遗传 ›› 2023, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (11): 1039-1051.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.23-160
章金怡1( ), 何禹墨1, 周晶雨2, 翁术锋1, 马慧霞1, 林太玥1, 徐颖1(
), 何禹墨1, 周晶雨2, 翁术锋1, 马慧霞1, 林太玥1, 徐颖1( )
)
收稿日期:2023-06-30
修回日期:2023-08-31
出版日期:2023-11-20
发布日期:2023-09-18
通讯作者:
徐颖
E-mail:20210700011@fudan.edu.cn;yingxu2520@fudan.edu.cn
作者简介:章金怡,硕士研究生,专业方向:微生物学。E-mail: 基金资助:
Jinyi Zhang1( ), Yumo He1, Jingyu Zhou2, Shufeng Weng1, Huixia Ma1, Taiyue Lin1, Ying Xu1(
), Yumo He1, Jingyu Zhou2, Shufeng Weng1, Huixia Ma1, Taiyue Lin1, Ying Xu1( )
)
Received:2023-06-30
Revised:2023-08-31
Published:2023-11-20
Online:2023-09-18
Contact:
Ying Xu
E-mail:20210700011@fudan.edu.cn;yingxu2520@fudan.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
环状RNA (circular RNA, circRNA)是一类缺乏5′-帽子和3′-poly(A)尾巴的非编码RNA,可以参与多种人类疾病的生物学过程。然而,对其在活动性肺结核(active pulmonary tuberculosis,ATB)中的诊断和功能价值却知之甚少。本研究旨在研究hsa_circ_0007460是否能作为ATB患者的潜在诊断生物标志物,并对其功能进行初探。通过实时荧光定量PCR (real-time quantitative fluorescent PCR,RT-qPCR)发现hsa_circ_0007460在32例ATB患者的外周血以及牛结核分枝杆菌的减毒株——BCG (bacillus Calmette-Guerin)感染的THP-1人源巨噬细胞中显著上调。受试者工作特征曲线(receiver operating curve, ROC)显示曲线下面积(the area under ROC curve, AUC)为0.7474,灵敏度76.67%,特异度78.13%。通过RNase R消化和放线菌素D抑制实验证实hsa_circ_0007460相较于其线性mRNA更加稳定,提示其有作为ATB的诊断生物标志物的潜力。通过蛋白质印迹(Western blot)、CCK-8 (cell counting kit-8)、平板计数、免疫荧光等实验表明hsa_circ_0007460能调控巨噬细胞凋亡和自噬。最后,通过生物信息学分析预测下游的miRNA和mRNA,构建了hsa_circ_0007460/hsa-miR-3127-5p/PATZ1轴。上述研究结果表明,hsa_circ_0007460在ATB患者外周血中显著上调,可以作为潜在的诊断生物标志物,且hsa_circ_0007460能促进巨噬细胞凋亡、抑制巨噬细胞自噬从而促进胞内BCG的存活。
章金怡, 何禹墨, 周晶雨, 翁术锋, 马慧霞, 林太玥, 徐颖. hsa_circ_0007460通过调节巨噬细胞的自噬和凋亡影响细胞内结核分枝杆菌的存活[J]. 遗传, 2023, 45(11): 1039-1051.
Jinyi Zhang, Yumo He, Jingyu Zhou, Shufeng Weng, Huixia Ma, Taiyue Lin, Ying Xu. Hsa_circ_0007460 affects the survival of intracellular Mycobacterium tuberculosis by regulating autophagy and apoptosis of macrophages[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2023, 45(11): 1039-1051.
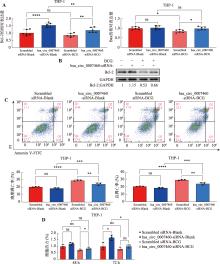
图4
hsa_circ_0007460影响巨噬细胞凋亡 A:用hsa_circ_0007460-siRNA或者Scrambled siRNA转染THP-1人源巨噬细胞24 h后,用BCG(MOI=10)感染48 h,通过qPCR检测凋亡相关基因的表达。B:用hsa_circ_0007460-siRNA或者Scrambled siRNA转染THP-1人源巨噬细胞24 h后,用BCG(MOI=10)感染48 h,通过WB检测Bcl-2的表达。C:用hsa_circ_0007460-siRNA或者Scrambled siRNA转染THP-1人源巨噬细胞24 h后,用BCG(MOI=10)感染48 h,通过流式细胞术检测细胞凋亡。D:用hsa_circ_0007460-siRNA或者Scrambled siRNA转染THP-1人源巨噬细胞24 h后,用BCG(MOI=10)感染48 h和72 h,通过CCK-8检测细胞活力。*P<0.05,**P<0.01, ***P<0.001,****P<0.0001,ns代表无统计学差异。"
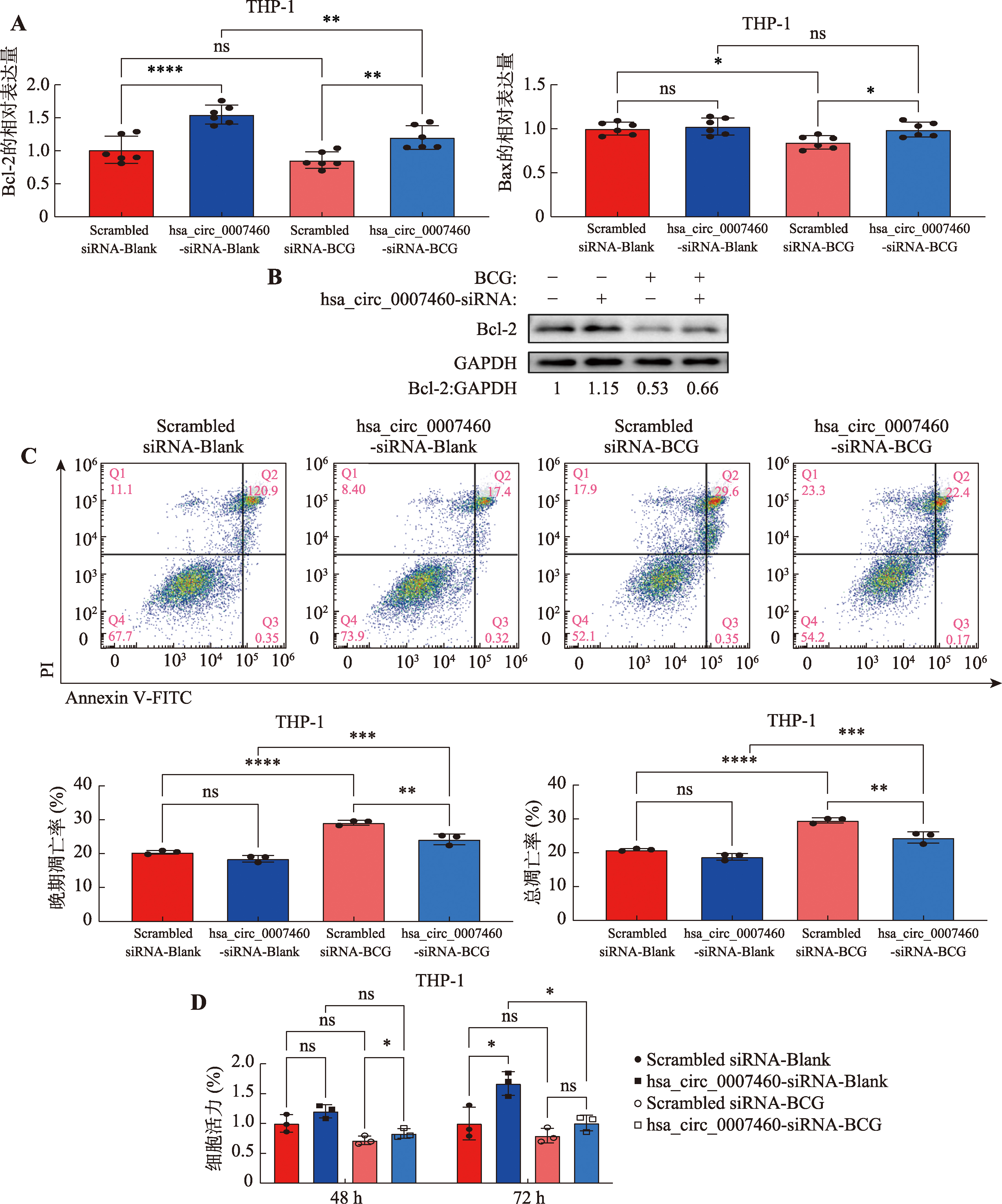
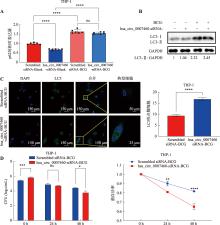
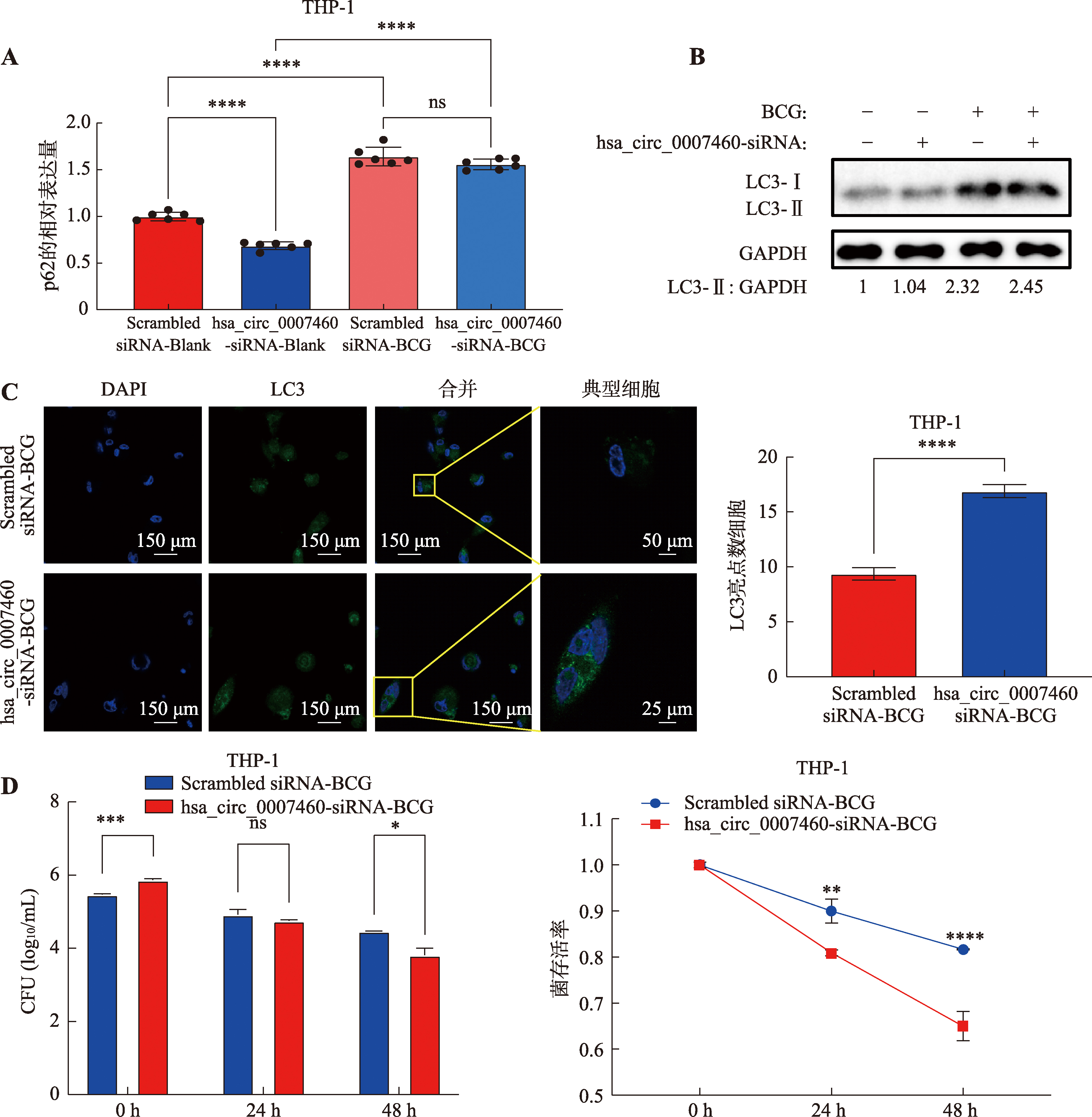
图5
hsa_circ_0007460影响巨噬细胞自噬 A:用hsa_circ_0007460-siRNA或者Scrambled siRNA转染THP-1人源巨噬细胞24 h后,用BCG (MOI=10)感染48 h,通过qPCR检测自噬相关基因的表达。B:用hsa_circ_0007460-siRNA或者Scrambled siRNA转染THP-1人源巨噬细胞24 h后,用BCG (MOI=10)感染48 h,通过WB检测LC3-II的表达。C:用hsa_circ_0007460-siRNA或者Scrambled siRNA转染THP-1人源巨噬细胞24 h后,用BCG (MOI=10)感染48 h,通过共聚焦检测LC3 puncta数量。D:用hsa_circ_0007460-siRNA或者Scrambled siRNA转染THP-1人源巨噬细胞24 h后,用BCG (MOI=10)感染,在0 h、24 h、48 h进行CFU涂板计数。*P<0.05,**P<0.01,***P<0.001,****P<0.0001,ns代表无统计学差异。"
| [1] | World Health Organization.Global tuberculosis report 2022. 2022. |
| [2] |
Dookie N, Rambaran S, Padayatchi N, Mahomed S, Naidoo K. Evolution of drug resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis: a review on the molecular determinants of resistance and implications for personalized care. J Antimicrob Chemother, 2018, 73(5): 1138-1151.
doi: 10.1093/jac/dkx506 |
| [3] |
Kaushik AC, Wu QQ, Lin L, Li HB, Zhao LQ, Wen ZL, Song YZ, Wu QH, Wang J, Guo XK, Wang HL, Yu XL, Wei DQ, Zhang SL. Exosomal ncRNAs profiling of mycobacterial infection identified miRNA-185-5p as a novel biomarker for tuberculosis. Brief Bioinform, 2021, 22(6): bbab210.
doi: 10.1093/bib/bbab210 |
| [4] |
Memczak S, Jens M, Elefsinioti A, Torti F, Krueger J, Rybak A, Maier L, Mackowiak SD, Gregersen LH, Munschauer M, Loewer A, Ziebold U, Landthaler M, Kocks C, Le Noble F, Rajewsky N. Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature, 2013, 495(7441): 333-338.
doi: 10.1038/nature11928 |
| [5] |
Liu HJ, Lu G, Wang WX, Jiang XR, Gu SS, Wang J, Yan X, He F, Wang J. A panel of circRNAs in the serum serves as biomarkers for Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Front Microbiol, 2020, 11: 1215.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01215 |
| [6] |
Huang ZK, Su RG, Deng Z, Xu JQ, Peng YP, Luo Q, Li JM. Identification of differentially expressed circular RNAs in human monocyte derived macrophages response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1): 13673.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-13885-0 |
| [7] |
Zhang XL, Zhang Q, Wu QG, Tang HC, Ye LX, Zhang QL, Hua DM, Zhang YB, Li F. Integrated analyses reveal hsa_circ_0028883 as a diagnostic biomarker in active tuberculosis. Infect Genet Evol, 2020, 83: 104323.
doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2020.104323 |
| [8] |
Yuk JM, Yoshimori T, Jo EK. Autophagy and bacterial infectious diseases. Exp Mol Med, 2012, 44(2): 99-108.
doi: 10.3858/emm.2012.44.2.032 pmid: 22257885 |
| [9] |
Shi HJ, Zhou Y, Jia ET, Liu ZY, Pan M, Bai YF, Zhao XW, Ge QY. Comparative analysis of circular RNA enrichment methods. RNA Biol, 2022, 19(1): 55-67.
doi: 10.1080/15476286.2021.2012632 |
| [10] |
Zhai WJ, Wu FJ, Zhang YY, Fu YR, Liu ZJ. The immune escape mechanisms of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(2): 340.
doi: 10.3390/ijms20020340 |
| [11] |
Deretic V. Multiple regulatory and effector roles of autophagy in immunity. Curr Opin Immunol, 2009, 21(1): 53-62.
doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2009.02.002 pmid: 19269148 |
| [12] |
Jayachandran R, Bosedasgupta S, Pieters J. Surviving the Macrophage: Tools and Tricks Employed by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol, 2013, 374: 189-209.
doi: 10.1007/82_2012_273 pmid: 23154833 |
| [13] |
Wang Y, Wang SC, Jing HY, Zhang TY, Song N, Xu SW. CircRNA-IGLL1/miR-15a/RNF43 axis mediates ammonia- induced autophagy in broilers jejunum via Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Environ Pollut, 2022, 292(Pt A): 118332.
doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.118332 |
| [14] | Wang CS, Chen RS, Zhu XT, Zhang XB.Long non-coding RNAs LINC00689 inhibits the apoptosis of human nucleus pulposus cells via miR-3127-5p/ATG7 axis- mediated autophagy. Open Med (Wars), 2022, 17(1): 1821-1832. |
| [15] |
Li J, Han JY, Zhao AM, Zhang GX. CircPAPPA regulates the proliferation, migration, invasion, apoptosis, and cell cycle of trophoblast cells through the miR-3127-5p/ HOXA7 Axis. Reprod Sci, 2022, 29(4): 1215-1225.
doi: 10.1007/s43032-021-00802-0 |
| [16] |
Huang YJ, Ren L, Li JJ, Zou HB. Long non-coding RNA PVT1/microRNA miR-3127-5p/NCK-associated protein 1-like axis participates in the pathogenesis of abdominal aortic aneurysm by regulating vascular smooth muscle cells. Bioengineered, 2021, 12(2): 12583-12596.
doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2010384 pmid: 34898354 |
| [17] | Yu Z, Wang YZ, Wang B, Zhai JW. Metformin affects paclitaxel sensitivity of ovarian cancer cells through autophagy mediated by long noncoding RNASNHG7/ miR-3127-5p axis. Cancer Biother Radiopharm, 2022, 37(9): 792-801. |
| [18] |
Friedman RC, Farh KKH, Burge CB, Bartel DP. Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res, 2009, 19(1): 92-105.
doi: 10.1101/gr.082701.108 pmid: 18955434 |
| [19] | Tritz R, Mueller BM, Hickey MJ, Lin AH, Gomez GG, Hadwiger P, Sah DWY, Muldoon L, Neuwelt EA, Kruse CA. siRNA down-regulation of the PATZ1 gene in human glioma cells increases their sensitivity to apoptotic stimuli. Cancer Ther, 2008, 6(B): 865-876. |
| [20] |
Fedele M, Crescenzi E, Cerchia L. The POZ/BTB and AT-Hook containing zinc finger 1 (PATZ1) transcription regulator: physiological functions and disease involvement. Int J Mol Sci, 2017, 18(12): 2524.
doi: 10.3390/ijms18122524 |
| [21] |
Ow JR, Ma H, Jean A, Goh Z, Lee YH, Chong YM, Soong R, Fu XY, Yang H, Wu Q. Patz1 regulates embryonic stem cell identity. Stem Cells Dev, 2014, 23(10): 1062-1073.
doi: 10.1089/scd.2013.0430 pmid: 24380431 |
| [22] |
Fedele M, Franco R, Salvatore G, Paronetto MP, Barbagal F, Pero R, Chiariotti L, Sette C, Tramontano D, Chieffi G, Fusco A, Chieffi P. PATZ1 gene has a critical role in the spermatogenesis and testicular tumours. J Pathol, 2008, 215(1): 39-47.
doi: 10.1002/path.2323 pmid: 18241078 |
| [23] |
Valentino T, Palmieri D, Vitiello M, Pierantoni GM, Fusco A, Fedele M. PATZ1 interacts with p53 and regulates expression of p53-target genes enhancing apoptosis or cell survival based on the cellular context. Cell Death Dis, 2013, 4(12): e963.
doi: 10.1038/cddis.2013.500 |
| [24] |
Guo S, Zhu KX, Yu WH, Wang T, Li S, Wang YX, Zhang CC, Guo JQ. SH3PXD2A-AS1/miR-330-5p/UBA2 ceRNA network mediates the progression of colorectal cancer through regulating the activity of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Environ Toxicol, 2021, 36(10): 1969-1980.
doi: 10.1002/tox.23038 pmid: 33073888 |
| [25] | Zhuang ZG, Zhang JA, Luo HL, Liu GB, Lu YB, Ge NH, Zheng BY, Li RX, Chen C, Wang X, Liu YQ, Liu FH, Zhou Y, Cai XZ, Chen ZW, Xu JF. The circular RNA of peripheral blood mononuclear cells: hsa_circ_0005836 as a new diagnostic biomarker and therapeutic target of active pulmonary tuberculosis. Mol Immunol, 2017, 90: 264-272. |
| [26] | Huang ZK, Yao FY, Liu J, Xu JQ, Guo Y, Su RG, Luo Q, Li JM.Up-regulation of circRNA-0003528 promotes Mycobacterium tuberculosis associated macrophage polarization via down-regulating miR-224-5p, miR-324-5p and miR-488-5p and up-regulating CTLA4. Aging (Albany NY), 2020, 12(24): 25658-25672. |
| [27] | Luo HL, Pi J, Zhang JA, Yang EZ, Xu H, Luo H, Shen L, Peng Y, Liu GB, Song CM, Li KY, Wu XJ, Zheng BY, Shen HB, Chen ZW, Xu JF.Circular RNA TRAPPC6B inhibits intracellular Mycobacterium tuberculosis growth while inducing autophagy in macrophages by targeting microRNA-874-3p. Clin Transl Immunology, 2021, 10(2): e1254. |
| [28] |
Szabo L, Salzman J. Detecting circular RNAs: bioinformatic and experimental challenges. Nat Rev Genet, 2016, 17(11): 679-692.
doi: 10.1038/nrg.2016.114 pmid: 27739534 |
| [29] |
Deretic V. Autophagy in immunity and cell-autonomous defense against intracellular microbes. Immunol Rev, 2011, 240(1): 92-104.
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2010.00995.x pmid: 21349088 |
| [30] |
Gutierrez MG, Master SS, Singh SB, Taylor GA, Colombo MI, Deretic V. Autophagy is a defense mechanism inhibiting BCG and Mycobacterium tuberculosis survival in infected macrophages. Cell, 2004, 119(6): 753-766.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2004.11.038 |
| [31] | Gajer P, Brotman RM, Bai GY, Sakamoto J, Schütte UME, Zhong X, Koenig SSK, Fu L, Ma ZS, Zhou X, Abdo Z, Forney LJ, Ravel J. Temporal dynamics of the human vaginal microbiota. Sci Transl Med, 2012, 4(132): 132ra52. |
| [1] | 王翠玲, 刘信燚, 王亚会, 张争, 王治东, 周钢桥. MCM2通过抑制p53信号通路促进胆管癌细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭[J]. 遗传, 2022, 44(3): 230-244. |
| [2] | 刘静, 易聪, 许师明. 蛋白质乙酰化修饰对自噬的调控作用[J]. 遗传, 2022, 44(1): 15-24. |
| [3] | 马克学, 李睿, 郭芳莹, 宋鸽鸽, 吴萌, 陈广文, 刘德增. 细胞自噬基因Atg6在涡虫中枢神经系统再生中的功能研究[J]. 遗传, 2021, 43(8): 792-801. |
| [4] | 陈万银, 颜一丹, 栾晓瑾, 王敏, 方杰. CG8005基因在果蝇睾丸生殖细胞中的功能分析[J]. 遗传, 2020, 42(11): 1122-1132. |
| [5] | 秦中勇, 石晓, 曹平平, 褚鹰, 管蔚, 杨楠, 程禾, 孙玉洁. 细胞凋亡反应中NOXA基因启动子发挥增强子功能调节BCL2基因表达[J]. 遗传, 2020, 42(11): 1110-1121. |
| [6] | 余同露,蔡栋梁,朱根凤,叶晓娟,闵太善,陈红岩,卢大儒,陈浩明. CSN4基因干扰对乳腺癌MDA-MB-231细胞增殖和凋亡的影响[J]. 遗传, 2019, 41(4): 318-326. |
| [7] | 冉茂良, 董莲花, 翁波, 曹蓉, 彭馥芝, 高虎, 罗荟, 陈斌. miR-362靶向ZNF644基因调控猪未成熟支持细胞的增殖和凋亡[J]. 遗传, 2018, 40(7): 572-584. |
| [8] | 施梦婷, 张莹, 周钢桥. TBC蛋白家族成员在人类疾病发生发展中的作用[J]. 遗传, 2018, 40(1): 12-21. |
| [9] | 王诗铭, 宋晓, 赵雪莹, 陈红岩, 王久存, 吴俊杰, 高志强, 钱吉, 白春学, 李强, 韩宝惠, 卢大儒. 自噬通路基因多态性与晚期非小细胞肺癌含铂化疗疗效的相关性分析[J]. 遗传, 2017, 39(3): 250-262. |
| [10] | 曾笑威, 刘翠翠, 韩凝, 边红武, 朱睦元. 植物自噬的调控因子和受体蛋白研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2016, 38(7): 644-650. |
| [11] | 赵建元,丁寄葳,米泽云,周金明,魏涛,岑山. HIV-1初始传播病毒Vpr基因遗传变异对诱导G2期阻滞及细胞凋亡的影响[J]. 遗传, 2015, 37(5): 480-486. |
| [12] | 王棋文, 靳伟, 常翠芳, 徐存拴. 基于IPA分析自噬对大鼠肝再生中树突状细胞的调节作用[J]. 遗传, 2015, 37(3): 276-282. |
| [13] | 毕丹,徐扬,逄越,李庆伟. 质膜组分磷脂酰丝氨酸外翻的分子调控机制[J]. 遗传, 2015, 37(2): 140-147. |
| [14] | 王棋文,常翠芳,谷宁宁,潘翠云,徐存拴. 自噬在肝再生中的作用[J]. 遗传, 2015, 37(11): 1116-1124. |
| [15] | 陈元渊, 陈红岩, 卢大儒. SNARE蛋白调控细胞自噬的分子机制[J]. 遗传, 2014, 36(6): 547-551. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||

www.chinagene.cn
备案号:京ICP备09063187号-4
总访问:,今日访问:,当前在线:
