遗传 ›› 2023, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (10): 904-921.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.23-139
夏凯( ), 刘芳美, 陈雨晴, 陈珊珊, 黄春莹, 赵学群, 沙如意, 黄俊(
), 刘芳美, 陈雨晴, 陈珊珊, 黄春莹, 赵学群, 沙如意, 黄俊( )
)
收稿日期:2023-06-08
修回日期:2023-08-11
出版日期:2023-10-20
发布日期:2023-08-23
通讯作者:
黄俊
E-mail:xiakai05@zust.edu.cn;huangjun@zust.edu.cn
作者简介:夏凯,博士,讲师,研究方向:微生物遗传与育种。E-mail: 基金资助:
Kai Xia( ), Fangmei Liu, Yuqing Chen, Shanshan Chen, Chunying Huang, Xuequn Zhao, Ruyi Sha, Jun Huang(
), Fangmei Liu, Yuqing Chen, Shanshan Chen, Chunying Huang, Xuequn Zhao, Ruyi Sha, Jun Huang( )
)
Received:2023-06-08
Revised:2023-08-11
Published:2023-10-20
Online:2023-08-23
Contact:
Jun Huang
E-mail:xiakai05@zust.edu.cn;huangjun@zust.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
解脂亚罗酵母(Yarrowia lipolytica)是赤藓糖醇生产中使用的主要菌种,复合诱变是选育优良菌株的常用方法。然而,诱变处理所引起的基因组变化尚待探索。本研究对前期获得的高产菌株CA20和原始菌株WT5进行基因组测序,并与已发布的8株解脂亚罗酵母进行比较基因组分析,旨在探究菌株CA20高产赤藓糖醇的机理以及不同菌株的基因组进化关系。结果显示,菌株CA20基因组大小为20,420,510 bp,GC碱基含量为48.97%,编码6330个CDS和649个ncRNA,菌株CA20和其他8株菌高度同源,平均核苷酸同源性(average nucleotide identity,ANI)> 99.50%,其中与菌株IBT 446和H222具有更近的亲缘关系。比较基因组分析显示,CA20和其他8株菌共有5342个核心基因,而CA20特有的65个基因主要参与物质跨膜运输和蛋白质转运过程。CA20基因组中含有166个碳水化合物活性酶(carbohydrate-active enzymes,CAZymes)基因,远多于其他菌株(108~137个),包括特有的4个糖苷水解酶类(glycoside hydrolases,GHs)、2个糖基转移酶类(glycosyltransferases,GTs)和13个碳水化合物酯酶类(carbohydrate esterases,CEs)。除转醛酶TAL1外,赤藓糖醇代谢途径有关酶在不同菌株中高度保守。此外,菌株CA20的赤藓糖醇产量和产率为190.97 g/L和1.33 g/L/h,显著高于WT5的128.61 g/L和0.92 g/L/h (P<0.001)。相比于WT5,CA20中5个基因发生移码变异,15个基因存在非同义突变位点,这些基因主要参与细胞分裂、细胞壁合成、蛋白质合成及稳态维持等过程。以上结果表明,解脂亚罗酵母基因组在进化过程中保守;生存环境不同是导致菌株间基因组差异的重要因素;基因组中CAZymes数量的差异是不同菌株间性能差异的原因之一;菌株CA20高产赤藓糖醇与其细胞结构及内环境稳定性的提升有关。本研究结果为赤藓糖醇高产菌株的定向选育提供基础。
夏凯, 刘芳美, 陈雨晴, 陈珊珊, 黄春莹, 赵学群, 沙如意, 黄俊. 基于比较基因组学的解脂亚罗酵母CA20高产赤藓糖醇机理及进化分析[J]. 遗传, 2023, 45(10): 904-921.
Kai Xia, Fangmei Liu, Yuqing Chen, Shanshan Chen, Chunying Huang, Xuequn Zhao, Ruyi Sha, Jun Huang. Mechanism and evolutionary analysis of Yarrowia lipolytica CA20 capable of producing erythritol with a high yield based on comparative genomics[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2023, 45(10): 904-921.
表1
基因组信息"
| 菌株 | 数据来源 | 大小(Mb) | GC% | 染色体数量 | 分离环境 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y. lipolytica CA20 | PRJNA957569 | 20.42 | 48.97 | 6 | 水果、蜂蜜和糖蜜混合物 |
| Y. lipolytica W29 | PRJNA437435 | 20.50 | 48.98 | 6 | 废水 |
| Y. lipolytica DSM 3286 | PRJNA641784 | 21.22 | 48.91 | 6 | 未记录 |
| Y. lipolytica 22301-5 | PRJNA802556 | 20.95 | 48.96 | 6 | 废水 |
| Y. lipolytica IBT 446 | PRJNA437435 | 19.86 | 49.09 | 6 | 奶酪 |
| Y. lipolytica H222 | PRJNA437435 | 19.72 | 49.11 | 6 | 泥土 |
| Y. lipolytica CLIB122 | PRJNA13837 | 20.55 | 48.98 | 6 | 未记录 |
| Y. lipolytica Po1f | PRJNA233955 | 20.62 | 49.01 | 6 | 废水 |
| Y. lipolytica WSH-Z06 | PRJEB5051 | 20.09 | 49.03 | 6 | 泥土 |
表3
不同解脂亚罗酵母中碳水化合物活性酶的数量"
| 菌株 | GHs | GTs | CBMs | CEs | AAs | 总和 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y. lipolytica CA20 | 55 | 60 | 8 | 25 | 18 | 166 |
| Y. lipolytica W29 | 56 | 60 | 8 | 2 | 10 | 136 |
| Y. lipolytica DSM 3286 | 55 | 60 | 8 | 2 | 12 | 137 |
| Y. lipolytica 22301-5 | 48 | 53 | 2 | 3 | 15 | 121 |
| Y. lipolytica IBT 446 | 46 | 48 | 2 | 3 | 9 | 108 |
| Y. lipolytica H222 | 44 | 50 | 3 | 4 | 12 | 113 |
| Y. lipolytica CLIB122 | 55 | 58 | 8 | 2 | 7 | 130 |
| Y. lipolytica PO1f | 45 | 52 | 3 | 3 | 14 | 117 |
| Y. lipolytica WSH-Z06 | 46 | 51 | 2 | 3 | 15 | 117 |
图11
菌株CA20和WT5的比较基因组分析 A:样本突变圈图,由外至内依次为基因组信息、SNP在基因组上的密度分布、Indel在基因组上的密度分布、SV在基因组上的密度分布;B:SNP和Indel的位点数量;C:位点变化引起的非同义突变(nonsynonymous mutation,NSM)、同义突变(synonymous mutation,SM)和移码变异(frameshift mutation,FSM)基因数量;D:染色体结构变异数量,包括染色体之间的易位(inter-chromosomal translocation,CTX)、插入(insertion,INS)、缺失(deletion,DEL)、倒位(inversion,INV)、染色体内部的易位(intra-chromosomal translocation,ITX)。"
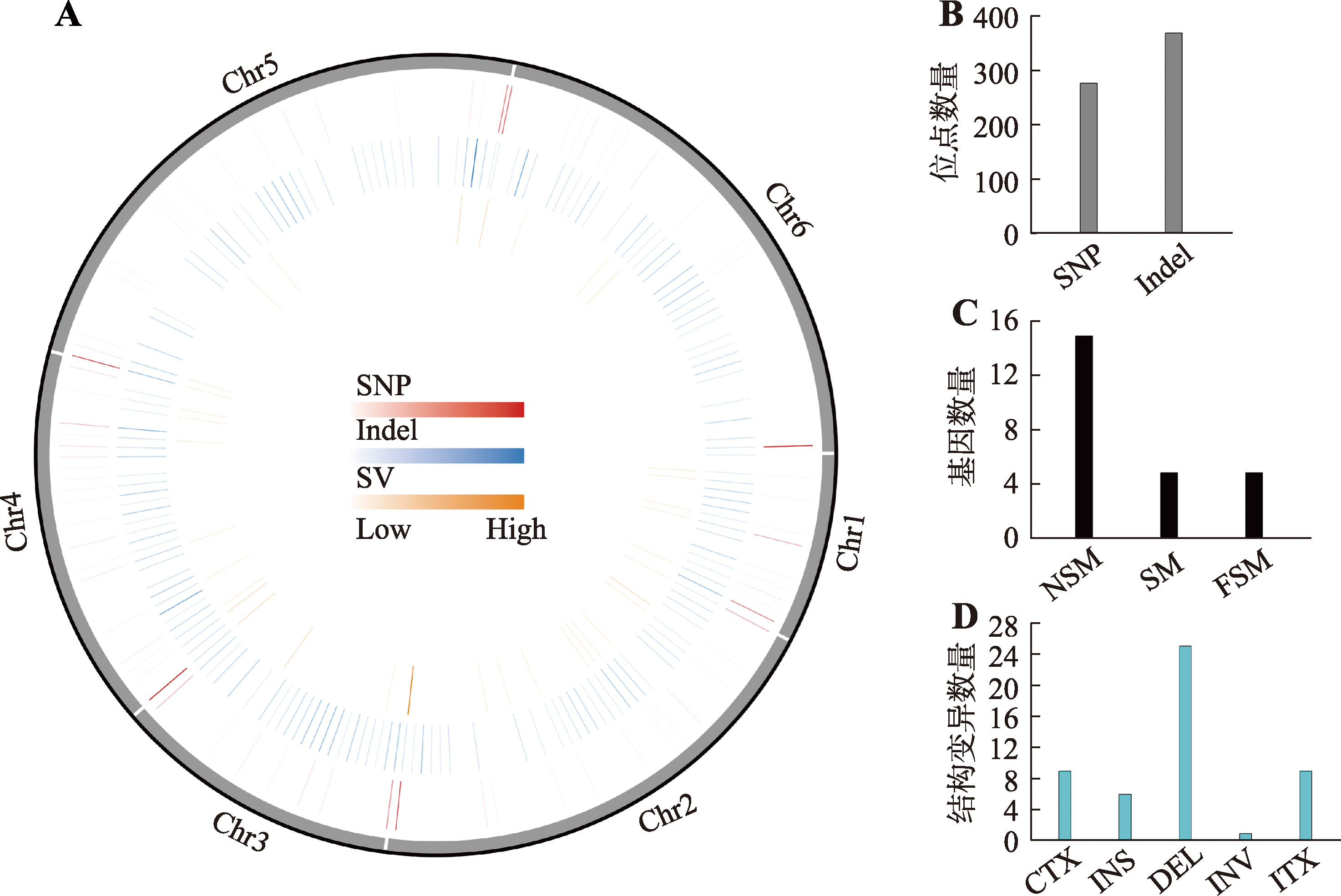
Table 4
SNP和INDEL突变所引起的蛋白编码序列变化"
| 序列号 | 功能 | 突变类型 | 突变位点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| VBB85012.1 | Scaffold protein | 非同义突变 | E1378G |
| RDW32605.1 | Putative methyltransferase | 非同义突变 | L11P |
| VBB85253.1 | Chitin transglycosylase | 非同义突变 | F308S |
| VBB85575.1 | Histone deacetylation protein Rxt3 | 非同义突变 | P230H |
| VBB85808.1 | Hypothetical protein | 非同义突变 | I609N |
| RDW34848.1 | Aspartate/glutamate/uridylate kinase | 非同义突变 | S502P |
| RDW40799.1 | LsmAD domain-domain-containing protein | 非同义突变 | R19G |
| RDW36538.1 | Cytochrome c/c1 heme-lyase | 非同义突变 | S50P |
| RDW34205.1 | Hypothetical protein B0I72DRAFT_135086 | 非同义突变 | L148I |
| VBB88378.1 | Vacuolar alpha mannosidase | 非同义突变 | R1042C |
| VBB88398.1 | Extracellular chitinase | 非同义突变 | L564P |
| VBB79189.1 | Disulfide isomerase precursor | 非同义突变 | S126P |
| SEI34914.1 | YALIA101S05e13674g1_1 | 非同义突变 | F64S |
| VBB87964.1 | Histone transcription regulator 3 | 非同义突变 | F367S |
| RDW50006.1 | Hypothetical protein B0I75DRAFT_142202 | 非同义突变 | P185A |
| SEI35917.1 | YALIA101S09e01662g1_1 | 移码变异 | 基因序列764位插入碱基T |
| RMI98785.1 | Hypothetical protein | 移码变异 | 基因序列1092位插入碱基T |
| SEI32238.1 | Protein kinases | 移码变异 | 基因序列1200位插入碱基A |
| CAG78388.1 | YALI0F18458p | 移码变异 | 基因序列564位插入碱基C |
| VBB88313.1 | Hypothetical protein | 移码变异 | 基因序列3030位A碱基变G碱基 |
| [1] | Liang PX, Cao MF, Li J, Wang QH, Dai ZJ. Expanding sugar alcohol industry: microbial production of sugar alcohols and associated chemocatalytic derivatives. Biotechnol Adv, 2023, 64: 108105. |
| [2] | Liu FM, Zhao XQ, Sha RY, Xia K, Huang J. Advances in microbial production of erythritol. Chin J Bioprocess Eng, 2022, 20(2): 195-205. |
| 刘芳美, 赵学群, 沙如意, 夏凯, 黄俊. 赤藓糖醇微生物合成研究进展. 生物加工过程, 2022, 20(2): 195-205. | |
| [3] | Erian AM, Sauer M. Utilizing yeasts for the conversion of renewable feedstocks to sugar alcohols-a review. Bioresour Technol, 2022, 346: 126296. |
| [4] | Daza-Serna L, Serna-Loaiza S, Masi A, Mach RL, Mach-Aigner AR, Friedl A. From the culture broth to the erythritol crystals: an opportunity for circular economy. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol, 2021, 105(11): 4467-4486. |
| [5] | Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology. Scientific consensus on erythritol. J Chin Inst Food Sci Technol, 2022, 22(12): 405-412. |
| 中国食品科学技术学会. 赤藓糖醇的科学共识. 中国食品学报, 2022, 22(12): 405-412. | |
| [6] | Liu XY, Yu XJ, He AY, Xia J, He JL, Deng YF, Xu N, Qiu ZY, Wang XY, Zhao PS. One-pot fermentation for erythritol production from distillers grains by the co-cultivation of Yarrowia lipolytica and Trichoderma reesei. Bioresour Technol, 2022, 351: 127053. |
| [7] | Zhang Y, Xu S, Wang N, Chi P, Zhang XY, Cheng HR. Construction and characterization of Yarrowia lipolytica strain with reduced foaming ability. Acta Microbiol Sin, 2022, 62(11): 4165-4175. |
| 张悦, 徐硕, 王楠, 池萍, 张馨月, 程海荣. 发酵产泡性能降低的解脂耶氏酵母菌株的获得及其评价. 微生物学报, 2022, 62(11): 4165-4175. | |
| [8] | Zhang L, Nie MY, Liu F, Chen J, Wei LJ, Hua Q. Multiple gene integration to promote erythritol production on glycerol in Yarrowia lipolytica. Biotechnol Lett, 2021, 43(7): 1277-1287. |
| [9] | Mirończuk AM, Biegalska A, Dobrowolski A. Functional overexpression of genes involved in erythritol synthesis in the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Biotechnol Biofuels, 2017, 10: 77. |
| [10] | Liang PX, Li J, Wang QH, Dai ZJ. Enhancing the thermotolerance and erythritol production of Yarrowia lipolytica by introducing heat-resistant devices. Front Bioeng Biotechnol, 2023, 11: 1108653. |
| [11] | Wang N, Chi P, Zou YW, Xu YR, Xu S, Bilal M, Fickers P, Cheng HR. Metabolic engineering of Yarrowia lipolytica for thermoresistance and enhanced erythritol productivity. Biotechnol Biofuels, 2020, 13: 176. |
| [12] | Mirończuk AM, Rakicka M, Biegalska A, Rymowicz W, Dobrowolski A. A two-stage fermentation process of erythritol production by yeast Y. lipolytica from molasses and glycerol. Bioresour Technol, 2015, 198: 445-455. |
| [13] | Qiu XL, Xu P, Zhao XR, Du GC, Zhang J, Li JH. Combining genetically-encoded biosensors with high throughput strain screening to maximize erythritol production in Yarrowia lipolytica. Metab Eng, 2020, 60: 66-76. |
| [14] | Liu XY, Yu XJ, Lv JS, Xu JX, Xia J, Wu Z, Zhang T, Deng YF. A cost-effective process for the coproduction of erythritol and lipase with Yarrowia lipolytica M53 from waste cooking oil. Food Bioprod Process, 2017, 103: 86-94. |
| [15] | Ghezelbash GR, Nahvi I, Emamzadeh R. Improvement of erythrose reductase activity, deletion of by-products and statistical media optimization for enhanced erythritol production from Yarrowia lipolytica mutant 49. Curr Microbiol, 2014, 69(2): 149-157 |
| [16] | Song B, Li XF, Shi ZY, Li CT, Fu YP, Li Y. Breeding of new Pleurotus ostreatus strain by mutation with60Co-γ irradiation. Acta Microbiol Sin, 2019, 59(11): 2155-2164. |
| 宋冰, 李雪飞, 史泽宇, 李长田, 付永平, 李玉. 钴60诱变选育平菇新菌株的研究. 微生物学报, 2019, 59(11): 2155-2164. | |
| [17] | Liu FM, Xia K, Peng YT, Zhao XQ, Sha RY, Huang J. Breeding of Yarrowia lipolytica strains with improved erythritol production by combined mutation and optimization of fermentation process. J Nucl Agric Sci, 2023, 37(5): 907-916. |
| 刘芳美, 夏凯, 彭艳婷, 赵学群, 沙如意, 黄俊. 复合诱变选育高产赤藓糖醇解脂亚罗酵母及其发酵工艺优化. 核农学报, 2023, 37(5): 907-916. | |
| [18] | Feng JY, He JK, Sun JY, Fu XZ, Yuan JA, Guo HP. Genome sequencing and comparative genome analysis of Pseudomonas boreopolis GO2, a strain producing bioflocculant with lignocellulosic biomass. Acta Microbiol Sin, 2023, 63(2): 786-804. |
| 冯嘉茵, 何继堃, 孙嘉怡, 符学志, 袁佳骜, 郭海朋. 利用木质纤维素类生物质产微生物絮凝剂Pseudomonas boreopolis GO2的全基因组测序及比较基因组学分析. 微生物学报, 2023, 63(2): 786-804. | |
| [19] | Xia K, Han CC, Xu J, Liang XL. Toxin-antitoxin HicAB regulates the formation of persister cells responsible for the acid stress resistance in Acetobacter pasteurianus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol, 2021, 105(2): 725-739. |
| [20] | Liu XY, Yu XJ, Xia J, Lv JS, Xu JX, Dai BL, Xu XQ, Xu JM. Erythritol production by Yarrowia lipolytica from okara pretreated with the in-house enzyme pools of fungi. Bioresour Technol, 2017, 244(Pt 1): 1089-1095. |
| [21] | Walker C, Dien B, Giannone RJ, Slininger P, Thompson SR, Trinh CT. Exploring proteomes of robust Yarrowia lipolytica isolates cultivated in biomass hydrolysate reveals key processes impacting mixed sugar utilization, lipid accumulation, and degradation. mSystems, 2021, 6(4): e0044321. |
| [22] | Liu LQ, Alper HS. Draft genome sequence of the oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica PO1f, a commonly used metabolic engineering host. Genome Announc, 2014, 2(4): e00652-14. |
| [23] | Park YK, Ledesma-Amaro R. What makes Yarrowia lipolytica well suited for industry? Trends Biotechnol, 2023, 41(2): 242-254. |
| [24] | Silva JP, Ticona ARP, Hamann PRV, Quirino BF, Noronha EF. Deconstruction of lignin: from enzymes to microorganisms. Molecules, 2021, 26(8): 2299. |
| [25] | Celińska E, Nicaud JM, Białas W. Hydrolytic secretome engineering in Yarrowia lipolytica for consolidated bioprocessing on polysaccharide resources: review on starch, cellulose, xylan, and inulin. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol, 2021, 105(3): 975-989. |
| [26] | Ryu S, Hipp J, Trinh CT. Activating and elucidating metabolism of complex sugars in Yarrowia lipolytica. Appl Environ Microbiol, 2015, 82(4): 1334-1345. |
| [27] | Moreno AD, Ibarra D, Fernández JL, Ballesteros M.Different laccase detoxification strategies for ethanol production from lignocellulosic biomass by the thermotolerant yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus CECT 10875. Bioresour Technol, 2012, 106: 101-109. |
| [28] | Sánchez C. Lignocellulosic residues: biodegradation and bioconversion by fungi. Biotechnol Adv, 2009, 27(2): 185-194. |
| [29] | Peng MF, Li PJ, Shan Y, Chen YQ, Yang DJ, Lei LC, Huang ZH, Yu KX. Comparative genome analysis of carbohydrate activity enzymes zymogram of Lactobacillus from Guangxi pickle. Food Ferment Ind, 2021, 47(4): 68-73. |
| 彭明芳, 李培骏, 单杨, 陈玉秋, 杨岱峻, 雷丽嫦, 黄芝辉, 余孔新. 比较基因组揭示广西酸菜乳杆菌碳水化合物活性酶谱. 食品与发酵工业, 2021, 47(4): 68-73. | |
| [30] | Lazar Z, Neuvéglise C, Rossignol T, Devillers H, Morin N, Robak M, Nicaud JM, Crutz-Le Coq AM. Characterization of hexose transporters in Yarrowia lipolytica reveals new groups of sugar porters involved in yeast growth. Fungal Genet Biol, 2017, 100: 1-12. |
| [31] | Hapeta P, Szczepańska P, Witkowski T, Nicaud JM, Crutz-Le Coq AM, Lazar Z. The Role of hexokinase and hexose transporters in preferential use of glucose over fructose and downstream metabolic pathways in the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(17): 9282. |
| [32] | Cheng HL, Wang SQ, Bilal M, Ge XM, Zhang C, Fickers P, Cheng HR. Identification, characterization of two NADPH-dependent erythrose reductases in the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica and improvement of erythritol productivity using metabolic engineering. Microb Cell Fact, 2018, 17(1): 133. |
| [33] | Qiu XL, Gu Y, Du GC, Zhang J, Xu P, Li JH. Conferring thermotolerant phenotype to wild-type Yarrowia lipolytica improves cell growth and erythritol production. Biotechnol Bioeng, 2021, 118(8): 3117-3127. |
| [34] | Yang LB, Zhan XB, Zheng ZY, Wu JR, Gao MJ, Lin CC. A novel osmotic pressure control fed-batch fermentation strategy for improvement of erythritol production by Yarrowia lipolytica from glycerol. Bioresour Technol, 2014, 151: 120-127. |
| [35] | Dickson RC, Sumanasekera C, Lester RL. Functions and metabolism of sphingolipids in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Prog Lipid Res, 2006, 45(6): 447-465. |
| [36] | Caspeta L, Nielsen J. Thermotolerant yeast strains adapted by laboratory evolution show trade-off at ancestral temperatures and preadaptation to other stresses. mBio, 2015, 6(4): e00431. |
| [37] | Li B, Liu N, Zhao XB. Response mechanisms of Saccharomyces cerevisiae to the stress factors present in lignocellulose hydrolysate and strategies for constructing robust strains. Biotechnol Biofuels Bioprod, 2022, 15(1): 28. |
| [38] | Caspeta L, Chen Y, Ghiaci P, Feizi A, Buskov S, Hallström BM, Petranovic D, Nielsen J. Altered sterol composition renders yeast thermotolerant. Science, 2014, 346(6205): 75-78. |
| [1] | 彭威, 冯蒙洁, 陈皓, 韩宝瑜. 双翅目昆虫基因组研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2020, 42(11): 1093-1109. |
| [2] | 张秀泉,王建,熊符,吕伟标,周远青,杨少民,张玉婷,田小燕,连蔚,徐湘民. 染色体10q24.31片段重复导致先天性缺指/缺趾畸形的一个家系致病机理分析[J]. 遗传, 2019, 41(8): 716-724. |
| [3] | 王一帆,李臻,潘教文,李颖秀,王庆国,管延安,刘炜. 谷子SiRLK35基因克隆及功能分析[J]. 遗传, 2017, 39(5): 413-422. |
| [4] | 李雪娟, 黄原, 雷富民. 山鹧鸪属鸟类线粒体基因组的比较及系统发育研究[J]. 遗传, 2014, 36(9): 912-920. |
| [5] | 冯俊,李光,王义权. 后生动物非编码保守元件[J]. 遗传, 2013, 35(1): 35-44. |
| [6] | 石雅丽,张锐,林芹,郭三堆. 植物体细胞胚胎发生受体类蛋白激酶的生物学功能[J]. 遗传, 2012, 34(5): 551-559. |
| [7] | 杨虹,马月辉,李蓓,芒来. 马基因组研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2010, 32(3): 211-218. |
| [8] | 潘增祥,许丹,张金璧,林飞,吴宝江,刘红林 . 基于直向同源序列的比较基因组学研究[J]. 遗传, 2009, 31(5): 457-457―463. |
| [9] | 李超波,胡丽丽,王振东,钟淑琦,雷蕾. 小鼠胚胎致密化起始的调控机制[J]. 遗传, 2009, 31(12): 1177-1184. |
| [10] | 田靖,赵志虎,陈惠鹏. 人类基因组中的保守非编码元件[J]. 遗传, 2009, 31(11): 1067-1076. |
| [11] | 陈红霖,王义琴,储成才,李平. 植物非寄主抗性研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2008, 30(8): 977-982. |
| [12] | 魏宗波,苗向阳,杨鸣琦,罗绪刚. MnSOD基因表达调控的研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2008, 30(7): 831-837. |
| [13] | 侯妍妍,应晓敏,李伍举. microRNA计算发现方法的研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2008, 30(6): 687-696. |
| [14] | 李小波,陈俭,吕炳建,来茂德. 应用CGH数据和树模型探索癌症的发病机理[J]. 遗传, 2008, 30(4): 407-412. |
| [15] | 王源秀,徐立安,黄敏仁,许远. 林木比较基因组学研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2007, 29(10): 1199-1199―1206. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||

www.chinagene.cn
备案号:京ICP备09063187号-4
总访问:,今日访问:,当前在线:
