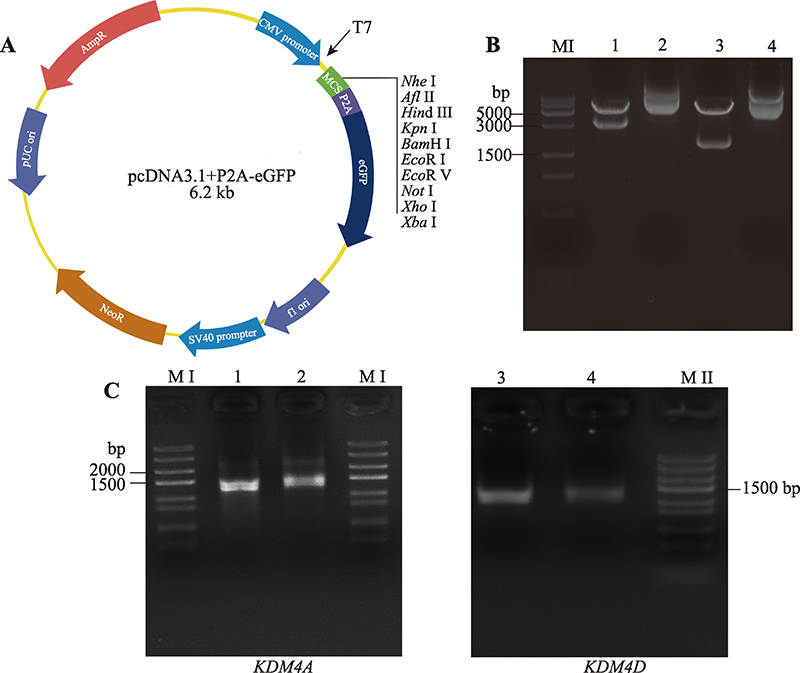
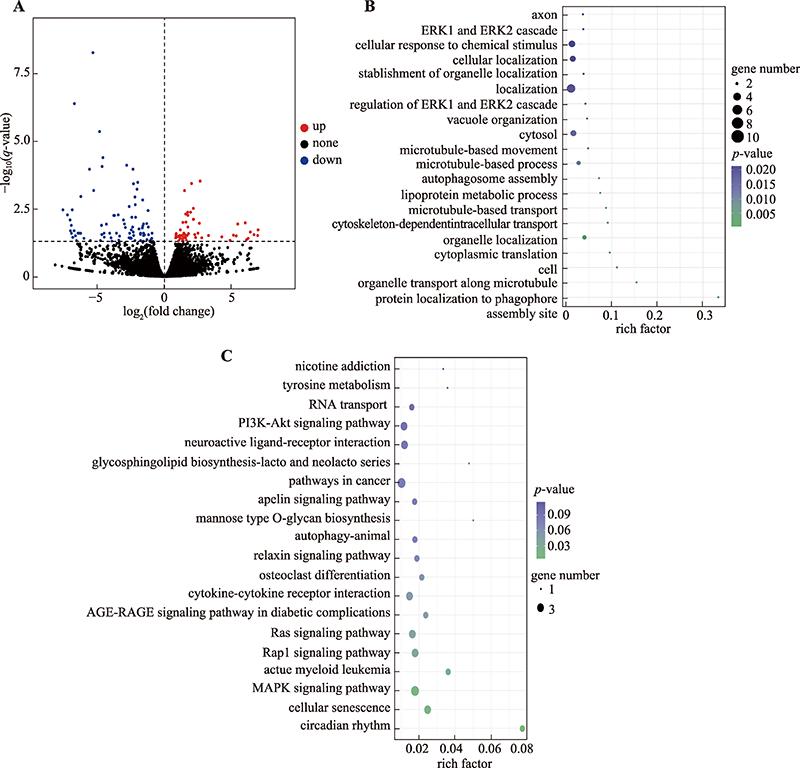
Hereditas(Beijing) ›› 2023, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (1): 67-77.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.22-244
• Research Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of overexpression of histone H3K9me3 demethylase on development of porcine cloned embryos
Yanan Li1,2,3( ), Xianjun Zhang1,2,3, Ning Zhang1,2,3, Yalin Liang1,2,3, Yuxing Zhang1,2,3, Huaxing Zhao1,2,3, Zicong Li1,2,3, Sixiu Huang1,2,3(
), Xianjun Zhang1,2,3, Ning Zhang1,2,3, Yalin Liang1,2,3, Yuxing Zhang1,2,3, Huaxing Zhao1,2,3, Zicong Li1,2,3, Sixiu Huang1,2,3( )
)
- 1. National Engineering Research Center for Breeding Swine Industry, College of Animal Science of South China Agricultural University, Guangzhou 510642, China
2. National & Local Joint Engineering Research Center for Breeding Animal Industry, Guangzhou 510642, China
3. Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Agro-animal Genomics and Molecular Breeding, Guangzhou 510642, China
-
Received:2022-07-18Revised:2022-11-08Online:2023-01-20Published:2022-11-28 -
Contact:Huang Sixiu E-mail:li321736803@163.com;sxhuang815@scau.edu.cn -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province(2019B1515210027);Guangdong Special Support Plan Local Innovation and Entrepreneurship Team(2019BT02N630);Guangdong Province Livestock and poultry Local Breed Protection and Development and Utilization Promotion Project]
Cite this article
Yanan Li, Xianjun Zhang, Ning Zhang, Yalin Liang, Yuxing Zhang, Huaxing Zhao, Zicong Li, Sixiu Huang. Effects of overexpression of histone H3K9me3 demethylase on development of porcine cloned embryos[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2023, 45(1): 67-77.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Table 1
Effects of injecting KDM4A mRNA and KDM4D mRNA at 1-cell stage on the developmental efficiency of porcine cloned embryos"
| 组别 | 胚胎数(n) | 卵裂数 | 卵裂率(%) | 囊胚数 | 囊胚率(%) | 囊胚细胞数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KDM4A | 308(8) | 228 | 74.03 ± 0.95 | 78 | 25.32 ± 0.74aA | 42.11 ± 2.39 |
| KDM4D | 295(8) | 217 | 73.45 ± 0.92 | 48 | 16.27 ± 0.77bB | 43.79 ± 2.70 |
| KDM4A+KDM4D | 216(7) | 155 | 71.76 ± 0.93 | 41 | 18.98 ± 1.01abAB | 38.59 ± 2.8 |
| 胚胎注射水(对照) | 345(9) | 250 | 72.46 ± 0.65 | 51 | 14.78 ± 0.87bB | 40.27 ± 2.22 |
Table 2
Effects of injecting KDM4A mRNA and KDM4D mRNA at 2-cell stage on the developmental efficiency of porcine cloned embryos"
| 组别 | 胚胎数(n) | 囊胚数 | 囊胚率(%) | 囊胚细胞数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KDM4A | 202(6) | 65 | 32.18 ± 1.67 | 35.18 ± 1.73ab |
| KDM4D | 243(7) | 73 | 30.04 ± 0.91 | 32.47 ± 1.75b |
| KDM4A+KDM4D | 88(3) | 26 | 29.55 ± 1.95 | 40.33 ± 4.00a |
| 胚胎注射水(对照) | 221(6) | 69 | 31.22 ± 1.40 | 35.44 ± 2.05ab |
| [1] | Liu Y, Li J, Løvendahl P, Schmidt M, Larsen K, Callesen H. In vitro manipulation techniques of porcine embryos: a meta-analysis related to transfers, pregnancies and piglets. Reprod Fertil Dev, 2015, 27(3): 429-439. |
| [2] | Yang XQ, Wu ZF, Li ZC. Advances in epigenetic reprogramming of somatic cells nuclear transfer in mammals. Hereditas (Beijing), 2019, 41(12): 1099-1109. |
| 杨旭琼, 吴珍芳, 李紫聪. 哺乳动物体细胞核移植表观遗传重编程研究进展. 遗传, 2019, 41(12): 1099-1109. | |
| [3] | Huang XW, Cheng XR, Wang N, Zhang YW, Liao C, Jin LH, Lei L. Histone variant H3.3 and its functions in reprogramming. Hereditas (Beijing), 2018, 40(3): 186-196. |
| 黄星卫, 程香荣, 王楠, 张雨薇, 廖辰, 金连弘, 雷蕾. 组蛋白H3变体H3.3及其在细胞重编程中的作用. 遗传, 2018, 40(3): 186-196. | |
| [4] | Chung YG, Matoba S, Liu YT, Eum JH, Lu F, Jiang W, Lee JE, Sepilian V, Cha KY, Lee DR, Zhang Y. Histone demethylase expression enhances human somatic cell nuclear transfer efficiency and promotes derivation of pluripotent stem cells. Cell Stem Cell, 2015, 17(6): 758-766. |
| [5] | Matoba S, Liu YT, Lu FL, Iwabuchi KA, Shen L, Inoue A, Zhang Y. Embryonic development following somatic cell nuclear transfer impeded by persisting histone methylation. Cell, 2014, 159(4): 884-895. |
| [6] | Meng FL, Stamms K, Bennewitz R, Green A, Oback F, Turner P, Wei JW, Oback B. Targeted histone demethylation improves somatic cell reprogramming into cloned blastocysts but not postimplantation bovine concepti. Biol Reprod, 2020, 103(1): 114-125. |
| [7] | Zhang YM, Wang QQ, Liu KL, Gao EE, Guan H, Hou J. Treatment of donor cells with recombinant KDM4D protein improves preimplantation development of cloned ovine embryos. Cytotechnology, 2018, 70(5): 1469-1477. |
| [8] | Liu Z, Cai YJ, Wang Y, Nie YH, Zhang CC, Xu YT, Zhang XT, Lu Y, Wang ZY, Poo M, Sun Q. Cloning of macaque monkeys by somatic cell nuclear transfer. Cell, 2018, 172(4): 881-887. |
| [9] | Janjic A, Wange LE, Bagnoli JW, Geuder J, Nguyen P, Richter D, Vieth B, Vick B, Jeremias I, Ziegenhain C, Hellmann I, Enard W. Prime-seq, efficient and powerful bulk RNA sequencing. Genome Biol, 2022, 23(1): 88. |
| [10] | Matoba S, Zhang Y. Somatic cell nuclear transfer reprogramming: mechanisms and applications. Cell Stem Cell, 2018, 23(4): 471-485. |
| [11] | Liu WQ, Liu XY, Wang CF, Gao YW, Gao R, Kou XC, Zhao YH, Li JY, Wu Y, Xiu WC, Wang S, Yin JQ, Liu W, Cai T, Wang H, Zhang Y, Gao SR. Identification of key factors conquering developmental arrest of somatic cell cloned embryos by combining embryo biopsy and single-cell sequencing. Cell Discov, 2016, 2: 16010. |
| [12] | Wu X, Li G, Ao Z, Shi JS, Cai GY, Liu DW, Wu ZF, Li ZC. Effects of overexpression of H3K9me3 demethylase on the in vitro developmental efficiency of cloned porcine embryos. Guangdong Agric Sci, 2017, 44(10): 96-101. |
| 吴霄, 李果, 敖政, 石俊松, 蔡更元, 刘德武, 吴珍芳, 李紫聪. 过表达H3K9me3去甲基化酶对猪克隆胚胎体外发育效率的影响. 广东农业科学, 2017, 44(10): 96-101. | |
| [13] | He XY, Tan C, Li ZC, Zhao CF, Shi JS, Zhou R, Wang XW, Jiang GL, Cai GY, Liu DW, Wu ZF. Characterization and comparative analyses of transcriptomes of cloned and in vivo fertilized porcine pre-implantation embryos. Biol Open, 2019, 8(4): bio039917. |
| [14] | Liu X, Chen L, Wang T, Zhou JL, Li ZK, Bu GW, Zhang JJ, Yin SY, Wu DY, Dou CL, Xu T, He HN, Zhu W, Yu LT, Liu ZT, Zhang X, Chen ZX, Miao YL. TDG is a pig-specific epigenetic regulator with insensitivity to H3K9 and H3K27 demethylation in nuclear transfer embryos. Stem Cell Reports, 2021, 16(11): 2674-2689. |
| [15] | Sankar A, Kooistra SM, Gonzalez JM, Ohlsson C, Poutanen M, Helin K. Maternal expression of the histone demethylase KDM4A is crucial for pre-implantation development. Development, 2017, 144(18): 3264-3277. |
| [16] | Lee JE, Chung YG, Eum JH, Lee Y, Lee DR. An efficient SCNT technology for the establishment of personalized and public human pluripotent stem cell banks. BMB Rep, 2016, 49(4): 197-198. |
| [17] | Ruan DG, Peng JY, Wang XS, Ouyang Z, Zou QJ, Yang Y, Chen FB, Ge WK, Wu H, Liu ZM, Zhao Y, Zhao BT, Zhang QJ, Lai CD, Fan NN, Zhou ZW, Liu QS, Li N, Jin Q, Shi H, Xie JK, Song H, Yang XY, Chen JK, Wang KP, Li XP, Lai LX. XIST derepression in active X chromosome hinders pig somatic cell nuclear transfer. Stem Cell Reports, 2018, 10(2): 494-508. |
| [18] | Weng XG, Cai MM, Zhang YT, Liu Y, Liu C, Liu ZH. Improvement in the in vitro development of cloned pig embryos after KDM4A overexpression and an H3K9me3 methyltransferase inhibitor treatment. Theriogenology, 2020, 146: 162-170. |
| [19] | Chen M, Zhu QS, Li C, Kou XC, Zhao YH, Li YH, Xu RM, Yang L, Yang LY, Gu L, Wang H, Liu XY, Jiang CZ, Gao SR. Chromatin architecture reorganization in murine somatic cell nuclear transfer embryos. Nat Commun, 2020, 11(1): 1813. |
| [20] | Feng Y, Zhao X, Li ZD, Luo C, Ruan ZY, Xu J, Shen PL, Deng YF, Jiang JR, Shi DS, Lu FH. Histone demethylase KDM4D could improve the developmental competence of buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT) embryos. Microsc Microanal, 2021, 27(2): 409-419. |
| [21] | Wang CF, Liu XY, Gao YW, Yang L, Li C, Liu WQ, Chen C, Kou XC, Zhao YH, Chen JY, Wang YX, Le RR, Wang H, Duan T, Zhang Y, Gao SR. Reprogramming of H3K9me3- dependent heterochromatin during mammalian embryo development. Nat Cell Biol, 2018, 20(5): 620-631. |
| [22] | Cao ZB, Li YS, Chen Z, Wang H, Zhang ML, Zhou NR, Wu RH, Ling YH, Fang FG, Li N, Zhang YH. Genome- wide dynamic profiling of histone methylation during nuclear transfer-mediated porcine somatic cell reprogramming. PLoS One, 2015, 10(12): e0144897. |
| [23] | Hernández-Rosas F, Hernández-Oliveras A, Flores-Peredo L, Rodríguez G, Zarain-Herzberg Á, Caba M, Santiago-García J. Histone deacetylase inhibitors induce the expression of tumor suppressor genes Per1 and Per2 in human gastric cancer cells. Oncol Lett, 2018, 16(2): 1981-1990. |
| [24] | Zhao Y, Huang SY, Tan XR, Long LF, He QM, Liang XY, Bai JW, Li QJ, Lin JY, Li YQ, Liu N, Ma J, Chen YP. N6-methyladenosine-modified CBX1 regulates nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression through heterochromatin formation and STAT1 activation. Adv Sci (Weinh), 2022, 30: e2205091. |
| [25] | Divisato G, Chiariello AM, Esposito A, Zoppoli P, Zambelli F, Elia MA, Pesole G, Incarnato D, Passaro F, Piscitelli S, Oliviero S, Nicodemi M, Parisi S, Russo T. Hmga2 protein loss alters nuclear envelope and 3D chromatin structure. BMC Biol, 2022, 20(1): 171. |
| [26] | Dong GZ, Zhang R, Hu Q, Martin EM, Qin YF, Lu CC, Xia YK, Wang XR, Du GZ. Prothioconazole induces cell cycle arrest by up-regulation of EIF4EBP1 in extravillous trophoblast cells. Arch Toxicol, 2022, 96(2): 559-570. |
| [27] | Mahdipour M, Leitoguinho AR, Zacarias Silva RA, van Tol HT, Stout TA, Rodrigues G, Roelen BA. TACC3 is important for correct progression of meiosis in bovine oocytes. PLoS One, 2015, 10(7): e0132591. |
| [28] | Heinemann-Yerushalmi L, Bentovim L, Felsenthal N, Vinestock RC, Michaeli N, Krief S, Silberman A, Cohen M, Ben-Dor S, Brenner O, Haffner-Krausz R, Itkin M, Malitsky S, Erez A, Zelzer E. BCKDK regulates the TCA cycle through PDC in the absence of PDK family during embryonic development. Dev Cell, 2021, 56(8): 1182-1194.e6. |
| [29] | Krieg AJ, Mullinax SR, Grimstad F, Marquis K, Constance E, Hong Y, Krieg SA, Roby KF. Histone demethylase KDM4A and KDM4B expression in granulosa cells from women undergoing in vitro fertilization. Assist Reprod Genet, 2018, 35(6): 993-1003. |
| [30] | Zoabi M, Nadar-Ponniah PT, Khoury-Haddad H, Usaj M, Budowski-Tal I, Haran T, Henn A, Mandel-Gutfreund Y, Ayoub N. RNA-dependent chromatin localization of KDM4D lysine demethylase promotes H3K9me3 demethylation. Nucleic Acids Res, 2014, 42(21): 13026-13038. |
| [31] | Zhang BY, Long QL, Wu SS, Xu QX, Song SL, Han L, Qian M, Ren XH, Liu HX, Jiang J, Guo JM, Zhang XL, Chang X, Fu Q, Lam EWF, Campisi J, Kirkland JL, Sun Y. KDM4 orchestrates epigenomic remodeling of senescent cells and potentiates the senescence-associated secretory phenotype. Nat Aging, 2021, 1(5): 454-472. |
| [32] | Massett ME, Monaghan L, Patterson S, Mannion N, Bunschoten RP, Hoose A, Marmiroli S, Liskamp RMJ, Jørgensen HG, Vetrie D, Michie AM, Huang X. A KDM4A-PAF1-mediated epigenomic network is essential for acute myeloid leukemia cell self-renewal and survival. Cell Death Dis, 2021, 12(6): 573. |
| [33] | Zhao JG, Hao YH, Ross JW, Spate LD, Walters EM, Samuel MS, Rieke A, Murphy CN, Prather RS. Histone deacetylase inhibitors improve in vitro and in vivo developmental competence of somatic cell nuclear transfer porcine embryos. Cell Reprogram, 2010, 12(1): 75-83. |
| [34] | Kishigami S, Mizutani E, Ohta H, Hikichi T, Thuan NV, Wakayama S, Bui HT, Wakayama T. Significant improvement of mouse cloning technique by treatment with trichostatin a after somatic nuclear transfer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2006, 340(1): 183-189. |
| [35] | Wang FC, Kou ZH, Zhang Y, Gao SR. Dynamic reprogramming of histone acetylation and methylation in the first cell cycle of cloned mouse embryos. Biol Reprod, 2007, 77(6): 1007-1016. |
| [36] | Inoue K, Kohda T, Sugimoto M, Sado T, Ogonuki N, Matoba S, Shiura H, Ikeda R, Mochida K, Fujii T, Sawai K, Otte AP, Tian XC, Yang XZ, Ishino F, Abe K, Ogura A. Impeding Xist expression from the active X chromosome improves mouse somatic cell nuclear transfer. Science, 2010, 330(6003): 496-499. |
| [37] | Li GL, Zhong CL, Ni S, Liu DW, Cai GY, Li ZC, Yang HQ, Wu ZF. Establishment of porcine Xist knockout model using CRISPR/Cas9 system. Hereditas (Beijing), 2016, 38(12): 1081-1089. |
| 李国玲, 钟翠丽, 倪生, 刘德武, 蔡更元, 李紫聪, 杨化强, 吴珍芳. 利用CRISPR/Cas9系统建立Xist基因敲除猪模型. 遗传, 2016, 38(12): 1081-1089. | |
| [38] | Matoba S, Wang HH, Jiang L, Lu FL, Iwabuchi KA, Wu XJ, Inoue K, Yang L, Press W, Lee JT, Ogura A, Shen L, Zhang Y. Loss of H3K27me 3 imprinting in somatic cell nuclear transfer embryos disrupts post-implantation development. Cell Stem Cell, 2018, 23(3): 343-354. |
| [1] | Wenrui Shi, Hongzhu Qu, Xiangdong Fang. Overview of multi-omics research in gout [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2023, 45(8): 643-657. |
| [2] | Fei Gao, Yu Wang, Jiaxiang Du, Xuguang Du, Jianguo Zhao, Dengke Pan, Sen Wu, Yaofeng Zhao. Advances and applications of genetically modified pig models in biomedical and agricultural field [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2023, 45(1): 6-28. |
| [3] | Mengxuan Xu, Ming Zhou. Advances of RNA polymerase IV in controlling DNA methylation and development in plants [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(7): 567-580. |
| [4] | Yan Zhao, Chenxin Wang, Tianming Yang, Chunshuang Li, Lihong Zhang, Dongni Du, Ruoxi Wang, Jing Wang, Min Wei, Xueqing Ba. Linking oxidative DNA lesion 8-OxoG to tumor development and progression [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(6): 466-477. |
| [5] | Hui Qu, Yi Liu, Yawen Chen, Hui Wang. Alteration of imprinted genes and offspring organ development caused by environmental factors [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(2): 107-116. |
| [6] | Yangjinghui Zhang, Peiyao Chang, Zishu Yang, Yuhang Xue, Xueqi Li, Yang Zhang. Advances in epigenetic modification affecting anthocyanin synthesis [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(12): 1117-1127. |
| [7] | Qingwen Zhao, Dongning Pan. Progress on the epigenetic regulation of adipose tissue thermogenesis [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(10): 867-880. |
| [8] | Jiayu Yu, Ting Chen, Zhihua Wang, Juan Zheng, Tianshu Zeng. Diagnosis, treatment and genetic analysis of a case of skin hyperpigmentation as the only manifestation with X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(10): 983-989. |
| [9] | Wang Ya'nan, Tao Xu, Wanpeng Wang, Qingzhu Zhang, Xie Li'nan. Role of epigenetic modifications in the development of crops essential traits [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2021, 43(9): 858-879. |
| [10] | Jiangping He, Jiekai Chen. Epigenetic control of transposable elements and cell fate decision [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2021, 43(9): 822-834. |
| [11] | Jie Yuan, Shiqing Cai. The regulatory mechanisms of behavioral and cognitive aging [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2021, 43(6): 545-570. |
| [12] | Tianyi Wang, Yingxiang Wang, Chenjiang You. Structural and functional characteristics of plant PHD domain-containing proteins [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2021, 43(4): 323-339. |
| [13] | Dingwei Peng, Ruiqiang Li, Wu Zeng, Min Wang, Xuan Shi, Jianhua Zeng, Xiaohong Liu, Yaoshen Chen, Zuyong He. Editing the cystine knot motif of MSTN enhances muscle development of Liang Guang Small Spotted pigs [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2021, 43(3): 261-270. |
| [14] | Qiang Wei, Yan Ao, Manman Yang, Tao Chen, Hu Han, Xingju Zhang, Ran Wang, Qiuju Xia, Fangfang Jiang, Yong Li. Identification of genomic insertion of dominant-negative GHR mutation transgenes in Wuzhishan pig using whole genome sequencing method [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2021, 43(12): 1149-1158. |
| [15] | Xiangqian Zhang, Nan Li, Xinming Xie. Design and exploration of epigenetic comprehensive experiments [J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2021, 43(12): 1179-1187. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||