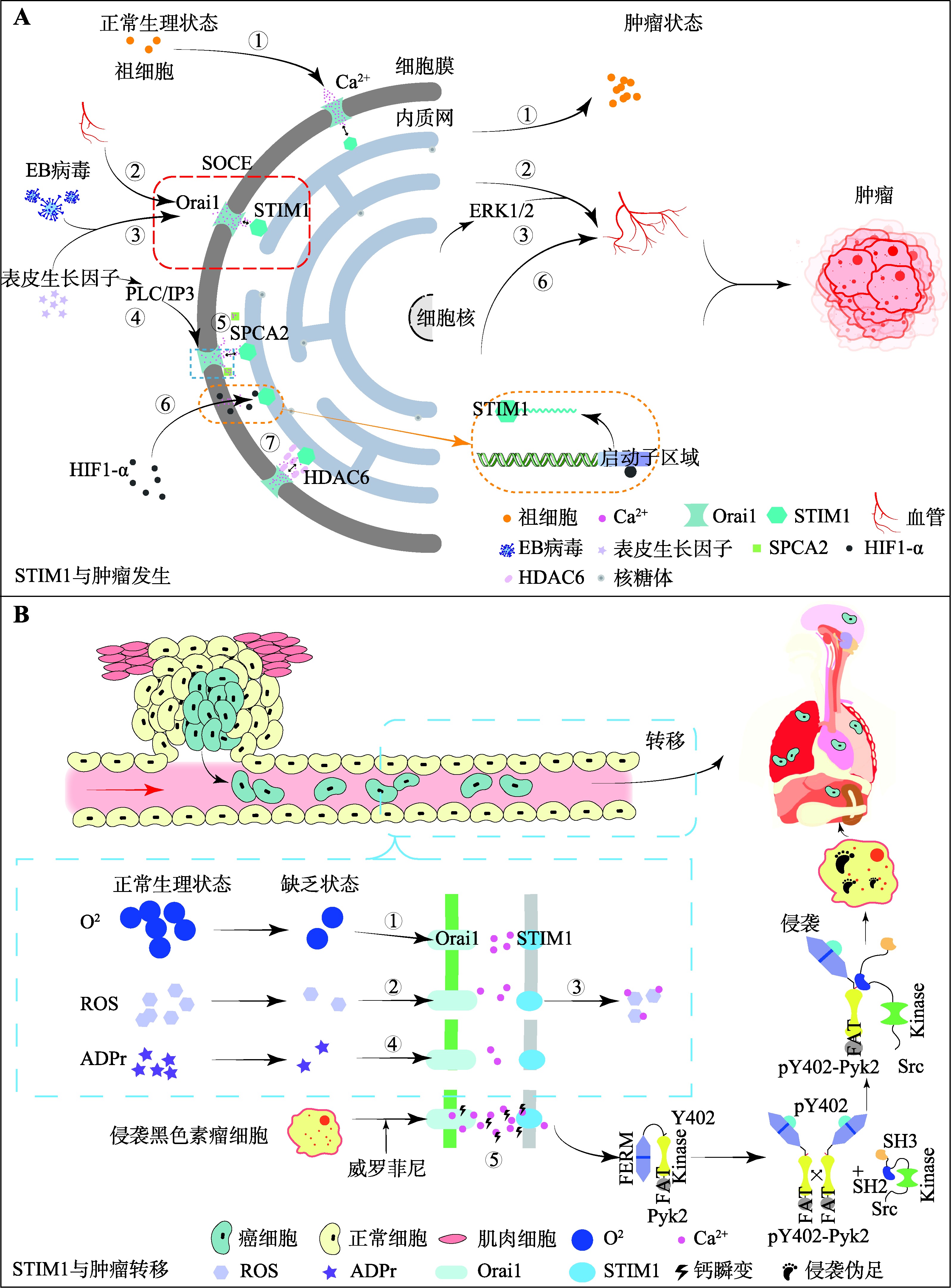
图2
STIM1在肿瘤发生与转移中的作用 A:STIM1与肿瘤发生。①STIM1和Orai1介导的SOCE控制祖细胞增殖;②STIM1和Orai1介导的SOCE影响血小管的形成;③EB病毒通过激活STIM1依赖性Ca2+信号促进EGF诱导的ERK1/2信号传导,促进鼻咽癌中的肿瘤血管生成;④表皮生长因子通过PLC/IP3通路刺激细胞内Ca2+的释放,导致SOCE的激活;⑤Orai1-SPCA2复合物的形成引发了一个不依赖于钙库并自发独立激活的Ca2+进入通路,调节乳腺癌肿瘤的发生;⑥HIF-1α与STIM1启动子结合,并调控其在PANC-1癌细胞中的表达;⑦HDAC6在宫颈癌细胞和正常宫颈上皮细胞之间对STIM1介导的SOCE的激活进行差异调节。B:STIM1与肿瘤转移。①STIM1作为内质网膜蛋白,能够感知和反应肿瘤微环境中的缺氧刺激;②STIM1作为膜蛋白,能够感知和反应肿瘤微环境中的ROS刺激;③STIM1介导ROS和Ca2+(作为应力反应信使)之间的耦合;④STIM1作为膜蛋白,能够感知和反应肿瘤微环境中的ADPr刺激;⑤威罗菲尼耐药细胞当中STIM1高表达,随后激活下游Pyk2-Src信号轴,从而启动侵袭伪足的形成,导致抗药性产生引起的肿瘤转移。"
| [1] |
Kurosaki T, Baba Y.Ca2+ signaling and STIM1. Prog Biophys Mol Biol, 2010, 103(1): 51-58.
doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2010.02.004 |
| [2] |
Oritani K, Kincade PW. Identification of stromal cell products that interact with pre-B cells. J Cell Biol, 1996, 134(3): 771-782.
doi: 10.1083/jcb.134.3.771 pmid: 8707854 |
| [3] |
Motiani RK, Hyzinski-García MC, Zhang XX, Henkel MM, Abdullaev IF, Kuo YH, Matrougui K, Mongin AA, Trebak M. STIM1 and Orai1 mediate CRAC channel activity and are essential for human glioblastoma invasion. Pflugers Arch, 2013, 465(9): 1249-1260.
doi: 10.1007/s00424-013-1254-8 |
| [4] |
Kondratska K, Kondratskyi A, Yassine M, Lemonnier L, Lepage G, Morabito A, Skryma R, Prevarskaya N. Orai1 and STIM1 mediate SOCE and contribute to apoptotic resistance of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2014, 1843(10): 2263-2269.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2014.02.012 pmid: 24583265 |
| [5] |
Flourakis M, Lehen'kyi V, Beck B, Raphaël M, Vandenberghe M, Abeele FV, Roudbaraki M, Lepage G, Mauroy B, Romanin C, Shuba Y, Skryma R, Prevarskaya N. Orai1 contributes to the establishment of an apoptosis-resistant phenotype in prostate cancer cells. Cell Death Dis, 2010, 1(9): e75.
doi: 10.1038/cddis.2010.52 |
| [6] |
Dubois C, Vanden Abeele F, Lehen'kyi V, Gkika D, Guarmit B, Lepage G, Slomianny C, Borowiec AS, Bidaux G, Benahmed M, Shuba Y, Prevarskaya N. Remodeling of channel-forming ORAI proteins determines an oncogenic switch in prostate cancer. Cancer Cell, 2014, 26(1): 19-32.
doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2014.04.025 pmid: 24954132 |
| [7] |
Yang N, Tang Y, Wang F, Zhang HB, Xu D, Shen YF, Sun SH, Yang GS. Blockade of store-operated Ca2+ entry inhibits hepatocarcinoma cell migration and invasion by regulating focal adhesion turnover. Cancer Lett, 2013, 330(2): 163-169.
doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2012.11.040 |
| [8] |
Kim JH, Lkhagvadorj S, Lee MR, Hwang KH, Chung HC, Jung JH, Cha SK, Eom M. Orai1 and STIM1 are critical for cell migration and proliferation of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2014, 448(1): 76-82.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.04.064 |
| [9] |
Abdullaev IF, Bisaillon JM, Potier M, Gonzalez JC, Motiani RK, Trebak M. Stim1 and Orai1 mediate CRAC currents and store-operated calcium entry important for endothelial cell proliferation. Circ Res, 2008, 103(11): 1289-1299.
doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000338496.95579.56 pmid: 18845811 |
| [10] |
Shen JL, Yang JL, Sang L, Sun R, Bai WY, Wang C, Sun Y, Sun JW. PYK2 mediates the BRAF inhibitor (vermurafenib)-induced invadopodia formation and metastasis in melanomas. Cancer Biol Med, 2021, 19(8): 1211-1223.
doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2020.0294 |
| [11] | Berridge MJ, Lipp P, Bootman MD. The versatility and universality of calcium signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2000, 1(1): 11-21. |
| [12] |
Lewis RS. Calcium signaling mechanisms in T lymphocytes. Annu Rev Immunol, 2001, 19: 497-521.
pmid: 11244045 |
| [13] |
Feske S. Calcium signalling in lymphocyte activation and disease. Nat Rev Immunol, 2007, 7(9): 690-702.
doi: 10.1038/nri2152 pmid: 17703229 |
| [14] |
Scharenberg AM, Humphries LA, Rawlings DJ. Calcium signalling and cell-fate choice in B cells. Nat Rev Immunol, 2007, 7(10): 778-789.
pmid: 17853903 |
| [15] |
Liou J, Kim ML, Heo WD, Jones JT, Myers JW, Ferrell JE, Meyer T. STIM is a Ca2+ sensor essential for Ca2+-store-depletion-triggered Ca2+ influx. Curr Biol, 2005, 15(13): 1235-1241.
doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2005.05.055 pmid: 16005298 |
| [16] |
Manji SS, Parker NJ, Williams RT, van Stekelenburg L, Pearson RB, Dziadek M, Smith PJ. STIM1: a novel phosphoprotein located at the cell surface. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2000, 1481(1): 147-155.
doi: 10.1016/s0167-4838(00)00105-9 pmid: 11004585 |
| [17] |
Williams RT, Senior PV, Van Stekelenburg L, Layton JE, Smith PJ, Dziadek MA. Stromal interaction molecule 1 (STIM1), a transmembrane protein with growth suppressor activity, contains an extracellular SAM domain modified by N-linked glycosylation. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2002, 1596(1): 131-137.
doi: 10.1016/s0167-4838(02)00211-x pmid: 11983428 |
| [18] |
Spassova MA, Soboloff J, He LP, Xu W, Dziadek MA, Gill DL. STIM1 has a plasma membrane role in the activation of store-operated Ca2+ channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2006, 103(11): 4040-4045.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0510050103 pmid: 16537481 |
| [19] |
Nelson HA, Roe MW. Molecular physiology and pathophysiology of stromal interaction molecules. Exp Biol Med (Maywood), 2018, 243(5): 451-472.
doi: 10.1177/1535370218754524 pmid: 29363328 |
| [20] |
Baba Y, Hayashi K, Fujii Y, Mizushima A, Watarai H, Wakamori M, Numaga T, Mori Y, Iino M, Hikida M, Kurosaki T. Coupling of STIM1 to store-operated Ca2+ entry through its constitutive and inducible movement in the endoplasmic reticulum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2006, 103(45): 16704-16709.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0608358103 |
| [21] |
Wu MM, Buchanan J, Luik RM, Lewis RS. Ca2+ store depletion causes STIM1 to accumulate in ER regions closely associated with the plasma membrane. J Cell Biol, 2006, 174(6): 803-813.
doi: 10.1083/jcb.200604014 |
| [22] |
Putney JW. Recent breakthroughs in the molecular mechanism of capacitative calcium entry (with thoughts on how we got here). Cell Calcium, 2007, 42(2): 103-110.
doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2007.01.011 pmid: 17349691 |
| [23] |
Luik RM, Wu MM, Buchanan J, Lewis RS. The elementary unit of store-operated Ca2+ entry: local activation of CRAC channels by STIM1 at ER-plasma membrane junctions. J Cell Biol, 2006, 174(6): 815-825.
doi: 10.1083/jcb.200604015 |
| [24] |
Baba Y, Kurosaki T. Physiological function and molecular basis of STIM1-mediated calcium entry in immune cells. Immunol Rev, 2009, 231(1): 174-188.
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2009.00813.x pmid: 19754897 |
| [25] | Herbert SP, Stainier DYR. Molecular control of endothelial cell behaviour during blood vessel morphogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2011, 12(9): 551-564. |
| [26] |
Oh-hora M, Rao A. Calcium signaling in lymphocytes. Curr Opin Immunol, 2008, 20(3): 250-258.
doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2008.04.004 pmid: 18515054 |
| [27] |
Lewis RS. The molecular choreography of a store- operated calcium channel. Nature, 2007, 446(7133): 284-287.
doi: 10.1038/nature05637 |
| [28] |
Partiseti M, Le Deist F, Hivroz C, Fischer A, Korn H, Choquet D. The calcium current activated by T cell receptor and store depletion in human lymphocytes is absent in a primary immunodeficiency. J Biol Chem, 1994, 269(51): 32327-32335.
pmid: 7798233 |
| [29] |
Picard C, McCarl CA, Papolos A, Khalil S, Lüthy K, Hivroz C, LeDeist F, Rieux-Laucat F, Rechavi G, Rao A, Fischer A, Feske S. STIM1 mutation associated with a syndrome of immunodeficiency and autoimmunity. N Engl J Med, 2009, 360(19): 1971-1980.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0900082 |
| [30] |
Oh-Hora M, Yamashita M, Hogan PG, Sharma S, Lamperti E, Chung W, Prakriya M, Feske S, Rao A. Dual functions for the endoplasmic reticulum calcium sensors STIM1 and STIM2 in T cell activation and tolerance. Nat Immunol, 2008, 9(4): 432-443.
doi: 10.1038/ni1574 pmid: 18327260 |
| [31] |
Demaurex N, Saul S. The role of STIM proteins in neutrophil functions. J Physiol, 2018, 596(14): 2699-2708.
doi: 10.1113/JP275639 |
| [32] |
Vig M, DeHaven WI, Bird GS, Billingsley JM, Wang HY, Rao PE, Hutchings AB, Jouvin MH, Putney JW, Kinet JP. Defective mast cell effector functions in mice lacking the CRACM1 pore subunit of store-operated calcium release-activated calcium channels. Nat Immunol, 2008, 9(1): 89-96.
doi: 10.1038/ni1550 pmid: 18059270 |
| [33] |
Berry CT, Liu XH, Myles A, Nandi S, Chen YH, Hershberg U, Brodsky IE, Cancro MP, Lengner CJ, May MJ, Freedman BD. BCR-induced Ca2+ signals dynamically tune survival, metabolic reprogramming, and proliferation of naive B cells. Cell Rep, 2020, 31(2): 107474.
doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.03.038 |
| [34] |
Trebak M, Kinet JP. Calcium signalling in T cells. Nat Rev Immunol, 2019, 19(3): 154-169.
doi: 10.1038/s41577-018-0110-7 pmid: 30622345 |
| [35] |
Desvignes L, Weidinger C, Shaw P, Vaeth M, Ribierre T, Liu MH, Fergus T, Kozhaya L, McVoy L, Unutmaz D, Ernst JD, Feske S. STIM1 controls T cell-mediated immune regulation and inflammation in chronic infection. J Clin Invest, 2015, 125(6): 2347-2362.
doi: 10.1172/JCI80273 pmid: 25938788 |
| [36] |
Chang CL, Chen YJ, Liou J. ER-plasma membrane junctions: Why and how do we study them? Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res, 2017, 1864(9): 1494-1506.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2017.05.018 |
| [37] |
Weber-Boyvat M, Kentala H, Lilja J, Vihervaara T, Hanninen R, Zhou Y, Peränen J, Nyman TA, Ivaska J, Olkkonen VM. OSBP-related protein 3 (ORP3) coupling with VAMP-associated protein A regulates R-Ras activity. Exp Cell Res, 2015, 331(2): 278-291.
doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2014.10.019 pmid: 25447204 |
| [38] |
Machaca K. Ca2+ signaling and lipid transfer 'pas a deux' at ER-PM contact sites orchestrate cell migration. Cell Calcium, 2020, 89: 102226.
doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2020.102226 pmid: 32505782 |
| [39] |
Tong JS, Tan LC, Im YJ. Structure of human ORP3 ORD reveals conservation of a key function and ligand specificity in OSBP-related proteins. PLoS One, 2021, 16(4): e0248781.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0248781 |
| [40] |
Lodola F, Laforenza U, Bonetti E, Lim D, Dragoni S, Bottino C, Ong HL, Guerra G, Ganini C, Massa M, Manzoni M, Ambudkar IS, Genazzani AA, Rosti V, Pedrazzoli P, Tanzi F, Moccia F, Porta C. Store-operated Ca2+ entry is remodelled and controls in vitro angiogenesis in endothelial progenitor cells isolated from tumoral patients. PLoS One, 2012, 7(9): e42541.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042541 |
| [41] |
Ye JX, Wei JZ, Luo Y, Deng YY, Que T, Zhang XJ, Liu F, Zhang JY, Luo XL. Epstein-barr virus promotes tumor angiogenesis by activating STIM1-dependent Ca2+ signaling in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Pathogens, 2021, 10(10): 1275.
doi: 10.3390/pathogens10101275 |
| [42] |
Pan Z, Ma JJ. Open Sesame: treasure in store- operated calcium entry pathway for cancer therapy. Sci China Life Sci, 2015, 58(1): 48-53.
doi: 10.1007/s11427-014-4774-3 |
| [43] |
Kokoska ER, Smith GS, Miller TA. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs attenuate proliferation of colonic carcinoma cells by blocking epidermal growth factor-induced Ca++ mobilization. J Gastrointest Surg, 2000, 4(2): 150-161.
pmid: 10675238 |
| [44] |
Feng MY, Grice DM, Faddy HM, Nguyen N, Leitch S, Wang YY, Muend S, Kenny PA, Sukumar S, Roberts- Thomson SJ, Monteith GR, Rao R. Store-independent activation of Orai1 by SPCA2 in mammary tumors. Cell, 2010, 143(1): 84-98.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.08.040 pmid: 20887894 |
| [45] |
Ay AS, Benzerdjeb N, Sevestre H, Ahidouch A, Ouadid-Ahidouch H. Orai3 constitutes a native store-operated calcium entry that regulates non small cell lung adenocarcinoma cell proliferation. PLoS One, 2013, 8(9): e72889.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0072889 |
| [46] | Chen YT, Chen YF, Chiu WT, Liu KY, Liu YL, Chang JY, Chang HC, Shen MR. Microtubule-associated histone deacetylase 6 supports the calcium store sensor STIM1 in mediating malignant cell behaviors. Cancer Res, 2013, 73(14): 4500-4509. |
| [47] |
Stupack DG, Cheresh DA. Integrins and angiogenesis. Curr Top Dev Biol, 2004, 64: 207-238.
pmid: 15563949 |
| [48] |
Martin P, Leibovich SJ. Inflammatory cells during wound repair: the good, the bad and the ugly. Trends Cell Biol, 2005, 15(11): 599-607.
doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2005.09.002 pmid: 16202600 |
| [49] |
Friedl P, Weigelin B. Interstitial leukocyte migration and immune function. Nat Immunol, 2008, 9(9): 960-969.
doi: 10.1038/ni.f.212 pmid: 18711433 |
| [50] |
Silva MT. When two is better than one: macrophages and neutrophils work in concert in innate immunity as complementary and cooperative partners of a myeloid phagocyte system. J Leukoc Biol, 2010, 87(1): 93-106.
doi: 10.1189/jlb.0809549 |
| [51] |
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell, 2011, 144(5): 646-674.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013 pmid: 21376230 |
| [52] |
Nabi IR. The polarization of the motile cell. J Cell Sci, 1999, 112(Pt 12): 1803-1811.
doi: 10.1242/jcs.112.12.1803 |
| [53] |
Pollard TD, Borisy GG. Cellular motility driven by assembly and disassembly of actin filaments. Cell, 2003, 112(4): 453-465.
doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(03)00120-x pmid: 12600310 |
| [54] |
Anderson TW, Vaughan AN, Cramer LP. Retrograde flow and myosin II activity within the leading cell edge deliver F-actin to the lamella to seed the formation of graded polarity actomyosin II filament bundles in migrating fibroblasts. Mol Biol Cell, 2008, 19(11): 5006-5018.
doi: 10.1091/mbc.E08-01-0034 pmid: 18799629 |
| [55] |
Le Clainche C, Carlier MF. Regulation of actin assembly associated with protrusion and adhesion in cell migration. Physiol Rev, 2008, 88(2): 489-513.
doi: 10.1152/physrev.00021.2007 pmid: 18391171 |
| [56] |
Keren K. Cell motility: the integrating role of the plasma membrane. Eur Biophys J, 2011, 40(9): 1013-1027.
doi: 10.1007/s00249-011-0741-0 |
| [57] |
Yamaguchi H, Wyckoff J, Condeelis J. Cell migration in tumors. Curr Opin Cell Biol, 2005, 17(5): 559-564.
doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2005.08.002 pmid: 16098726 |
| [58] |
Gupta GP, Massagué J. Cancer metastasis: building a framework. Cell, 2006, 127(4): 679-695.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.11.001 pmid: 17110329 |
| [59] |
Waris G, Ahsan H. Reactive oxygen species: role in the development of cancer and various chronic conditions. J Carcinog, 2006, 5: 14.
pmid: 16689993 |
| [60] |
Nielsen N, Lindemann O, Schwab A. TRP channels and STIM/ORAI proteins: sensors and effectors of cancer and stroma cell migration. Br J Pharmacol, 2014, 171(24): 5524-5540.
doi: 10.1111/bph.2014.171.issue-24 |
| [61] |
Luke JJ, Flaherty KT, Ribas A, Long GV. Targeted agents and immunotherapies: optimizing outcomes in melanoma. Nat Rev Clin Oncol, 2017, 14(8): 463-482.
doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2017.43 pmid: 28374786 |
| [62] |
Cantwell-Dorris ER, O'Leary JJ, Sheils OM. BRAFV600E: implications for carcinogenesis and molecular therapy. Mol Cancer Ther, 2011, 10(3): 385-394.
doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-10-0799 pmid: 21388974 |
| [63] |
Kim A, Cohen MS. The discovery of vemurafenib for the treatment of BRAF-mutated metastatic melanoma. Expert Opin Drug Discov, 2016, 11(9): 907-916.
doi: 10.1080/17460441.2016.1201057 |
| [64] |
Wagle N, Emery C, Berger MF, Davis MJ, Sawyer A, Pochanard P, Kehoe SM, Johannessen CM, Macconaill LE, Hahn WC, Meyerson M, Garraway LA. Dissecting therapeutic resistance to RAF inhibition in melanoma by tumor genomic profiling. J Clin Oncol, 2011, 29(22): 3085-3096.
doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.33.2312 pmid: 21383288 |
| [65] |
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A.Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin, 2020, 70(1): 7-30.
doi: 10.3322/caac.v70.1 |
| [66] |
Kutschat AP, Hamdan FH, Wang X, Wixom AQ, Najafova Z, Gibhardt CS, Kopp W, Gaedcke J, Ströbel P, Ellenrieder V, Bogeski I, Hessmann E, Johnsen SA. STIM1 mediates calcium-dependent epigenetic reprogramming in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res, 2021, 81(11): 2943-2955.
doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-2874 pmid: 33436389 |
| [67] |
Wang J, Shen JL, Zhao KL, Hu JM, Dong JX, Sun JW. STIM1 overexpression in hypoxia microenvironment contributes to pancreatic carcinoma progression. Cancer Biol Med, 2019, 16(1): 100-108.
doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2018.0304 pmid: 31119050 |
| [68] |
Liang XJ, Xie JS, Liu H, Zhao RJ, Zhang W, Wang HD, Pan HM, Zhou YB, Han WD. STIM1 deficiency in intestinal epithelium attenuates colonic inflammation and tumorigenesis by reducing ER stress of goblet cells. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022, 14(1): 193-217.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2022.03.007 pmid: 35367664 |
| [69] |
Tang J, Ye SF, Wang MQ, Li J, Meng X, Liu F. Stromal interaction molecule 1 promotes tumor growth in Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Genomics, 2020, 112(3): 2146-2153.
doi: S0888-7543(19)30780-3 pmid: 31843504 |
| [70] |
Xia JL, Wang HQ, Huang HX, Sun L, Dong ST, Huang N, Shi M, Bin JP, Liao YL, Liao WJ. Elevated Orai1 and STIM1 expressions upregulate MACC1 expression to promote tumor cell proliferation, metabolism, migration, and invasion in human gastric cancer. Cancer Lett, 2016, 381(1): 31-40.
doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.07.014 pmid: 27431311 |
| [71] |
Bausch B, Jilg C, Gläsker S, Vortmeyer A, Lützen N, Anton A, Eng C, Neumann HPH. Renal cancer in von Hippel-Lindau disease and related syndromes. Nat Rev Nephrol, 2013, 9(9): 529-538.
doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2013.144 pmid: 23897319 |
| [72] |
Cohen HT, McGovern FJ. Renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med, 2005, 353(23): 2477-2490.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMra043172 |
| [73] |
Janzen NK, Kim HL, Figlin RA, Belldegrun AS. Surveillance after radical or partial nephrectomy for localized renal cell carcinoma and management of recurrent disease. Urol Clin North Am, 2003, 30(4): 843-852.
doi: 10.1016/S0094-0143(03)00056-9 |
| [74] |
Monteith GR, McAndrew D, Faddy HM, Roberts-Thomson SJ. Calcium and cancer: targeting Ca2+ transport. Nat Rev Cancer, 2007, 7(7): 519-530.
doi: 10.1038/nrc2171 pmid: 17585332 |
| [75] | Crino PB, Nathanson KL, Henske EP. The tuberous sclerosis complex. N Engl J Med, 2006, 355(13): 1345-1356. |
| [76] |
Peng H, Liu J, Sun Q, Chen R, Wang Y, Duan J, Li C, Li B, Jing Y, Chen X, Mao Q, Xu KF, Walker CL, Li J, Wang J, Zhang H. mTORC1 enhancement of STIM1-mediated store-operated Ca2+ entry constrains tuberous sclerosis complex-related tumor development. Oncogene, 2013, 32(39): 4702-4711.
doi: 10.1038/onc.2012.481 pmid: 23108404 |
| [77] |
Pascual-Caro C, Orantos-Aguilera Y, Sanchez-Lopez I, de Juan-Sanz J, Parys JB, Area-Gomez E, Pozo-Guisado E, Martin-Romero FJ. STIM1 deficiency leads to specific down-regulation of ITPR3 in SH-SY5Y cells. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(18): 6598.
doi: 10.3390/ijms21186598 |
| [78] |
Pascual-Caro C, Berrocal M, Lopez-Guerrero AM, Alvarez-Barrientos A, Pozo-Guisado E, Gutierrez- Merino C, Mata AM, Martin-Romero FJ. STIM1 deficiency is linked to Alzheimer's disease and triggers cell death in SH-SY5Y cells by upregulation of L-type voltage-operated Ca2+ entry. J Mol Med (Berl), 2018, 96(10): 1061-1079.
doi: 10.1007/s00109-018-1677-y pmid: 30088035 |
| [79] | Xie JS, Ma GL, Zhou LJ, He L, Zhang Z, Tan P, Huang ZX, Fang SH, Wang TL, Lee YT, Wen SF, Siwko S, Wang LQ, Liu JD, Du YC, Zhang NX, Liu XX, Han L, Huang Y, Wang R, Wang YJ, Zhou YB, Han WD. Identification of a STIM1 splicing variant that promotes glioblastoma growth. Adv Sci (Weinh), 2022, 9(11): e2103940. |
| [80] |
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A.Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin, 2015, 65(2): 87-108.
doi: 10.3322/caac.21262 |
| [81] |
Yang SY, Zhang JJ, Huang XY. Orai1 and STIM1 are critical for breast tumor cell migration and metastasis. Cancer Cell, 2009, 15(2): 124-134.
doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2008.12.019 pmid: 19185847 |
| [82] |
Pan SL, Zhao XX, Shao C, Fu BJ, Huang YY, Zhang N, Dou XJ, Zhang Z, Qiu YL, Wang R, Jin MH, Kong DX. STIM1 promotes angiogenesis by reducing exosomal miR-145 in breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells. Cell Death Dis, 2021, 12(1): 38.
doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-03304-0 pmid: 33414420 |
| [83] |
Yang YF, Jiang ZS, Wang B, Chang LL, Liu J, Zhang LN, Gu L. Expression of STIM1 is associated with tumor aggressiveness and poor prognosis in breast cancer. Pathol Res Pract, 2017, 213(9): 1043-1047.
doi: S0344-0338(17)30459-4 pmid: 28869106 |
| [84] |
Cheng HY, Wang SQ, Feng RQ. STIM1 plays an important role in TGF-β-induced suppression of breast cancer cell proliferation. Oncotarget, 2016, 7(13): 16866-16878.
doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7619 pmid: 26919241 |
| [85] |
Chen YT, Chen YF, Chiu WT, Wang YK, Chang HC, Shen MR. The ER Ca2+ sensor STIM1 regulates actomyosin contractility of migratory cells. J Cell Sci, 2013, 126(Pt 5): 1260-1267.
doi: 10.1242/jcs.121129 |
| [86] |
Huang CC, Lin MR, Yang YC, Hsu YW, Wong HSC, Chang WC. Germline genetic association between stromal interaction molecule 1 (STIM1) and clinical outcomes in breast cancer patients. J Pers Med, 2020, 10(4): 287.
doi: 10.3390/jpm10040287 |
| [87] |
O'Grady S, Morgan MP. Calcium transport and signalling in breast cancer: functional and prognostic significance. Semin Cancer Biol, 2021, 72: 19-26.
doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.12.006 pmid: 31866475 |
| [88] |
Gross S, Hooper R, Tomar D, Armstead AP, Shanas N, Mallu P, Joshi H, Ray S, Chong PLG, Astsaturov I, Farma JM, Cai KQ, Chitrala KN, Elrod JW, Zaidi MR, Soboloff J. Suppression of Ca2+ signaling enhances melanoma progression. EMBO J, 2022, 41(19): e110046.
doi: 10.15252/embj.2021110046 |
| [89] |
Wong HSC, Chang WC. Single-cell melanoma transcriptomes depicting functional versatility and clinical implications of STIM1 in the tumor microenvironment. Theranostics, 2021, 11(11): 5092-5106.
doi: 10.7150/thno.54134 |
| [90] |
Sun JW, Lu FJ, He HF, Shen JL, Messina J, Mathew R, Wang DP, Sarnaik AA, Chang WC, Kim M, Cheng HP, Yang SY. STIM1- and Orai1-mediated Ca2+ oscillation orchestrates invadopodium formation and melanoma invasion. J Cell Biol, 2014, 207(4): 535-548.
doi: 10.1083/jcb.201407082 |
| [91] | Sun JW, Lin SC, Keeley T, Yang SY. Disseminating melanoma cells surf on calcium waves. Mol Cell Oncol, 2015, 2(4): e1002714. |
| [92] |
Wang YD, Wang HY, Pan T, Li L, Li JM, Yang HY. STIM1 silencing inhibits the migration and invasion of A549 cells. Mol Med Rep, 2017, 16(3): 3283-3289.
doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7010 pmid: 28713917 |
| [93] |
Saint Fleur-Lominy S, Maus M, Vaeth M, Lange I, Zee I, Suh D, Liu C, Wu XJ, Tikhonova A, Aifantis I, Feske S. STIM1 and STIM2 mediate cancer-induced inflammation in T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cell Rep, 2018, 24(11): 3045-3060.e5.
doi: S2211-1247(18)31301-9 pmid: 30208327 |
| [94] |
Asghar MY, Lassila T, Paatero I, Nguyen VD, Kronqvist P, Zhang JX, Slita A, Löf C, Zhou Y, Rosenholm J, Törnquist K. Stromal interaction molecule 1 (STIM1) knock down attenuates invasion and proliferation and enhances the expression of thyroid-specific proteins in human follicular thyroid cancer cells. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2021, 78(15): 5827-5846.
doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-03880-0 pmid: 34155535 |
| [95] |
Xu YX, Zhang S, Niu HY, Ye YJ, Hu F, Chen S, Li XF, Luo XH, Jiang S, Liu YH, Chen YN, Li JY, Xiang R, Li N. STIM1 accelerates cell senescence in a remodeled microenvironment but enhances the epithelial-to- mesenchymal transition in prostate cancer. Sci Rep, 2015, 5: 11754.
doi: 10.1038/srep11754 |
| [96] |
Zhou YB, Gu P, Li J, Li F, Zhu J, Gao P, Zang YC, Wang YC, Shan YX, Yang DR. Suppression of STIM1 inhibits the migration and invasion of human prostate cancer cells and is associated with PI3K/Akt signaling inactivation. Oncol Rep, 2017, 38(5): 2629-2636.
doi: 10.3892/or.2017.5961 pmid: 29048678 |
| [97] |
Zang J, Zuo DQ, Shogren KL, Gustafson CT, Zhou ZF, Thompson MA, Guo RW, Prakash YS, Lu LC, Guo W, Maran A, Yaszemski MJ. STIM1 expression is associated with osteosarcoma cell survival. Chin J Cancer Res, 2019, 31(1): 203-211.
doi: 10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2019.01.15 |
| [98] |
Ritchie MF, Zhou YD, Soboloff J. WT1/EGR1- mediated control of STIM1 expression and function in cancer cells. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed), 2011, 16(7): 2402-2415.
doi: 10.2741/3862 |
| [99] |
Lee SK, Kweon YC, Lee AR, Lee YY, Park CY. Metastasis enhancer PGRMC1 boosts store-operated Ca2+ entry by uncoiling Ca2+ sensor STIM1 for focal adhesion turnover and actomyosin formation. Cell Rep, 2022, 38(3): 110281.
doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.110281 |
| [100] |
Faris P, Rumolo A, Tapella L, Tanzi M, Metallo A, Conca F, Negri S, Lefkimmiatis K, Pedrazzoli P, Lim D, Montagna D, Moccia F. Store-operated Ca2+ entry is up-regulated in tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes from metastatic colorectal cancer patients. Cancers (Basel), 2022, 14(14): 3312.
doi: 10.3390/cancers14143312 |
| [101] |
Zhang Z, Liu X, Feng B, Liu N, Wu Q, Han Y, Nie Y, Wu K, Shi Y, Fan D. STIM1, a direct target of microRNA-185, promotes tumor metastasis and is associated with poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene, 2016, 35(46): 6043.
doi: 10.1038/onc.2016.140 pmid: 27375024 |
| [102] |
Zhuang R, Rao JN, Zou TT, Liu L, Xiao L, Cao S, Hansraj NZ, Gorospe M, Wang JY. miR-195 competes with HuR to modulate stim1 mRNA stability and regulate cell migration. Nucleic Acids Res, 2013, 41(16): 7905-7919.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt565 pmid: 23804758 |
| [103] |
Lv ZY, Yi DL, Zhang C, Xie YJ, Huang H, Fan ZC, Liu X.miR-541-3p inhibits the viability and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells via targeting STIM1. Mol Med Rep, 2021, 23(5): 312.
doi: 10.3892/mmr |
| [104] |
Ho KH, Chang CK, Chen PH, Wang YJ, Chang WC, Chen KC. miR-4725-3p targeting stromal interacting molecule 1 signaling is involved in xanthohumol inhibition of glioma cell invasion. J Neurochem, 2018, 146(3): 269-288.
doi: 10.1111/jnc.14459 |
| [105] |
Yang YF, Jiang ZS, Ma N, Wang B, Liu J, Zhang LN, Gu L. MicroRNA-223 targeting STIM1 inhibits the biological behavior of breast cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2018, 45(2): 856-866.
doi: 10.1159/000487180 pmid: 29414804 |
| [106] |
Wang JY, Sun J, Huang MY, Wang YS, Hou MF, Sun Y, He H, Krishna N, Chiu SJ, Lin S, Yang S, Chang WC. STIM1 overexpression promotes colorectal cancer progression, cell motility and COX-2 expression. Oncogene, 2015, 34(33): 4358-4367.
doi: 10.1038/onc.2014.366 pmid: 25381814 |
| [107] |
Chen YW, Lai CS, Chen YF, Chiu WT, Chen HC, Shen MR. STIM1-dependent Ca2+ signaling regulates podosome formation to facilitate cancer cell invasion. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1): 11523.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-11273-2 |
| [108] |
Ge CL, Zeng BZ, Li RL, Li Z, Fu QF, Wang WW, Wang ZY, Dong SW, Lai ZC, Wang Y, Xue YB, Guo JY, Di TN, Song X. Knockdown of STIM1 expression inhibits non-small-cell lung cancer cell proliferation in vitro and in nude mouse xenografts. Bioengineered, 2019, 10(1): 425-436.
doi: 10.1080/21655979.2019.1669518 |
| [109] | Algariri ES, Mydin RBSMN, Moses EJ, Okekpa SI, Rahim NAA, Yusoff NM. Knockdown of stromal interaction molecule 1 (STIM1) suppresses acute myeloblastic leukemia-M5 cell line survival through inhibition of reactive oxygen species activities. Turk J Haematol, 2023, 40(1): 11-17. |
| [110] |
Lin YS, Lin YH, Nguyen Thi M, Hsiao SC, Chiu WT. STIM1 controls the focal adhesion dynamics and cell migration by regulating SOCE in osteosarcoma. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 23(1): 162.
doi: 10.3390/ijms23010162 |
| [111] |
Li YS, Guo B, Xie QC, Ye DY, Zhang DX, Zhu Y, Chen HX, Zhu B.STIM1 mediates hypoxia-driven hepatocarcinogenesis via interaction with HIF-1. Cell Rep, 2015, 12(3): 388-395.
doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.06.033 pmid: 26166565 |
| [112] |
Chen YF, Chiu WT, Chen YT, Lin PY, Huang HJ, Chou CY, Chang HC, Tang MJ, Shen MR. Calcium store sensor stromal-interaction molecule 1-dependent signaling plays an important role in cervical cancer growth, migration, and angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2011, 108(37): 15225-15230.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1103315108 |
| [113] | Lu FJ, Sun JW, Zheng QX, Li JH, Hu YZ, Yu P, He HF, Zhao Y, Wang XH, Yang SY, Cheng HP. Imaging elemental events of store-operated Ca2+ entry in invading cancer cells with plasmalemmal targeted sensors. J Cell Sci, 2019, 132(6): jcs224923. |
| [114] | van Dorp S, Qiu RY, Choi UB, Wu MM, Yen M, Kirmiz M, Brunger AT, Lewis RS. Conformational dynamics of auto-inhibition in the ER calcium sensor STIM1. eLife, 2021, 10: e6619. |
| [115] |
Guo L, Li ZS, Wang HL, Ye CY, Zhang DC. Carboxyamido-triazole inhibits proliferation of human breast cancer cells via G(2)/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Eur J Pharmacol, 2006, 538(1-3): 15-22.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.03.036 pmid: 16696967 |
| [116] |
Perabo FGE, Demant AW, Wirger A, Schmidt DH, Sitia M, Wardelmann E, Müller SC, Kohn EC. Carboxyamido-triazole (CAI) reverses the balance between proliferation and apoptosis in a rat bladder cancer model. Anticancer Res, 2005, 25(2A): 725-729.
pmid: 15868902 |
| [117] |
Ge S, Rempel SA, Divine G, Mikkelsen T. Carboxyamido-triazole induces apoptosis in bovine aortic endothelial and human glioma cells. Clin Cancer Res, 2000, 6(4): 1248-1254.
pmid: 10778947 |
| [118] |
Mignen O, Brink C, Enfissi A, Nadkarni A, Shuttleworth TJ, Giovannucci DR, Capiod T. Carboxyamidotriazole- induced inhibition of mitochondrial calcium import blocks capacitative calcium entry and cell proliferation in HEK-293 cells. J Cell Sci, 2005, 118(Pt 23): 5615-5623.
doi: 10.1242/jcs.02663 |
| [119] |
Enfissi A, Prigent S, Colosetti P, Capiod T. The blocking of capacitative calcium entry by 2-aminoethyl diphenylborate (2-APB) and carboxyamidotriazole (CAI) inhibits proliferation in Hep G2 and Huh-7 human hepatoma cells. Cell Calcium, 2004, 36(6): 459-467.
pmid: 15488595 |
| [120] |
Padar S, Bose DD, Livesey JC, Thomas DW. 2-Aminoethoxydiphenyl borate perturbs hormone- sensitive calcium stores and blocks store-operated calcium influx pathways independent of cytoskeletal disruption in human A549 lung cancer cells. Biochem Pharmacol, 2005, 69(8): 1177-1186.
doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2005.01.011 |
| [121] |
Kazerounian S, Pitari GM, Shah FJ, Frick GS, Madesh M, Ruiz-Stewart I, Schulz S, Hajnóczky G, Waldman SA. Proliferative signaling by store-operated calcium channels opposes colon cancer cell cytostasis induced by bacterial enterotoxins. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 2005, 314(3): 1013-1022.
pmid: 15937149 |
| [122] |
Koslowski M, Sahin U, Dhaene K, Huber C, Türeci O. MS4A12 is a colon-selective store-operated calcium channel promoting malignant cell processes. Cancer Res, 2008, 68(9): 3458-3466.
doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-5768 pmid: 18451174 |
| [123] | Hao QG, Sun FG, Yan CH, Sun JW. Progress on the role and mechanism of MT1-MMP in tumor metastasis. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(9): 745-755. |
| 郝庆刚, 孙凤桂, 严程浩, 孙建伟. MT1-MMP在肿瘤转移中的研究进展. 遗传, 2022, 44(9): 745-755. | |
| [124] |
Sukumaran P, Nascimento Da Conceicao V, Sun YY, Ahamad N, Saraiva LR, Selvaraj S, Singh BB. Calcium signaling regulates autophagy and apoptosis. Cells, 2021, 10(8): 2125.
doi: 10.3390/cells10082125 |
| [1] | 张宏博, 孙凤桂, 孙建伟, 汤琦, 张旭. 乳腺肿瘤干细胞在乳腺癌发生、发展及耐药中的作用[J]. 遗传, 2025, 47(10): 1099-1117. |
| [2] | 张译文, 黄琴, 吴艳芸, 孙月, 韦永龙. LIN28A/B在肿瘤发生发展中的作用研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2024, 46(6): 452-465. |
| [3] | 常栋, 刘享享, 刘睿, 孙建伟. FSCN1在乳腺癌发生发展中的作用及其调控机制[J]. 遗传, 2023, 45(2): 115-127. |
| [4] | 程香荣,胡兴琳,姜琦,黄星卫,王楠,雷蕾. 核糖体DNA转录的表观调控与肿瘤发生[J]. 遗传, 2019, 41(3): 185-192. |
| [5] | 胡清霞,高昂,曾炜佳,王妍馨,董金堂,朱正茂. 高等哺乳动物LEM结构域蛋白家族的研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2015, 37(2): 128-139. |
| [6] | 杨丽华, 沈星凯, 李静秋, 杨杰, 乐燕萍, 龚朝辉. 微RNA通过调节上皮间质转化影响肿瘤转移[J]. 遗传, 2014, 36(7): 637-645. |
| [7] | 魏永永,侯静,唐文如,罗瑛. p53与Ras协同及其在肿瘤发生中的作用[J]. 遗传, 2012, 34(12): 1513-1521. |
| [8] | 张振武,安洋,滕春波. miR-17-92基因簇microRNAs对哺乳动物器官发育及肿瘤发生的调控[J]. 遗传, 2009, 31(11): 1094-1100. |
| [9] | 吴易阳 李岭. MicroRNA与肿瘤相关的信号转导通路[J]. 遗传, 2007, 29(12): 1419-1428. |
| [10] | 张玮玮,黄惠芳,李庆伟,马飞. Y-box结合蛋白功能及对肿瘤发生的影响[J]. 遗传, 2006, 28(9): 1153-1160. |
| [11] | 李艳凤,张强,朱大海. 泛素介导的蛋白质降解与肿瘤发生[J]. 遗传, 2006, 28(12): 1591-1591~1596. |
| [12] | 史忠诚,于旸,李 钰,傅松滨. rab5a基因在肿瘤转移中的作用研究[J]. 遗传, 2005, 27(5): 694-698. |
| [13] | 黄昀,杨焕杰,金焰,李慧敏,傅松滨. 13q14断裂重排与非小细胞肺癌转移潜能关系的研究[J]. 遗传, 2005, 27(4): 531-534. |
| [14] | 李钰,宋岩,陆纲,邹荣,邹亚男,张贵寅,李璞. 一个与非小细胞肺癌转移相关的基因――RAB5A基因[J]. 遗传, 1999, 21(4): 6-10. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||

www.chinagene.cn
备案号:京ICP备09063187号-4
总访问:,今日访问:,当前在线:
