遗传 ›› 2020, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (5): 506-518.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.20-070
• 研究报告 • 上一篇
胡雅丽1,2,3, 戴睿2,3,4,5, 刘永鑫2,3,4, 张婧赢2,3,4, 胡斌2, 储成才2, 袁怀波1( ), 白洋2,3,4,5(
), 白洋2,3,4,5( )
)
收稿日期:2020-03-15
修回日期:2020-04-16
出版日期:2020-05-20
发布日期:2020-04-26
通讯作者:
袁怀波,白洋
E-mail:yuanhuaibo001@163.com;ybai@genetics.ac.cn
作者简介:胡雅丽,在读硕士研究生,专业方向:根系微生物组。E-mail:2017111262@mail.hfut.edu.cn|戴睿,在读博士研究生,专业方向:根系微生物组,生物信息学。E-mail: raydai@genetics.ac.cn; 胡雅丽和戴睿为并列第一作者。
基金资助:
Yali Hu1,2,3, Rui Dai2,3,4,5, Yongxin Liu2,3,4, Jingying Zhang2,3,4, Bin Hu2, Chengcai Chu2, Huaibo Yuan1( ), Yang Bai2,3,4,5(
), Yang Bai2,3,4,5( )
)
Received:2020-03-15
Revised:2020-04-16
Online:2020-05-20
Published:2020-04-26
Contact:
Yuan Huaibo,Bai Yang
E-mail:yuanhuaibo001@163.com;ybai@genetics.ac.cn
Supported by:摘要:
植物的各项生命活动与其根系微生物组密不可分,且根系微生物组的组成易受到植物生长环境和基因型的影响。为进一步探究中国北方地区种植的不同品种水稻根系微生物组的差异及其相互作用机制,本研究以种植于北京昌平和上庄农场的水稻典型品种日本晴(Nipponbare)和IR24为研究对象,基于16S rRNA基因扩增子测序技术获得根系微生物组序列,利用多样性分析、组成型分析、机器学习的随机森林和网络分析等方法,对旺盛生长期的两种不同品种的水稻根系微生物组进行详细比较。研究发现,种植地点和水稻基因型显著影响了水稻根系微生物组的群落结构,不同基因型导致了根系微生物组在物种分类组成上以及细菌间相互关系的差异,而且根系微生物组能作为生物标记跨地点区分宿主的基因型。本研究结果为深入理解我国北方种植的水稻根系微生物组的组成规律以及从根系微生物与植物互作的角度对品种进行改良提供了数据和理论基础。
胡雅丽, 戴睿, 刘永鑫, 张婧赢, 胡斌, 储成才, 袁怀波, 白洋. 水稻典型品种日本晴和IR24根系微生物组的解析[J]. 遗传, 2020, 42(5): 506-518.
Yali Hu, Rui Dai, Yongxin Liu, Jingying Zhang, Bin Hu, Chengcai Chu, Huaibo Yuan, Yang Bai. Analysis of rice root bacterial microbiota of Nipponbare and IR24[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2020, 42(5): 506-518.

图1
种植地点和品种差异影响水稻根系微生物组成 A:基于样品间Bray Curtis距离的主坐标分析(PCoA)。日本晴和IR24的根系微生物组在PCoA的第一轴上(PCo 1)按种植地点开,第二轴上(PCo 2)按基因型分开,组间差异显著(PERMANOVA, P < 0.001)。CP:昌平;SZ:上庄;坐标轴标题括号中显示整体差异的解释率百分比。B:日本晴和IR24根系微生物组的丰富度指数(richness index,样品内物种多样性)。箱线图中框内横线表示中位数,上下边缘分别代表上下四分位数,边缘上的延长线在无异常值时至极值,但最长不超过1.5倍上下四分位数的分布区间。各组间丰富度指数差异不明显,最小显著差异法(least significant difference, LSD)比较组间差异,4组均为a表示地点和基因型对根系微生物组的Alpha多样性影响不显著(P > 0.05)。"
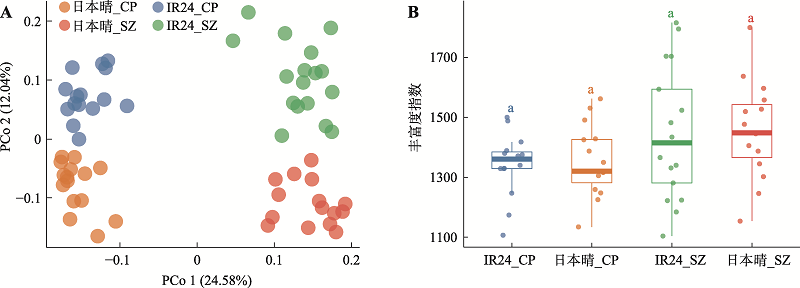
图2
日本晴和IR24的根系微生物组在门/纲级分布上存在差异 柱状图展示每个样品中根系微生物组的物种组成(门和纲水平的相对丰度)。变形菌门(Proteobacteria)因丰度较高在纲水平展开为alpha-、beta-、gamma-和delta-变形菌4个纲,其余为门水平。Acidobacteria:酸杆菌门;Actinobacteria:放线菌门;Bacteroidetes:拟杆菌门;Firmicutes:厚壁菌门;Spirochaetes:螺旋体门。在两个种植地区,IR24根系微生物中的beta-变形菌纲显著高于日本晴,而拟杆菌门和gamma-变形菌纲在日本晴的根系微生物组中丰度更高,此外放线菌门(上庄)和delta-变形菌纲(昌平)只在一个地区在两基因型间有显著差异(Wilcoxon秩和检验,P < 0.05,FDR < 0.2)。CP:昌平;SZ:上庄。每组样品的数量为:IR2_CP (n = 15),日本晴_CP (n = 15),IR24_SZ (n = 17),日本晴_SZ (n = 15)。"
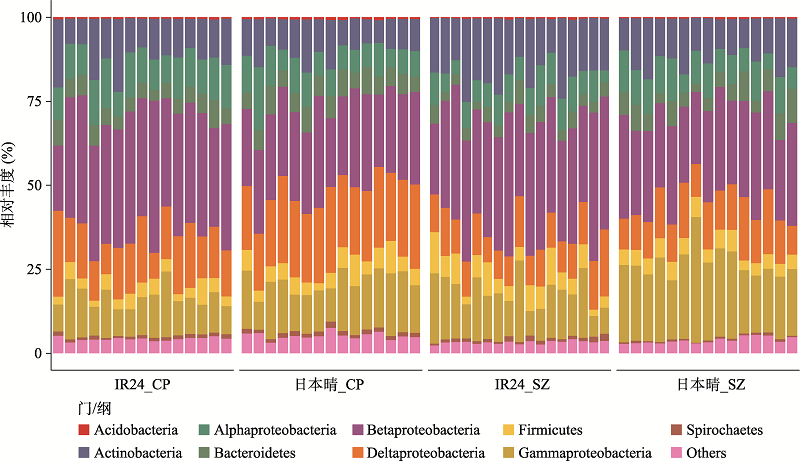
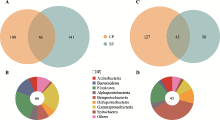
图3
日本晴和IR24根系的差异OTU及对应门纲水平分类组成 A:在两个种植地点中日本晴根系富集的OTUs。与IR24相比,日本晴在昌平(CP)和上庄(SZ)分别有166个和207个OTU富集,且其中有66个OTU在这两个种植地区都富集(Wilcoxon秩和检验用于比较差异OTUs,当P < 0.05、FDR < 0.2且差异倍数 > 1.2时,认为该OTU在两组样品间存在差异)。B:日本晴在两个种植地区均富集的根系OTUs的分类组成。共同富集的66个OTU大部分属于拟杆菌门,厚壁菌门和gamma-变形菌纲。C:在两个种植地点中IR24根系富集的OTUs。与日本晴相比,IR24在昌平和上庄分别有172个和135个富集OTUs,且其中有45个OTUs在这两个种植地区都富集。D:IR24在两个种植地区均富集的根系OTU的分类组成。共同富集的45个OTU大部分属于beta-变形菌纲,厚壁菌门和delta-变形菌纲。从图中可知,水稻基因型影响了微生物在根系的富集。Actinobacteria:放线菌门;Bacteroidetes:拟杆菌门;Firmicutes:厚壁菌门;Spirochaetes:螺旋体门;其余为alpha-、beta-、delta-、gamma-变形菌纲。"

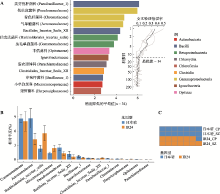
图4
基于根系微生物组的随机森林分类模型能较精准预测日本晴 A:随机森林分类模型中重要性排前14的生物标记菌。采用随机森林分类法,对昌平和上庄地区的IR24和日本晴根系微生物组(共34个样品)在科水平进行了分类,并在纲水平着色。生物标记菌按照对模型准确度的重要性由高到低排序,展示前14个。图右侧小图表示十倍交叉验证错误率,当标记菌个数超过14个时,模型的错误率较低且稳定。B:标记菌在日本晴和IR24根系微生物组中的相对丰度。蓝色为日本晴,橙色为IR24。C:用随机森林分类模型对两个基因型做分类预测。该模型基于样品的根系微生物组成判断样品的基因型。前两行样品为日本晴,后两行样品为IR24,蓝色表示样品基因型被预测为日本晴,橙色则是预测为IR24。CP:昌平;SZ:上庄。Actinobacteria:放线菌纲;Bacilli:杆菌纲;Betaproteobacteria:beta-变形菌纲;Chlamydiia:衣原体纲;Chloroflexia:绿弯菌纲;Clostridia:梭菌纲;Gammaproteobacteria:gamma-变形菌纲;Opitutae:丰佑菌纲。"
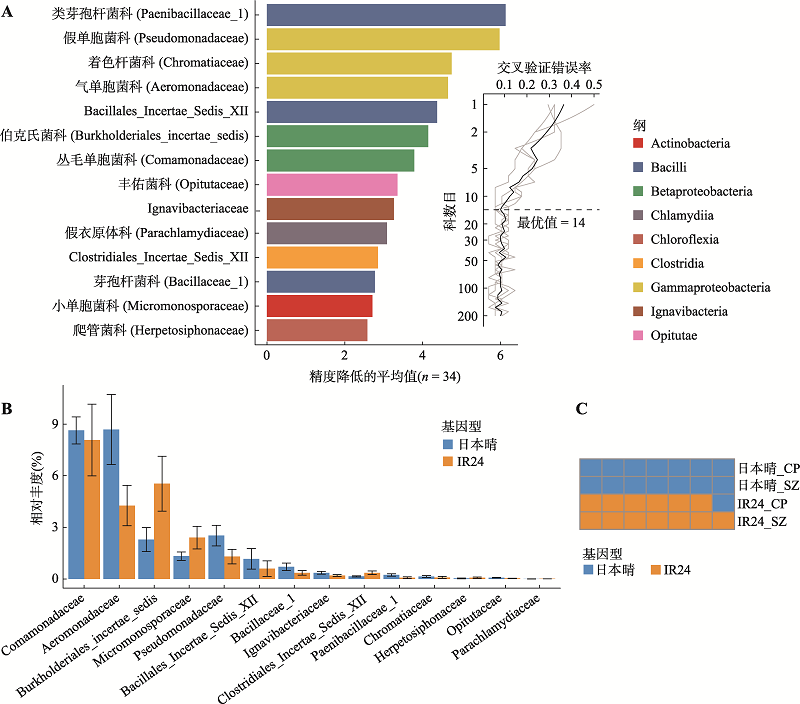
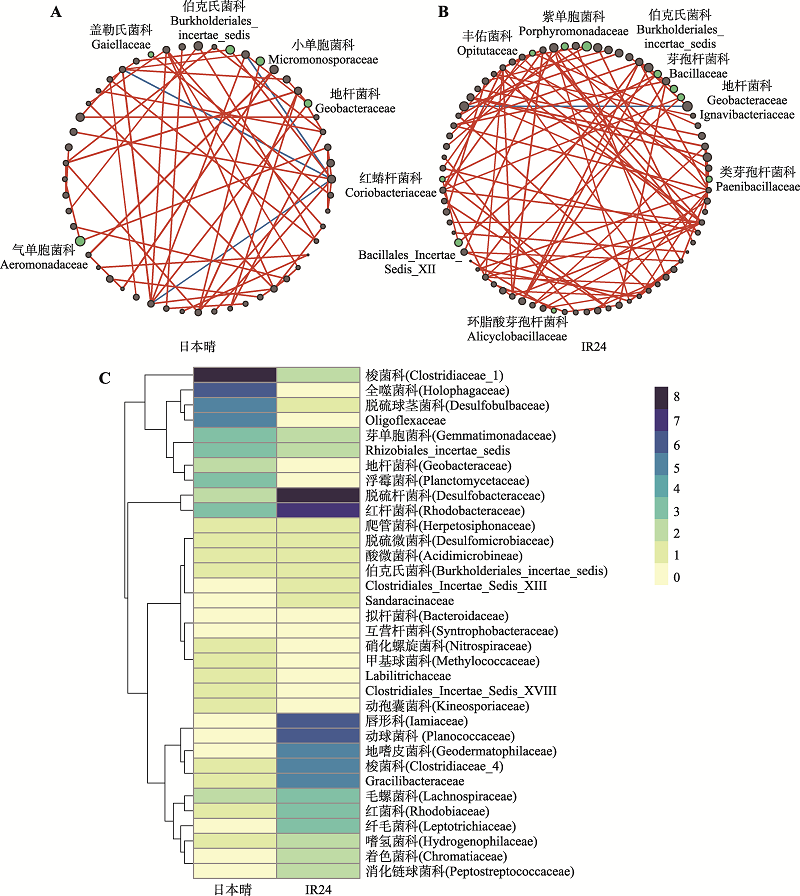
图5
日本晴和IR24的根系菌群形成的共存网络有明显区别 A:日本晴的微生物群落在科水平形成的共存网络。网络中共有52个节点,59条边。B:IR24的微生物群落在科水平形成的共存网络。网络中共有76个节点,93条边。共存网络关系利用Pearson相关系数判断科水平菌间相关性(P < 0.05,|r| > 0.7),网络中每个节点代表一个科,节点大小表示该科在每组样品中的平均相对丰度。其中绿色节点为科水平在两个基因型间存在差异的根系菌(Wilcoxon秩和检验,P < 0.05、FDR < 0.2且差异倍数 > 1.2)。连接节点的边表示该两个节点间的相关性,红色为正相关,蓝色为负相关,线条粗细与相关性高低成正比。C:两个基因型网络间共有菌的连接紧密度比较。两个网络中共有34个菌,统计其中每个菌作为节点与网络中其他菌的关联度(即连接该节点的边的个数)。CP:昌平;SZ:上庄。"
| [1] | Lundberg DS, Lebeis SL, Paredes SH, Yourstone S, Gehring J, Malfatti S, Tremblay J, Engelbrektson A, Kunin V, Rio TGd, Edgar RC, Eickhorst T, Ley RE, Hugenholtz P, Tringe SG, Dangl JL . Defining the core Arabidopsis thaliana root microbiome. Nature, 2012,488(7409):86-90. |
| [2] | Bulgarelli D, Rott M, Schlaeppi K, Ver Loren van Themaat E, Ahmadinejad N, Assenza F, Rauf P, Huettel B, Reinhardt R, Schmelzer E, Peplies J, Gloeckner FO, Amann R, Eickhorst T, Schulze-Lefert P. Revealing structure and assembly cues for Arabidopsis root-inhabiting bacterial microbiota. Nature, 2012,488(7409):91-95. |
| [3] | Müller DB, Vogel C, Bai Y, Vorholt JA . The plant microbiota: systems-level insights and perspectives. Annu Rev Genet, 2016,50(1):211-234. |
| [4] | Bai Y, Qian JM, Zhou JM, Qian W . Crop Microbiome: breakthrough technology for agriculture. Bull Chin Acad Sci, 2017,32(3):260-265. |
| 白洋, 钱景美, 周俭民, 钱韦 . 农作物微生物组:跨越转化临界点的现代生物技术. 中国科学院院刊, 2017,32(3):260-265. | |
| [5] | Durán P, Thiergart T, Garrido-Oter R, Agler M, Kemen E, Schulze-Lefert P, Hacquard S . Microbial interkingdom interactions in roots promote Arabidopsis survival. Cell, 2018,175(4):973-983. |
| [6] |
Hiruma K, Gerlach N, Sacristán S, Nakano RT, Hacquard S, Kracher B, Neumann U, Ramírez D, Bucher M, O’Connell RJ, Schulze-Lefert P,. Root endophyte colletotrichum tofieldiae confers plant fitness benefits that are phosphate status dependent. Cell, 2016,165(2):464-474.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.02.028 |
| [7] |
Wang XL, Wang ET . NRT1.1B connects root microbiota and nitrogen use in rice. Bull Bot, 2019,54(3):285-287.
doi: 10.11983/CBB19060 |
|
王孝林, 王二涛 . 根际微生物促进水稻氮利用的机制. 植物学报, 2019,54(3):285-287.
doi: 10.11983/CBB19060 |
|
| [8] | Kwak MJ, Kong HG, Choi K, Kwon SK, Song JY, Lee J, Lee PA, Choi SY, Seo M, Lee HJ, Jung EJ, Park H, Roy N, Kim H, Lee MM, Rubin EM, Lee SW, Kim JF . Rhizosphere microbiome structure alters to enable wilt resistance in tomato. Nat Biotechnol, 2018,36:1100-1109. |
| [9] | Wang XF, Wei Z, Yang KM, Wang JN, Jousset A, Xu YC, Shen QR, Friman VP . Phage combination therapies for bacterial wilt disease in tomato. Nat Biotechnol, 2019,37(12):1513-1520. |
| [10] | Carrión VJ, Perez-Jaramillo J, Cordovez V, Tracanna V, de Hollander M, Ruiz-Buck D, Mendes LW, van Ijcken WFJ, Gomez-Exposito R, Elsayed SS, Mohanraju P, Arifah A, van der Oost J, Paulson JN, Mendes R, van Wezel GP, Medema MH, Raaijmakers JM. Pathogen-induced activation of disease-suppressive functions in the endophytic root microbiome. Science, 2019,366(6465):606-612. |
| [11] | Zhang JY, Liu YX, Zhang N, Hu B, Jin T, Xu HR, Qin Y, Yan PX, Zhang XN, Guo XX, Hui J, Cao SY, Wang X, Wang C, Wang H, Qu BY, Fan GY, Yuan LX, Garrido-Oter R, Chu CC, Bai Y . NRT1.1B is associated with root microbiota composition and nitrogen use in field-grown rice. Nat Biotechnol, 2019,37(6):676-684. |
| [12] | Castrillo G, Teixeira PJPL, Paredes SH, Law TF, de Lorenzo L, Feltcher ME, Finkel OM, Breakfield NW, Mieczkowski P, Jones CD, Paz-Ares J, Dangl JL. Root microbiota drive direct integration of phosphate stress and immunity. Nature, 2017,543(7646):513-518. |
| [13] | Van Deynze A, Zamora P, Delaux PM, Heitmann C, Jayaraman D, Rajasekar S, Graham D, Maeda J, Gibson D, Schwartz KD, Berry AM, Bhatnagar S, Jospin G, Darling A, Jeannotte R, Lopez J, Weimer BC, Eisen JA, Shapiro HY, Ané JM, Bennett AB . Nitrogen fixation in a landrace of maize is supported by a mucilage-associated diazotrophic microbiota. PLoS Biol, 2018,16(8):e2006352. |
| [14] |
Wang C, Bai Y . Maize aerial roots fix atmospheric N2 by interacting with nitrogen fixing bacteria (in Chinese). Sci Sin Vitae, 2019,49(1):89-90.
doi: 10.1360/N052018-00215 |
|
王超, 白洋 . 玉米可利用气生根进行高效生物固氮. 中国科学:生命科学, 2019,49(1):89-90.
doi: 10.1360/N052018-00215 |
|
| [15] | Huang AC, Jiang T, Liu YX, Bai YC, Reed J, Qu B, Goossens A, Nützmann HW, Bai Y, Osbourn A. A specialized metabolic network selectively modulates Arabidopsis root microbiota. Science, 2019, 364(6440): eaau6389. |
| [16] | Yuan J, Zhao J, Wen T, Zhao M, Li R, Goossens P, Huang Q, Bai Y, Vivanco JM, Kowalchuk GA, Berendsen RL, Shen Q . Root exudates drive the soil-borne legacy of aboveground pathogen infection. Microbiome, 2018,6(1):156. |
| [17] | Bai Y, Müller DB, Srinivas G, Garrido-Oter R, Potthoff E, Rott M, Dombrowski N, Münch PC, Spaepen S, Remus-Emsermann M, Hüttel B, McHardy AC, Vorholt JA, Schulze-Lefert P. Functional overlap of the Arabidopsis leaf and root microbiota. Nature, 2015,528(7582):364-369. |
| [18] | Chen QW, Jiang T, Liu YX, Liu HL, Zhao T, Liu ZX, Gan XC, Hallab A, Wang XM, He J, Ma YH, Zhang FX, Jin T, Schranz ME, Wang Y, Bai Y, Wang GD . Recently duplicated sesterterpene (C25) gene clusters in Arabidopsis thaliana modulate root microbiota. Science China Life Sciences, 2019,62(7):947-958. |
| [19] | Wang W, Yang J, Zhang J, Liu YX, Tian CP, Qu BY, Gao CL, Xin PY, Cheng SJ, Zhang WJ, Miao P, Li L, Zhang XJ, Chu JF, Zuo JR, Li JY, Bai Y, Lei XG, Zhou JM . An Arabidopsis secondary metabolite directly targets expression of the bacterial type III secretion system to inhibit bacterial virulence. Cell Host Microbe, 2020,27(4):601-613. |
| [20] | Chen T, Nomura K, Wang XL, Sohrabi R, Xu J, Yao YL, Paasch BC, Ma L, Kremer J, Cheng YT, Zhang L, Wang N, Wang ET, Xin XF, He SY . A plant genetic network for preventing dysbiosis in the phyllosphere. Nature, 2020,580(7804):653-657. |
| [21] | Edwards J, Johnson C, Santos-Medellín C, Lurie E, Podishetty NK, Bhatnagar S, Eisen JA, Sundaresan V . Structure, variation, and assembly of the root-associated microbiomes of rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2015,112(8):E911-E920. |
| [22] | Zhang JY, Zhang N, Liu YX, Zhang XN, Hu B, Qin Y, Xu HR, Wang H, Guo XX, Qian JM, Wang W, Zhang PF, Jin T, Chu CC, Bai Y . Root microbiota shift in rice correlates with resident time in the field and developmental stage. Science China Life Sciences, 2018,61(6):613-621. |
| [23] | Edwards JA, Santos-Medellín CM, Liechty ZS, Nguyen B, Lurie E, Eason S, Phillips G, Sundaresan V . Compositional shifts in root-associated bacterial and archaeal microbiota track the plant life cycle in field-grown rice. PLoS Biol, 2018,16(2):e2003862. |
| [24] | Chen SM, Waghmode TR, Sun RB, Kuramae EE, Hu CS, Liu BB . Root-associated microbiomes of wheat under the combined effect of plant development and nitrogen fertilization. Microbiome, 2019,7(1):136. |
| [25] |
Shi Y, Li YT, Xiang XJ, Sun RB, Yang T, He D, Zhang KP, Ni YY, Zhu YG, Adams JM, Chu HY . Spatial scale affects the relative role of stochasticity versus determinism in soil bacterial communities in wheat fields across the North China Plain. Microbiome, 2018,6(1):27.
doi: 10.1186/s40168-018-0409-4 |
| [26] | Sun RB, Li WY, Dong WX, Tian YP, Hu CS, Liu BB . Tillage changes vertical distribution of soil bacterial and fungal communities. Front Microbiol, 2018,9:699. |
| [27] | Walters WA, Jin Z, Youngblut N, Wallace JG, Sutter J, Zhang W, González-Peña A, Peiffer J, Koren O, Shi QJ, Knight R, Glavina del Rio T, Tringe SG, Buckler ES, Dangl JL, Ley RE,. Large-scale replicated field study of maize rhizosphere identifies heritable microbes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2018,115(28):7368-7373. |
| [28] | Wei Z, Gu Y, Friman VP, Kowalchuk GA, Xu YC, Shen QR , Jousset A. Initial soil microbiome composition and functioning predetermine future plant health. Sci Adv, 2019,5(9): eaaw0759. |
| [29] | Xiong W, Song YQ, Yang KM, Gu Y, Wei Z, Kowalchuk GA, Xu YC, Jousset A, Shen QR, Geisen S . Rhizosphere protists are key determinants of plant health. Microbiome, 2020,8(1):27. |
| [30] | Jin T, Wang YY, Huang YY, Xu J, Zhang PF, Wang N, Liu X, Chu HY, Liu G, Jiang HG, Li YZ, Xu J, Kristiansen K, Xiao L, Zhang YZ, Zhang GY, Du GH, Zhang HB, Zou HF, Zhang HF, Jie ZY, Liang SS, Jia HJ, Wan JW, Lin DC, Li JY, Fan GY, Yang HM, Wang J, Bai Y, Xu X . Taxonomic structure and functional association of foxtail millet root microbiome. GigaScience, 2017,6(10):1-12. |
| [31] | Liu YX, Qin Y, Bai Y . Reductionist synthetic community approaches in root microbiome research. Curr Opin Microbiol, 2019,49:97-102. |
| [32] | Fan KK, Weisenhorn P, Gilbert JA, Shi Y, Bai Y, Chu HY . Soil pH correlates with the co-occurrence and assemblage process of diazotrophic communities in rhizosphere and bulk soils of wheat fields. Soil Biol Biochem, 2018,121:185-192. |
| [33] | Mori A, Kirk GJD, Lee JS, Morete MJ, Nanda AK, Johnson-Beebout SE, Wissuwa M . Rice genotype differences in tolerance of zinc-deficient soils: evidence for the importance of root-induced changes in the rhizosphere. Front Plant Sci, 2016,6:1160. |
| [34] | Fan KK, Delgado-Baquerizo M, Guo XS, Wang DZ, Wu YY, Zhu M, Yu W, Yao HY, Zhu YG, Chu HY . Suppressed N fixation and diazotrophs after four decades of fertilization. Microbiome, 2019,7(1):143. |
| [35] | Zhao Q, Feng Q, Lu HY, Li Y, Wang AH, Tian QL, Zhan QL, Lu YQ, Zhang L, Huang T, Wang YC, Fan DL, Zhao Y, Wang ZQ, Zhou CC, Chen JY, Zhu CR, Li WJ, Weng QJ, Xu Q, Wang ZX, Wei XH, Han B, Huang XH . Pan-genome analysis highlights the extent of genomic variation in cultivated and wild rice. Nat Genet, 2018,50(2):278-284. |
| [36] | Wang W, Hu B, Yuan DY, Liu YQ, Che RH, Hu YC, Ou SJ, Liu YX, Zhang ZH, Wang H, Li H, Jiang ZM, Zhang ZL, Gao XK, Qiu YH, Meng XB, Liu YX, Bai Y, Liang Y, Wang YQ, Zhang LH, Li LG, Sodmergen S, Jing HC, Li JY, Chu CC . Expression of the nitrate transporter gene OsNRT1.1A/OsNPF6.3 confers high yield and early maturation in rice. Plant Cell, 2018,30(3):638-651. |
| [37] | Stein JC, Yu Y, Copetti D, Zwickl DJ, Zhang L, Zhang C, Chougule K, Gao D, Iwata A, Goicoechea JL, Wei S, Wang J, Liao Y, Wang M, Jacquemin J, Becker C, Kudrna D, Zhang J, Londono CEM, Song X, Lee S, Sanchez P, Zuccolo A, Ammiraju JSS, Talag J, Danowitz A, Rivera LF, Gschwend AR, Noutsos C, Wu CC, Kao SM, Zeng JW, Wei FJ, Zhao Q, Feng Q, El Baidouri M, Carpentier MC, Lasserre E, Cooke R, Rosa Farias Dd, da Maia LC, dos Santos RS, Nyberg KG, McNally KL, Mauleon R, Alexandrov N, Schmutz J, Flowers D, Fan C, Weigel D, Jena KK, Wicker T, Chen M, Han B, Henry R, Hsing YC, Kurata N, de Oliveira AC, Panaud O, Jackson SA, Machado CA, Sanderson MJ, Long M, Ware D, Wing RA. Genomes of 13 domesticated and wild rice relatives highlight genetic conservation, turnover and innovation across the genus Oryza. Nat Genet, 2018,50(2):285-296. |
| [38] | Guo XX, Zhang XN, Qin Y, Liu YX, Zhang JY, Zhang N, Wu K, Qu BY, He ZS, Wang X, Zhang XJ, Hacquard S, Fu XD, Bai Y . Host-associated quantitative abundance profiling reveals the microbial load variation of root microbiome. Plant Commun, 2020,1(1):100003. |
| [39] | Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Peña AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI, Huttley GA, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koenig JE, Ley RE, Lozupone CA, McDonald D, Muegge BD, Pirrung M, Reeder J, Sevinsky JR, Turnbaugh PJ, Walters WA, Widmann J, Yatsunenko T, Zaneveld J, Knight R. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods, 2010,7(5):335-336. |
| [40] | Bolyen E, Rideout JR, Dillon MR, Bokulich NA, Abnet CC, Al-Ghalith GA, Alexander H, Alm EJ, Arumugam M, Asnicar F, Bai Y, Bisanz JE, Bittinger K, Brejnrod A, Brislawn CJ, Brown CT, Callahan BJ, Caraballo- Rodríguez AM, Chase J, Cope EK, Da Silva R, Diener C, Dorrestein PC, Douglas GM, Durall DM, Duvallet C, Edwardson CF, Ernst M, Estaki M, Fouquier J, Gauglitz JM, Gibbons SM, Gibson DL, Gonzalez A, Gorlick K, Guo J, Hillmann B, Holmes S, Holste H, Huttenhower C, Huttley GA, Janssen S, Jarmusch AK, Jiang L, Kaehler BD, Kang KB, Keefe CR, Keim P, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koester I, Kosciolek T, Kreps J, Langille MGI, Lee J, Ley R, Liu YX, Loftfield E, Lozupone C, Maher M, Marotz C, Martin BD, McDonald D, McIver LJ, Melnik AV, Metcalf JL, Morgan SC, Morton JT, Naimey AT, Navas-Molina JA, Nothias LF, Orchanian SB, Pearson T, Peoples SL, Petras D, Preuss ML, Pruesse E, Rasmussen LB, Rivers A, Robeson MS, Rosenthal P, Segata N, Shaffer M, Shiffer A, Sinha R, Song SJ, Spear JR, Swafford AD, Thompson LR, Torres PJ, Trinh P, Tripathi A, Turnbaugh PJ, Ul-Hasan S, van der Hooft JJJ, Vargas F, Vázquez-Baeza Y, Vogtmann E, von Hippel M, Walters W, Wan Y, Wang M, Warren J, Weber KC, Williamson CHD, Willis AD, Xu ZZ, Zaneveld JR, Zhang Y, Zhu Q, Knight R, Caporaso JG. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat Biotechnol, 2019,37(8):852-857. |
| [41] | Edgar RC . Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics, 2010,26(19):2460-2461. |
| [42] | Liu YX, Qin Y, Guo XX, Bai Y . Methods and applications for microbiome data analysis. Hereditas(Beijing), 2019,41(9):845-826. |
| 刘永鑫, 秦媛, 郭晓璇, 白洋 . 微生物组数据分析方法与应用. 遗传, 2019,41(9):845-826. | |
| [43] | Zheng MS, Zhou N, Liu SF, Dang CY, Liu YX, He SS, Zhao YJ, Liu W, Wang XK . N2O and NO emission from a biological aerated filter treating coking wastewater: main source and microbial community. J Clean Prod, 2019,213:365-374. |
| [44] | Oksanen J, Kindt R, Legendre P, O’Hara B, Stevens MHH, Oksanen MJ, Suggests M,. The vegan package. Community Ecology Package, 2007,10:631-637. |
| [45] | Wickham H . Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis. Springer, 2016. |
| [46] | Liaw A, Wiener M . Classification and regression by randomForest. R News, 2002,2(3):18-22. |
| [47] | Qian XB, Liu YX, Ye XH, Zheng WJ, Lv SX, Mo MJ, Lin JJ, Wang WQ, Wang WH, Zhang XN, Lu MP . Gut microbiota in children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis: characteristics, biomarker identification, and usefulness in clinical prediction. BMC Genomics, 2020,21(1):286. |
| [48] | Csardi G, Nepusz T . The igraph software package for complex network research. InterJ Complex Systems, 2006,1695(5):1-9. |
| [49] | Wang JF, Zheng JY, Shi WY, Du N, Xu XM, Zhang YM, Ji PF, Zhang FY, Jia Z, Wang YP, Zheng Z, Zhang HP, Zhao FQ . Dysbiosis of maternal and neonatal microbiota associated with gestational diabetes mellitus. Gut, 2018,67(9):1614-1625. |
| [50] | Deng Y, Jiang YH, Yang YF, He ZL, Luo F, Zhou JZ . Molecular ecological network analyses. BMC Bioinformatics, 2012,13(1):113. |
| [51] | National Genomics Data Center Members and Partners. Database resources of the national genomics data center in 2020. Nucleic Acids Res, 2020,48(D1):D24-D33. |
| [52] | Wang YQ, Song FH, Zhu JW, Zhang SS, Yang YD, Chen TT, Tang BX, Dong LL, Ding N, Zhang Q, Bai ZX, Dong XN, Chen HX, Sun MY, Zhai SA, Sun YB, Yu L, Lan L, Xiao JF, Fang XD, Lei HX, Zhang Z, Zhao WM . GSA: Genome sequence archive. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics, 2017,15(1):14-18. |
| [53] | Zhang CL, Zhang YM, Ding ZJ, Bai Y . Contribution of microbial inter-kingdom balance to plant health. Mol Plant, 2019,12(2):148-149. |
| [54] | Toju H, Peay KG, Yamamichi M, Narisawa K, Hiruma K, Naito K, Fukuda S, Ushio M, Nakaoka S, Onoda Y, Yoshida K, Schlaeppi K, Bai Y, Sugiura R, Ichihashi Y, Minamisawa K, Kiers ET . Core microbiomes for sustainable agroecosystems. Nat Plants, 2018,4(5):247-257. |
| [55] | Xie JP, Han YB, Liu G, Bai LQ . Research advances on microbial genetics in China in 2015. Hereditas(Beijing), 2016,38(9):765-790. |
| 谢建平, 韩玉波, 刘钢, 白林泉 . 2015年中国微生物遗传学研究领域若干重要进展. 遗传, 2016,38(9):765-790. | |
| [56] | Wen CL, Sun CJ, Yang N . The concepts and research progress: from heritability to microbiability. Hereditas (Beijing), 2019,41(11):1023-1040. |
| 文超良孙从佼, 杨宁 . 从遗传力到肠菌力:概念及研究进展. 遗传, 2019,41(11):1023-1040. | |
| [57] | Liu BB, Zhang XJ, Bakken LR, Snipen L, Frostegård Å . Rapid succession of actively transcribing denitrifier populations in agricultural soil during an anoxic spell. Front Microbiol, 2019,9:3208. |
| [58] | Zhang KP, Shi Y, Cui XQ, Yue P, Li KH, Liu XJ, Tripathi BM, Chu HY . Salinity is a key determinant for soil microbial communities in a desert ecosystem. mSystems, 2019,4(1):e00225-00218. |
| [59] |
Lebeis SL, Paredes SH, Lundberg DS, Breakfield N, Gehring J, McDonald M, Malfatti S, Glavina del Rio T, Jones CD, Tringe SG, Dangl JL. Salicylic acid modulates colonization of the root microbiome by specific bacterial taxa. Science, 2015,349(6250):860-864.
doi: 10.1126/science.aaa8764 |
| [60] | Voges MJEEE, Bai Y, Schulze-Lefert P, Sattely ES . Plant-derived coumarins shape the composition of an Arabidopsis synthetic root microbiome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2019,116(25):12558-12565. |
| [61] | Zamioudis C, Korteland J, Van Pelt JA, van Hamersveld M, Dombrowski N, Bai Y, Hanson J, Van Verk MC, Ling HQ, Schulze-Lefert P, Pieterse CMJ,. Rhizobacterial volatiles and photosynthesis-related signals coordinate MYB72 expression in Arabidopsis roots during onset of induced systemic resistance and iron-deficiency responses. Plant J, 2015,84(2):309-322. |
| [62] | Niu B, Paulson JN, Zheng X, Kolter R . Simplified and representative bacterial community of maize roots. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2017,114(12):E2450-E2459. |
| [63] | Hu B, Wang W, Ou SJ, Tang JY, Li H, Che RH, Zhang ZH, Chai XY, Wang HR, Wang YQ, Liang CZ, Liu LC, Piao ZZ, Deng QY, Deng K, Xu C, Liang Y, Zhang LH, Li LG, Chu CC . Variation in NRT1.1B contributes to nitrate-use divergence between rice subspecies. Nat Genet, 2015,47(7):834-838. |
| [64] | Getzke F, Thiergart T, Hacquard S . Contribution of bacterial-fungal balance to plant and animal health. Curr Opin Microbiol, 2019,49:66-72. |
| [65] | Kim PJ, Price ND . Genetic co-occurrence network across sequenced microbes. PLoS Comput Biol, 2011,7(12):e1002340. |
| [1] | 吕娇, 龚一富, 章丽, 胡媛, 王何瑜. 基于WGCNA发掘缺磷、红光和黄光处理下三角褐指藻岩藻黄素合成关键基因[J]. 遗传, 2023, 45(3): 237-249. |
| [2] | 孔永强, 刘金凯, 顾佳琪, 徐景怡, 郑雨诺, 魏以梁, 伍少远. 南-北方汉族人、韩国人和日本人遗传划分机器学习模型优化方案[J]. 遗传, 2022, 44(11): 1028-1043. |
| [3] | 陈应坚,廖苑君,林帆,孙胜南,赵小蕾,覃继恒,饶绍奇. 基于转录组数据的网络分析挖掘鼻咽癌与口腔鳞癌的共享功能模块[J]. 遗传, 2019, 41(2): 146-157. |
| [4] | 张桂珊, 杨勇, 张灵敏, 戴宪华. 机器学习方法在CRISPR/Cas9系统中的应用[J]. 遗传, 2018, 40(9): 704-723. |
| [5] | 赵学彤, 杨亚东, 渠鸿竹, 方向东. 组学时代下机器学习方法在临床决策支持中的应用[J]. 遗传, 2018, 40(9): 693-703. |
| [6] | 彭哲也,唐紫珺,谢民主. 机器学习方法在基因交互作用探测中的研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2018, 40(3): 218-226. |
| [7] | 罗旭红 刘志芳 董长征. 基因水平的关联分析方法[J]. 遗传, 2013, 35(9): 1065-1071. |
| [8] | 李秀领,杨松柏,唐中林,李奎,刘榜,樊斌. 大白猪和通城猪全基因组选择性清扫分析[J]. 遗传, 2012, 34(10): 1271-1281. |
| [9] | 侯妍妍,应晓敏,李伍举. microRNA计算发现方法的研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2008, 30(6): 687-696. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||

www.chinagene.cn
备案号:京ICP备09063187号-4
总访问:,今日访问:,当前在线:
