遗传 ›› 2025, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (5): 589-599.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.24-266
但露凤1,2( ), 褚以文1,2, 王欣荣1,2, 何向伟3(
), 褚以文1,2, 王欣荣1,2, 何向伟3( )
)
收稿日期:2024-10-14
修回日期:2024-12-18
出版日期:2025-04-25
发布日期:2025-01-07
通讯作者:
何向伟,博士,教授,博士生导师,研究方向:研究染色体结构表观遗传稳定性的分子机理。E-mail: 1187853534@qq.com作者简介:但露凤,博士,讲师,研究方向:微生物遗传、表观遗传的稳定性。E-mail: danlufeng@zju.edu.cn
基金资助:
Lufeng Dan1,2( ), Yiwen Chu1,2, Xinrong Wang1,2, Xiangwei He3(
), Yiwen Chu1,2, Xinrong Wang1,2, Xiangwei He3( )
)
Received:2024-10-14
Revised:2024-12-18
Published:2025-04-25
Online:2025-01-07
Supported by:摘要:
发生在DNA序列水平或表观遗传水平的可逆遗传突变可以调控不稳定遗传的表型,其可逆性使得生物体能更好更快地适应外界多变的环境,但也正是因为其遗传的不稳定性,在传统研究(尤其是针对耐药性调控的研究)中往往被忽略。本研究利用雷帕霉素(+咖啡因)对野生型裂殖酵母菌株进行了耐药突变株的分离,共得到173株耐药突变株,经传代培养和子代耐药性试验,发现14株耐药株存在遗传不稳定现象。进一步研究表明,其中部分菌株的不稳定遗传耐药性受到ssp1位点可逆的DNA序列改变调控。本研究对雷帕霉素作为临床抗肿瘤药物治疗过程中易产生不稳定耐药性的分子机制提供了新的思路和相关的科学依据,并为解决其耐药性问题提供了可能的新作用靶点。
但露凤, 褚以文, 王欣荣, 何向伟. 裂殖酵母中不稳定遗传耐药菌株的筛选及其运用[J]. 遗传, 2025, 47(5): 589-599.
Lufeng Dan, Yiwen Chu, Xinrong Wang, Xiangwei He. Screening and application of unstable genetically resistant strains in fission yeast[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2025, 47(5): 589-599.
表1
本研究所用菌株的基因型及其来源"
| 菌株名称 | 基因型 | 来源 |
|---|---|---|
| 446 (野生型) | h- ade6-210, leu1-32, ura4D | 何向伟实验室 |
| 447 (野生型) | h+, ade6-216, leu1-32, ura4D | 何向伟实验室 |
| gaf1∆ | h?, gaf1∆::kanMX6, ade6∆::hphMX6, cnt2::ade6-natMX6, leu1-32, ura4D | 基因敲除库 |
| Epm101 | h-, ssp1MTD-AGCCA, ade-210, leu1-32, ura4D | 本研究筛选 |
| Epm102 | h-, ssp1MTD-GCTTT, ade-210, leu1-32, ura4D | 本研究筛选 |
| Epm201-206 | h+, ssp1MTD-GTCGTCCG, ade-210, leu1-32, ura4D | 本研究筛选 |
| Epm103-108 | h-, ade-210, leu1-32, ura4, 未知改变 | 本研究筛选 |
| Epm102-R | h-, ssp1MTD-GCTTT, ade-210, leu1-32, ura4D | 本研究分离 |
| Epm102-S | h-, ade6-210, leu1-32, ura4D | 本研究分离 |
| ssp1∆ | h-, ssp1∆::kanMX6, leu1-32, ura4D | 本研究构建 |
| Epm101-wt | h-, ssp1wt::kanMX6, leu1-32, ura4D | 本研究构建 |
| Epm102-wt | h-, ssp1wt::kanMX6, leu1-32, ura4D | 本研究构建 |
表4
随着无药条件下传代时间的增加,部分耐药菌株后代耐药性情况统计"
| 菌株 | 无药处理第1天 | 无药处理第5天 | 无药处理第10天 | 无药处理第15天 | 无药处理第20天 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% |
| gaf1△ | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| Epm101 | 100% | 100% | 93.5% | 9.7% | 0% |
| Epm102 | 100% | 100% | 97.5% | 35% | 0% |
| Epm201 | 100% | 97% | 90.8% | 7.8% | 0% |
| Epm202 | 100% | 100% | 100% | 67% | 1% |
| Epm203 | 100% | 100% | 80% | 5% | 0% |
| Epm204 | 100% | 100% | 99% | 74% | 1% |
| Epm205 | 99.4% | 95.4% | 55.8% | 0.6% | 0% |
表5
不稳定遗传突变菌株进行耐药性调控基因遗传连锁分析结果统计"
| 回交 | 回交比(R∶S ) | 杂交 | 杂交比(R∶S ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Epm201×WT | 2∶2 (37/42) | Epm101×Epm201 | 4∶0 (19/19) |
| Epm203×WT | 2∶2 (38/39) | Epm102×Epm201 | 4∶0 (25/26) |
| Epm205×WT | 2∶2 (46/46) | Epm101×Epm205 | 4∶0 (20/20) |
| Epm206×WT | 2∶2 (36/36) | Epm102×Epm205 | 4∶0 (24/24) |
| Epm103×WT | 2∶2 (23/24) | Epm201×Epm205 | 4∶0 (36/37) |
| Epm104×WT | 2∶2 (37/37) | Epm203×Epm205 | 4∶0 (26/26) |
| Epm105×WT | 2∶2 (16/17) | Epm106×Epm103 | 4∶0 (16/16) |
| Epm106×WT | 2∶2 (30/30) | Epm106×Epm104 | 4∶0 (26/26) |
| Epm107×WT | 2∶2 (26/27) | Epm106×Epm105 | 4∶0 (17/17) |
| Epm108×WT | 2∶2 (20/20) | Epm106×Epm107 | 4∶0 (20/20) |
| Epm103×WT | 2∶2 (23/24) | Epm106×Epm108 | 4∶0 (15/15) |
| Epm104×Epm105 | 4∶0 (11/11) | ||
| Epm206×Epm106 | 3∶1 (11/17),2∶2 (6/17) |

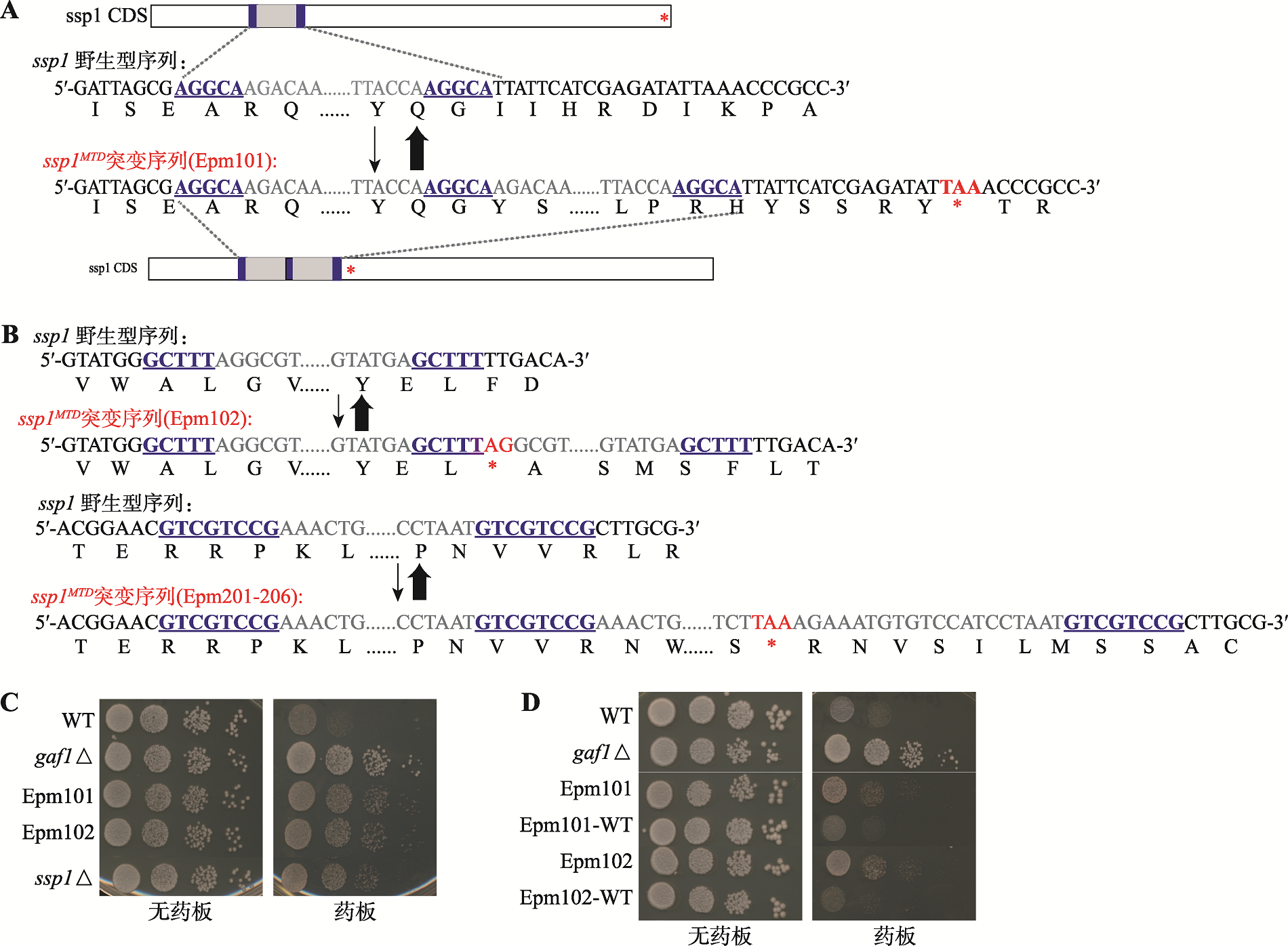
图4
ssp1位点可逆的短片段重复(ssp1MTDs)调控不稳定遗传的耐药性 A:ssp1位点发生短片段串联重复的示意图与DNA序列。示意图中深蓝色方格代表发生重复序列两端的微型同源臂(microhomology pairs)、灰色方格代表微型同源臂间的间隔序列、红色星号代表终止密码子,DNA序列简图中深蓝色标注序列为微型同源臂序列、灰色标注序列为微型同源臂间的间隔序列、红色标注序列为终止密码子序列。 B:发生在ssp1位点的另外两个短片段串联重复的DNA序列情况。C和D:基因敲除与回补实验验证ssp1位点发生的可逆短片段重复是调控不稳定遗传耐药性的原因;Epm101-wt、Epm102-wt表示发生ssp1MTDs突变的序列替换为野生型序列。"
| [1] |
Farlow A, Long HG, Arnoux S, Sung W, Doak TG, Nordborg M, Lynch M. The Spontaneous mutation rate in the fission yeast schizosaccharomyces pombe. Genetics, 2015, 201(2): 737-744.
pmid: 26265703 |
| [2] |
Muñoz-López M, García-Pérez JL. DNA transposons: nature and applications in genomics. Current Genomics, 2010, 11(2): 115-128.
pmid: 20885819 |
| [3] |
Blake KL, O'Neill AJ. Transposon library screening for identification of genetic loci participating in intrinsic susceptibility and acquired resistance to antistaphylococcal agents. J Antimicrob Chemother, 2013, 68(1): 12-16.
pmid: 23045225 |
| [4] |
Hannan AJ. Tandem repeats mediating genetic plasticity in health and disease. Nat Rev Genet, 2018, 19(5): 286-298.
pmid: 29398703 |
| [5] |
Gemayel R, Vinces MD, Legendre M, Verstrepen KJ. Variable tandem repeats accelerate evolution of coding and regulatory sequences. Annu Rev Genet, 2010, 44: 445-477.
pmid: 20809801 |
| [6] |
Crimi C, Benincasa G, Cirri S, Mutes R, Faenza M, Napoli C. Clinical epigenetics and multidrug-resistant bacterial infections: host remodelling in critical illness. Epigenetics, 2020, 15(10): 1021-1034.
pmid: 32290755 |
| [7] |
Ragunathan K, Jih G, Moazed D. Epigenetics. Epigenetic inheritance uncoupled from sequence-specific recruitment. Science, 2015, 348(6230): 1258699.
pmid: 25831549 |
| [8] |
Torres-Garcia S, Yaseen I, Shukla M, Audergon PNCB, White SA, Pidoux AL, Allshire AC. Epigenetic gene silencing by heterochromatin primes fungal resistance. Nature, 2020, 585(7825): 453-458.
pmid: 32908306 |
| [9] |
Calo S, Shertz-Wall C, Lee SC, Bastidas RJ, Nicolás FE, Granek JA, Mieczkowski P, Torres-Martínez S, Ruiz- Vázquez RM, Cardenas ME, Heitman J. Antifungal drug resistance evoked via RNAi-dependent epimutations. Nature, 2014, 513(7519): 555-558.
pmid: 25079329 |
| [10] |
Chang Z, Billmyre RB, Lee SC, Heitman J. Broad antifungal resistance mediated by RNAi-dependent epimutation in the basal human fungal pathogen Mucor circinelloides. PLoS Genet, 2019, 15(2): e1007957.
pmid: 30742617 |
| [11] |
Calo S, Nicolás FE, Lee SC, Vila A, Cervantes M, Torres-Martinez S, Ruiz-Vazquez RM, Cardenas ME, Heitman J. A non-canonical RNA degradation pathway suppresses RNAi-dependent epimutations in the human fungal pathogen Mucor circinelloides. PLoS Genet, 2017, 13(3): e1006686.
pmid: 28339467 |
| [12] |
Saxton RA, Sabatini DM. mTOR signaling in growth, metabolism, and disease. Cell, 2017, 168(6): 960-976.
pmid: 28283069 |
| [13] |
Gwinn DM, Shackelford DB, Egan DF, Mihaylova MM, Mery A, Vasquez DS, Turk BE, Shaw RJ. AMPK phosphorylation of raptor mediates a metabolic checkpoint. Mol Cell, 2008, 168(6): 960-976.
pmid: 18439900 |
| [14] |
Hardie DG. AMPK—sensing energy while talking to other signaling pathways. Cell Metab, 2014, 20(6): 939-952.
pmid: 25448702 |
| [15] |
Kim DH, Sarbassov DD, Ali SM, King JE, Latek RR, Erdjument-Bromag HE, Tempst P, Sabatini DM. mTOR interacts with raptor to form a nutrient-sensitive complex that signals to the cell growth machinery. Cell, 2002, 110(2): 163-175.
pmid: 12150925 |
| [16] |
Gaubitz C, Oliveira TM, Prouteau M, Leitner A, Karuppasamy M, Konstantinidou G, Rispal D, Eltschinger S, Robinson GC, Thore S, Aebersold R, Schaffitzel C, Loewith R. Molecular basis of the rapamycin insensitivity of target of rapamycin complex 2. Mol Cell, 2015, 58(6): 977-988.
pmid: 26028537 |
| [17] |
Laplante M, Sabatini DM. mTOR signaling in growth control and disease. Cell, 2012, 149(2): 274-293.
pmid: 22500797 |
| [18] |
Saitoh S, Mori A, Uehara L, Masuda F, Soejima S, Yanagida M. Mechanisms of expression and translocation of major fission yeast glucose transporters regulated by CaMKK/phosphatases, nuclear shuttling, and TOR. Mol Biol Cell, 2015, 149(2): 274-293.
pmid: 25411338 |
| [19] |
Otsubo Y, Yamamato M. TOR signaling in fission yeast. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol, 2008, 149(2): 274-293.
pmid: 18756382 |
| [20] |
Laor D, Cohen A, Kupiec M, Weisman R. TORC1 regulates developmental responses to nitrogen stress via regulation of the GATA transcription factor Gaf1. mBio, 2015, 6(4): e00959.
pmid: 26152587 |
| [21] |
Loewith R, Jacinto E, Wullschleger S, Lorberg A, Crespo JL, Bonenfant D, Oppliger W, Jenoe P, Hall MN. Two TOR complexes, only one of which is rapamycin sensitive, have distinct roles in cell growth control. Mol Cell, 2002, 10(3): 457-468.
pmid: 12408816 |
| [22] |
Rallis C, Maury LL, Georgescu T, Pancaldi V, Bahler J. Systematic screen for mutants resistant to TORC1 inhibition in fission yeast reveals genes involved in cellular ageing and growth. Biol Open, 2014, 3(2): 161-171.
pmid: 24463365 |
| [23] |
Rallis C, Codlin S, Bähler J. TORC1 signaling inhibition by rapamycin and caffeine affect lifespan, global gene expression, and cell proliferation of fission yeast. Aging Cell, 2013, 12(4): 563-573.
pmid: 23551936 |
| [24] |
Li WZ, Yi J, Agbu P, Zhou Z, Kelley RL, Kallgren S, Jia ST, He XW. Replication stress affects the fidelity of nucleosome-mediated epigenetic inheritance. PLoS Genet, 2017, 12(4): 563-573.
pmid: 28749973 |
| [25] |
Ekwall K, Thon G. Spore analysis and tetrad dissection of schizosaccharomyces pombe. Cold Spring Harb Protoc, 2017, 2017(7): pdb.prot091710.
pmid: 28679703 |
| [26] |
Escorcia W, Forsburg SL. Tetrad dissection in fission yeast. Methods Mol Biol, 2018, 1721: 179-187.
pmid: 29423857 |
| [27] |
Verstrepen KJ, Jansen A, Lewitter F, Fink GR. Intragenic tandem repeats generate functional variability. Nat Genet, 2005, 37(9): 986-990.
pmid: 16086015 |
| [28] |
Dan LF, Li YZ, Chen SH, Liu JB, Wang Y, Li FT, He XW, Carey LB. A rapidly reversible mutation generates subclonal genetic diversity and unstable drug resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2021, 118(43): e2019060118.
pmid: 34675074 |
| [29] |
Davie E, Forte GMA, Petersen J. Nitrogen regulates AMPK to control TORC1 signaling. Curr Biol, 2015, 25(4): 445-454.
pmid: 25639242 |
| [30] |
Livnat A, Love AC. Mutation and evolution: conceptual possibilities. Bioessays, 2024, 46(2): e2300025.
pmid: 38254311 |
| [31] | Liu ZY, Ren H, Chen C, Zhang JJ, Zhang XM, Shi Y, Shi LY, Chen Y, Cheng F, Jia L, Chen M, Fan QW, Zhang JR, Li WT, Wang MC, Ren ZL, Liu YC, Ni M, Sun HY, Yan JW. Actual mutational research of 19 autosomal STRs based on restricted mutation model and big data. Hereditas (Beijing), 2021, 43(10): 949-961. |
| 刘志勇, 任贺, 陈冲, 张京晶, 张晓梦, 石妍, 石林玉, 陈滢, 程凤, 贾莉, 陈曼, 范庆炜, 张家榕, 李万婷, 王萌春, 任子林, 刘雅诚, 倪铭, 孙宏钰, 严江伟. 基于有限突变模型和大规模数据的19个常染色体STR的实际突变率研究. 遗传, 2021, 43(10): 949-961. |
| [1] | 安梦婷, 郭冠麟, 吴杰, 孙文靖, 贾学渊. 基于生物信息学分析胃癌双微体中增强子的调控机制[J]. 遗传, 2025, 47(5): 558-572. |
| [2] | 阿卜力米提·阿卜杜喀迪尔, 张其奥, 李佩波, 谢建平. 分枝杆菌生物被膜发育调控与抗生素耐药菌防控新措施研发[J]. 遗传, 2024, 46(1): 34-45. |
| [3] | 陈湖星, 徐蕾, 李静, 郭政, 敖露. 基于结直肠癌细胞系MIC50相关基因对的基础耐药 评分模型构建[J]. 遗传, 2020, 42(6): 577-585. |
| [4] | 祝力骋,卢俊婉,王建,许腾,徐娟华. 肺炎克雷伯菌blaCARB-2基因的分布及结构分析[J]. 遗传, 2018, 40(7): 593-600. |
| [5] | 陈昱帆, 刘诗胤, 梁志彬, 吕明发, 周佳暖, 张炼辉. 群体感应与微生物耐药性[J]. 遗传, 2016, 38(10): 881-893. |
| [6] | 高薇1, 史伟1, 陈长会2, 文德年3, 田进2, 姚开虎1. 临床肺炎链球菌常见序列型青霉素耐药性的流行病学研究[J]. 遗传, 2016, 38(10): 940-947. |
| [7] | 杨盛智, 吴国艳, 龙梅, 邓雯文, 王红宁, 邹立扣. 鸡蛋生产链中沙门氏菌对抗生素及消毒剂的耐药性研究[J]. 遗传, 2016, 38(10): 948-956. |
| [8] | 杨延成,程航,周人杰,饶贤才. SCCmec遗传元件及其在耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌分子分型中的应用[J]. 遗传, 2015, 37(5): 442-451. |
| [9] | 高琼,黄海辉. 艰难梭菌耐药性及耐药机制研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2015, 37(5): 458-464. |
| [10] | 张跃进, 常清利, 汪倩, 卢俊婉, 王欢, 李佩珍, 应俊, 包其郁, 胡云良. 临床分离肺炎克雷伯菌Ⅰ类整合子的结构与功能[J]. 遗传, 2014, 36(6): 603-610. |
| [11] | 王倩,崔志峰. 真菌的多向耐药性ABC转运蛋白[J]. 遗传, 2011, 33(10): 1048-1056. |
| [12] | 王,霞,孙丹凤,房静远. mTOR信号途径与表观遗传关系的研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2006, 28(12): 1585-1585~1590. |
| [13] | 张春玉,冯源熙,李,璞,傅松滨. 介导多药耐药的ABC转运蛋白超家族与MTX耐药性的关系研究[J]. 遗传, 2006, 28(10): 1201-1205. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||

www.chinagene.cn
备案号:京ICP备09063187号-4
总访问:,今日访问:,当前在线:
