遗传 ›› 2022, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (7): 567-580.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.22-063
收稿日期:2022-03-08
修回日期:2022-06-07
出版日期:2022-07-20
发布日期:2022-06-21
通讯作者:
周明
E-mail:21907017@zju.edu.cn;mingzhou@zju.edu.cn
作者简介:许梦萱,在读硕士研究生,专业方向:植物学。E-mail: 基金资助:Received:2022-03-08
Revised:2022-06-07
Online:2022-07-20
Published:2022-06-21
Contact:
Zhou Ming
E-mail:21907017@zju.edu.cn;mingzhou@zju.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
DNA甲基化是一类稳定可遗传的表观遗传修饰,在调控基因表达、沉默转座子和维持基因组稳定性等方面发挥重要作用。植物中,DNA从头甲基化通过RNA指导的DNA甲基化(RNA-directed DNA methylation, RdDM)途径建立。植物特有的DNA依赖的RNA聚合酶IV (DNA-dependent RNA polymerase IV, Pol IV)是RdDM途径核心蛋白,转录产生非编码RNA,通过RdDM途径引导从头建立DNA甲基化,进而调控植物基因表达和生长发育。Pol IV行使功能受多个蛋白调控:组蛋白阅读器SHH1 (SAWADEE homeodomain homolog 1)识别H3K9甲基化引导Pol IV到基因组特定位点;染色质重塑因子CLSY (CLASSY)蛋白家族协助Pol IV识别靶位点;RNA依赖的RNA聚合酶2 (RNA-dependent RNA polymerase 2, RDR2)将Pol IV转录产生的单链RNA转换成双链RNA。本文总结了Pol IV及其调控蛋白调控植物DNA甲基化和发育的研究进展,以期为DNA甲基化研究和农作物育种提供参考。
许梦萱, 周明. 植物RNA聚合酶IV调控DNA甲基化和发育的研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2022, 44(7): 567-580.
Mengxuan Xu, Ming Zhou. Advances of RNA polymerase IV in controlling DNA methylation and development in plants[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(7): 567-580.
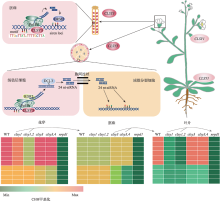
图2
CLSY家族调控拟南芥组织和细胞特异性DNA甲基化模式 以拟南芥为例,CLSY1主要在成熟的叶片和莲座叶中表达,CLSY3主要在胚珠和绒毡层细胞中特异性表达,CLSY2和CLSY4的表达量较低,图中未显示。胚珠中,CLSY3招募Pol IV与一个特定的motif相关,且可以调控siren loci的甲基化。绒毡层细胞中,CLSY3招募Pol IV产生的24 nt-siRNAs通过胞间连丝进入减数分裂细胞,调控精细胞中24 nt-siRNAs水平和DNA甲基化状态,控制拟南芥跨代遗传信息传递。不同的组织中,CLSY家族基因调控拟南芥组织特异性DNA甲基化模式。CLSY家族基因的DNA甲基化模式示意图根据文献[55]修改绘制。绒毡层中CLSY3的表达根据文献[62]修改绘制。"
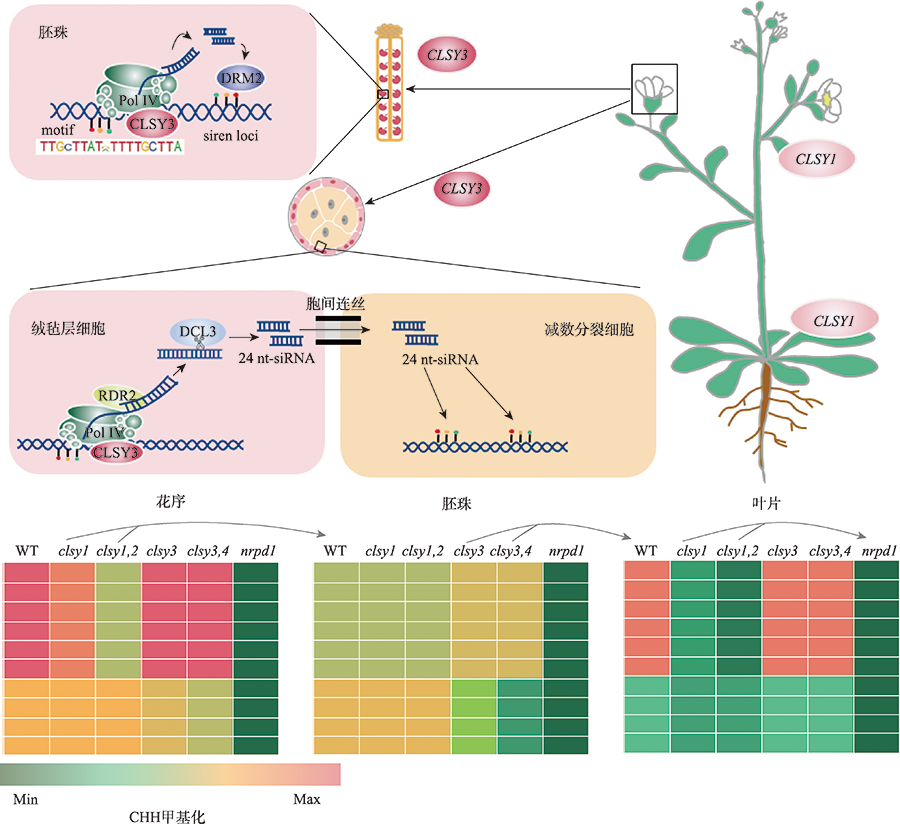
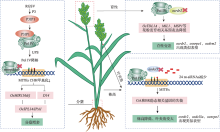
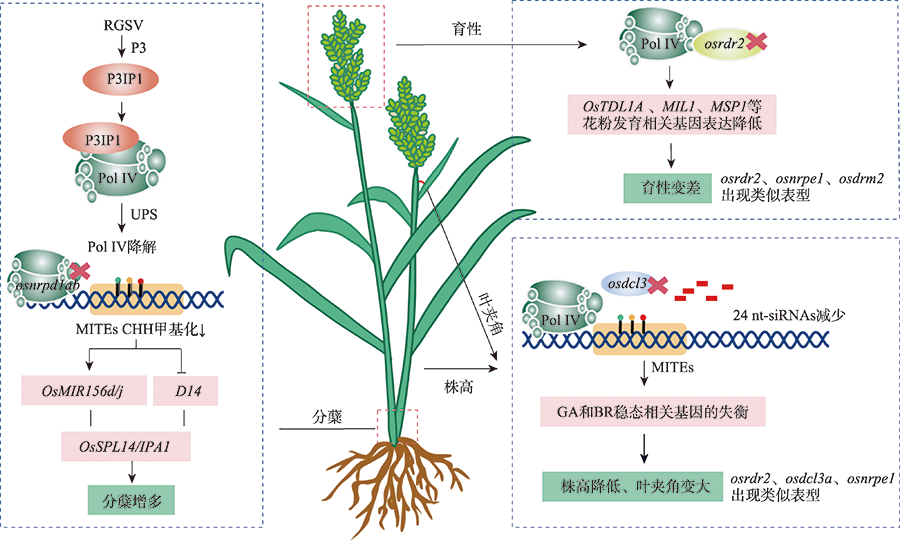
图3
Pol IV调控水稻重要农艺性状 在水稻中,水稻草状矮化病毒(RGSV)P3蛋白可以诱导P3IP1特异性高表达,增强OsNRPD1a的泛素化,通过泛素蛋白酶体系统(UPS)依赖性降解。水稻OsNRPD1a和OsNRPD1b表达的降低导致微型反向重复转座元件(MITE)CHH甲基化显著降低,从而影响调控水稻分蘖的关键农艺学重要基因(OsMIR156d/j和D14)的表达,进而导致水稻分蘖增多。在osrdr2突变体中,Pol IV转录产生的ssRNA无法复制成dsRNA,进而导致OsTDL1A、MIL1、MSP1等花粉发育相关基因表达降低,水稻育性变差。在osdcl3突变体中,24 nt-siRNAs数量显著变少,同时GA和BR稳态相关基因的失衡,水稻植株出现株高降低和叶夹角变大的表型。"
| [1] |
Law JA, Jacobsen SE. Establishing, maintaining and modifying DNA methylation patterns in plants and animals. Nat Rev Genet, 2010, 11(3):204-220.
doi: 10.1038/nrg2719 |
| [2] |
He XJ, Chen TP, Zhu JK. Regulation and function of DNA methylation in plants and animals. Cell Res, 2011, 21(3):442-465.
doi: 10.1038/cr.2011.23 |
| [3] |
Elhamamsy AR. DNA methylation dynamics in plants and mammals: overview of regulation and dysregulation. Cell Biochem Funct, 2016, 34(5):289-298.
doi: 10.1002/cbf.3183 pmid: 27003927 |
| [4] | Wang RX, Xu JH. Genomic DNA methylation and histone methylation. Hereditas (Beijing), 2014, 36(3):191-199. |
| 王瑞娴, 徐建红. 基因组DNA甲基化及组蛋白甲基化. 遗传, 2014, 36(3):191-199. | |
| [5] |
Zhang HM, Lang ZB, Zhu JK. Dynamics and function of DNA methylation in plants. Nat Rev Mol Cell Bio, 2018, 19(8):489-506.
doi: 10.1038/s41580-018-0016-z |
| [6] |
Li E, Bestor TH, Jaenisch R. Targeted mutation of the DNA methyltransferase gene results in embryonic lethality. Cell, 1992, 69(6):915-926.
doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90611-f pmid: 1606615 |
| [7] |
Robertson KD. DNA methylation and human disease. Nat Rev Genet, 2005, 6(8):597-610.
pmid: 16136652 |
| [8] |
Cortellino S, Xu JF, Sannai M, Moore R, Caretti E, Cigliano A, Le Coz M, Devarajan K, Wessels A, Soprano D, Abramowitz LK, Bartolomei MS, Rambow F, Bassi MR, Bruno T, Fanciulli M, Renner C, Klein-Szanto AJ, Matsumoto Y, Kobi D, Davidson I, Alberti C, Larue L, Bellacosa A. Thymine DNA glycosylase is essential for active DNA demethylation by linked deamination-base excision repair. Cell, 2011, 146(1):67-79.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.06.020 pmid: 21722948 |
| [9] |
Finnegan EJ, Peacock WJ, Dennis ES. Reduced DNA methylation in Arabidopsis thaliana results in abnormal plant development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1996, 93(16):8449-8454.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.16.8449 |
| [10] |
Lindroth AM, Cao XF, Jackson JP, Zilberman D, Mccallum CM, Henikoff S, Jacobsen SE. Requirement of CHROMOMETHYLASE3 for maintenance of CpXpG methylation. Science, 2001, 292(5524):2077-2080.
pmid: 11349138 |
| [11] |
Saze H, Scheid OM, Paszkowski J. Maintenance of CpG methylation is essential for epigenetic inheritance during plant gametogenesis. Nat Genet, 2003, 34(1):65-69.
doi: 10.1038/ng1138 |
| [12] |
Stroud H, Greenberg MVC, Feng SH, Bernatavichute YV, Jacobsen SE. Comprehensive analysis of silencing mutants reveals complex regulation of the Arabidopsis methylome. Cell, 2013, 152(1-2):352-364.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.10.054 pmid: 23313553 |
| [13] |
Stroud H, Do T, Du JM, Zhong XH, Feng SH, Johnson L, Patel DJ, Jacobsen SE. Non-CG methylation patterns shape the epigenetic landscape in Arabidopsis. Nat Struct Mol Biol, 2014, 21(1):64-72.
doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2735 pmid: 24336224 |
| [14] |
Cao XF, Jacobsen SE. Role of the Arabidopsis DRM methyltransferases in de novo DNA methylation and gene silencing. Curr Biol, 2002, 12(13):1138-1144.
doi: 10.1016/S0960-9822(02)00925-9 |
| [15] |
Gong ZZ, Morales-Ruiz T, Ariza RR, Roldán-Arjona T, David L, Zhu JK. ROS1, a repressor of transcriptional gene silencing in Arabidopsis, encodes a DNA glycosylase/lyase. Cell, 2002, 111(6):803-814.
doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(02)01133-9 |
| [16] |
Ortega-Galisteo AP, Morales-Ruiz T, Ariza RR, Roldán- Arjona T. Arabidopsis DEMETER-LIKE proteins DML2 and DML3 are required for appropriate distribution of DNA methylation marks. Plant Mol Biol, 2008, 67(6):671-681.
doi: 10.1007/s11103-008-9346-0 pmid: 18493721 |
| [17] |
Tang K, Lang ZB, Zhang H, Zhu JK. The DNA demethylase ROS1 targets genomic regions with distinct chromatin modifications. Nat Plants, 2016, 2(11):16169.
doi: 10.1038/nplants.2016.169 pmid: 27797352 |
| [18] |
Liu R, Lang ZB. The mechanism and function of active DNA demethylation in plants. J Integr Plant Biol, 2020, 62(1):148-159.
doi: 10.1111/jipb.12879 |
| [19] | Kima S, Park J, Lee J, Lee KK, Park O, Choi H, Seo PJ, Cho H, Frost JM, Fischer RL, Choi Y, Ohme-Takagi M. The DME demethylase regulates sporophyte gene expression, cell proliferation, differentiation, and meristem resurrection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2021, 118(29): e2026806118. |
| [20] |
Matzke MA, Mosher RA. RNA-directed DNA methylation: an epigenetic pathway of increasing complexity. Nat Rev Genet, 2014, 15(6):394-408.
doi: 10.1038/nrg3683 |
| [21] |
Napoli C, Lemieux C, Jorgensen R. Introduction of a chimeric chalcone synthase gene into petunia results in reversible co-suppression of homologous genes in trans. Plant Cell, 1990, 2(4):279-289.
doi: 10.2307/3869076 |
| [22] |
van der Krol AR, Mur LA, Beld M, Mol JN, Stuitje AR. Flavonoid genes in petunia: addition of a limited number of gene copies may lead to a suppression of gene expression. Plant Cell, 1990, 2(4):291-299.
pmid: 2152117 |
| [23] |
Herr AJ, Jensen MB, Dalmay T, Baulcombe DC. RNA polymerase IV directs silencing of endogenous DNA. Science, 2005, 308(5718):118-120.
pmid: 15692015 |
| [24] |
Wierzbicki AT, Haag JR, Pikaard CS. Noncoding transcription by RNA polymerase Pol IVb/Pol V mediates transcriptional silencing of overlapping and adjacent genes. Cell, 2008, 135(4):635-648.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.09.035 pmid: 19013275 |
| [25] |
Zhai JX, Bischof S, Wang HF, Feng SH, Lee T, Teng C, Chen XY, Park SY, Liu LS, Gallego-Bartolome J, Liu WL, Henderson IR, Meyers BC, Ausin I, Jacobsen SE. A one precursor one siRNA model for Pol IV-dependent siRNA biogenesis. Cell, 2015, 163(2):445-455.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.09.032 |
| [26] |
Blevins T, Podicheti R, Mishra V, Marasco M, Wang J, Rusch D, Tang H, Pikaard CS. Identification of Pol IV and RDR2-dependent precursors of 24 nt siRNAs guiding de novo DNA methylation in Arabidopsis. Elife, 2015, 4:e09591.
doi: 10.7554/eLife.09591 |
| [27] |
Li SF, Vandivier LE, Tu B, Gao L, Won SY, Li SB, Zheng BL, Gregory BD, Chen XM. Detection of Pol IV/RDR2-dependent transcripts at the genomic scale in Arabidopsis reveals features and regulation of siRNA biogenesis. Genome Res, 2015, 25(2):235-245.
doi: 10.1101/gr.182238.114 |
| [28] |
Huang K, Wu XX, Fang CL, Xu ZG, Zhang HW, Gao J, Zhou CM, You LL, Gu ZX, Mu WH, Feng Y, Wang JW, Zhang Y. Pol IV and RDR2: a two-RNA-polymerase machine that produces double-stranded RNA. Science, 2021, 374(6575):1579-1586.
doi: 10.1126/science.abj9184 pmid: 34941388 |
| [29] |
Singh J, Mishra V, Wang F, Huang H, Pikaard CS. Reaction mechanisms of Pol IV, RDR2, and DCL3 drive RNA channeling in the siRNA-directed DNA methylation pathway. Mol Cell, 2019, 75(3):576-589.
doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.07.008 |
| [30] |
Yang ZY, Ebright YW, Yu B, Chen XM. HEN1 recognizes 21-24 nt small RNA duplexes and deposits a methyl group onto the 2' OH of the 3' terminal nucleotide. Nucleic Acids Res, 2006, 34(2):667-675.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkj474 |
| [31] |
Havecker ER, Wallbridge LM, Hardcastle TJ, Bush MS, Kelly KA, Dunn RM, Schwach F, Doonan JH, Baulcombe DC. The Arabidopsis RNA-directed DNA methylation argonautes functionally diverge based on their expression and interaction with target loci. Plant Cell, 2010, 22(2):321-334.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.109.072199 |
| [32] |
Duan CG, Zhang HM, Tang K, Zhu XH, Qian WQ, Hou Y, Wang BS, Lang ZB, Zhao Y, Wang XG, Wang PC, Zhou JP, Liang GM, Liu N, Wang CG, Zhu JK. Specific but interdependent functions for Arabidopsis AGO4 and AGO6 in RNA-directed DNA methylation. EMBO J, 2015, 34(5):581-592.
doi: 10.15252/embj.201489453 |
| [33] |
Johnson LM, Du JM, Hale CJ, Bischof S, Feng SH, Chodavarapu RK, Zhong XH, Marson G, Pellegrini M, Segal DJ, Patel DJ, Jacobsen SE. SRA- and SET-domain- containing proteins link RNA polymerase V occupancy to DNA methylation. Nature, 2014, 507(7490):124-128.
doi: 10.1038/nature12931 |
| [34] |
Wongpalee SP, Liu SH, Gallego-Bartolomé J, Leitner A, Aebersold R, Liu WL, Yen L, Nohales MA, Kuo PH, Vashisht AA, Wohlschlegel JA, Feng SH, Kay SA, Zhou ZH, Jacobsen SE. CryoEM structures of Arabidopsis DDR complexes involved in RNA-directed DNA methylation. Nat Commun, 2019, 10(1):3916.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11759-9 pmid: 31477705 |
| [35] |
El-Shami M, Pontier D, Lahmy S, Braun L, Picart C, Vega D, Hakimi MA, Jacobsen SE, Cooke R, Lagrange T. Reiterated WG/GW motifs form functionally and evolutionarily conserved ARGONAUTE-binding platforms in RNAi-related components. Gene Dev, 2007, 21(20):2539-2544.
doi: 10.1101/gad.451207 pmid: 17938239 |
| [36] |
Zhou M, Law JA. RNA Pol IV and V in gene silencing: Rebel polymerases evolving away from Pol II's rules. Curr Opin Plant Biol, 2015, 27:154-164.
doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2015.07.005 |
| [37] |
Ream TS, Haag JR, Wierzbicki AT, Nicora CD, Norbeck AD, Zhu JK, Hagen G, Guilfoyle TJ, Pasa-Tolić L, Pikaard CS. Subunit compositions of the RNA-silencing enzymes Pol IV and Pol V reveal their origins as specialized forms of RNA polymerase II. Mol Cell, 2009, 33(2):192-203.
doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.12.015 |
| [38] |
Luo J, Hall BD. A multistep process gave rise to RNA polymerase IV of land plants. J Mol Evol, 2007, 64(1):101-112.
doi: 10.1007/s00239-006-0093-z |
| [39] |
Huang Y, Kendall T, Forsythe ES, Dorantes-Acosta A, Li SF, Caballero-Pérez J, Chen XM, Arteaga-Vázquez M, Beilstein MA, Mosher RA. Ancient origin and recent innovations of RNA polymerase IV and V. Mol Biol Evol, 2015, 32(7):1788-1799.
doi: 10.1093/molbev/msv060 pmid: 25767205 |
| [40] |
Wang YQ, Ma H. Step-wise and lineage-specific diversification of plant RNA polymerase genes and origin of the largest plant-specific subunits. New Phytol, 2015, 207(4):1198-1212.
doi: 10.1111/nph.13432 |
| [41] |
Zhang XY, Henderson IR, Lu C, Green PJ, Jacobsen SE. Role of RNA polymerase IV in plant small RNA metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2007, 104(11):4536-4541.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0611456104 |
| [42] |
Xu L, Yuan K, Yuan M, Meng XB, Chen M, Wu JG, Li JY, Qi YJ. Regulation of rice tillering by RNA-directed DNA methylation at miniature inverted-repeat transposable elements. Mol Plant, 2020, 13(6):851-863.
doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2020.02.009 |
| [43] | Law JA, Vashisht AA, Wohlschlegel JA, Jacobsen SE. SHH1, a homeodomain protein required for DNA methylation, as well as RDR2, RDM4, and chromatin remodeling factors, associate with RNA Polymerase IV. PLoS Genet, 2011, 7(7): e1002195. |
| [44] |
Law JA, Du JM, Hale CJ, Feng SH, Krajewski K, Palanca AMS, Strahl BD, Patel DJ, Jacobsen SE. Polymerase IV occupancy at RNA-directed DNA methylation sites requires SHH1. Nature, 2013, 498(7454):385-389.
doi: 10.1038/nature12178 |
| [45] |
Zhang H, Ma ZY, Zeng L, Tanaka K, Zhang CJ, Ma J, Bai G, Wang PC, Zhang SW, Liu ZW, Cai T, Tang K, Liu RY, Shi XB, He XJ, Zhu JK. DTF1 is a core component of RNA-directed DNA methylation and may assist in the recruitment of Pol IV. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2013, 110(20):8290-8295.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1300585110 |
| [46] |
Smith LM, Pontes O, Searle I, Yelina N, Yousafzai FK, Herr AJ, Pikaard CS, Baulcombe DC. An SNF2 protein associated with nuclear RNA silencing and the spread of a silencing signal between cells in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell, 2007, 19(5):1507-1521.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.107.051540 pmid: 17526749 |
| [47] |
Kanno T, Mette MF, Kreil DP, Aufsatz W, Matzke M, Matzke AJM. Involvement of putative SNF2 chromatin remodeling protein DRD1 in RNA-directed DNA methylation. Curr Biol, 2004, 14(9):801-805.
doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2004.04.037 |
| [48] |
Hu YF, Zhu N, Wang XM, Yi QQ, Zhu DY, Lai Y, Zhao Y. Analysis of rice Snf2 family proteins and their potential roles in epigenetic regulation. Plant Physiol Bioch, 2013, 70:33-42.
doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2013.05.001 |
| [49] |
Lusser A, Kadonaga JT. Chromatin remodeling by ATP- dependent molecular machines. BioEssays, 2003, 25(12):1192-1200.
doi: 10.1002/bies.10359 |
| [50] |
Mohrmann L, Verrijzer CP. Composition and functional specificity of SWI2/SNF2 class chromatin remodeling complexes. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2005, 1681(2-3):59-73.
pmid: 15627498 |
| [51] |
Clapier CR, Cairns BR. The biology of chromatin remodeling complexes. Annu Rev Biochem, 2009, 78:273-304.
doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.77.062706.153223 pmid: 19355820 |
| [52] |
Hohmann AF, Vakoc CR. A rationale to target the SWI/SNF complex for cancer therapy. Trends Genet, 2014, 30(8):356-363.
doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2014.05.001 pmid: 24932742 |
| [53] |
Yang DL, Zhang GP, Wang LL, Li JW, Xu DC, Di CR, Tang K, Yang L, Zeng L, Miki D, Duan CG, Zhang HM, Zhu JK. Four putative SWI2/SNF2 chromatin remodelers have dual roles in regulating DNA methylation in Arabidopsis. Cell Discov, 2018, 4:55.
doi: 10.1038/s41421-018-0056-8 |
| [54] |
Zhou M, Palanca AMS, Law JA. Locus-specific control of the de novo DNA methylation pathway in Arabidopsis by the CLASSY family. Nat Genet, 2018, 50(6):865-873.
doi: 10.1038/s41588-018-0115-y |
| [55] |
Zhou M, Coruh C, Xu GH, Martins LM, Bourbousse C, Lambolez A, Law JA. The CLASSY family controls tissue-specific DNA methylation patterns in Arabidopsis. Nat Commun, 2022, 13(1):244.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-27690-x |
| [56] |
He XJ, Hsu YF, Zhu SH, Liu HL, Pontes O, Zhu JH, Cui XP, Wang CS, Zhu JK. A conserved transcriptional regulator is required for RNA-directed DNA methylation and plant development. Genes Dev, 2009, 23(23):2717-2722.
doi: 10.1101/gad.1851809 |
| [57] |
Kanno T, Bucher E, Daxinger L, Huettel B, Kreil DP, Breinig F, Lind M, Schmitt MJ, Simon SA, Gurazada SG, Meyers BC, Lorkovic ZJ, Matzke AJM, Matzke M. RNA-directed DNA methylation and plant development require an IWR1-type transcription factor. EMBO Rep, 2010, 11(1):65-71.
doi: 10.1038/embor.2009.246 |
| [58] |
Chan ZL, Wang YP, Cao MJ, Gong YH, Mu ZX, Wang HQ, Hu YL, Deng X, He XJ, Zhu JK. RDM4 modulates cold stress resistance in Arabidopsis partially through the CBF-mediated pathway. New Phytol, 2016, 209(4):1527-1539.
doi: 10.1111/nph.13727 |
| [59] |
Kawakatsu T, Stuart T, Valdes M, Breakfield N, Schmitz RJ, Nery JR, Urich MA, Han XW, Lister R, Benfey PN, Ecker JR. Unique cell-type-specific patterns of DNA methylation in the root meristem. Nat Plants, 2016, 2(5):16058.
doi: 10.1038/nplants.2016.58 pmid: 27243651 |
| [60] |
Kawakatsu T, Nery JR, Castanon R, Ecker JR. Dynamic DNA methylation reconfiguration during seed development and germination. Genome Biol, 2017, 18(1):171.
doi: 10.1186/s13059-017-1251-x pmid: 28911331 |
| [61] |
Narsai R, Gouil Q, Secco D, Srivastava A, Karpievitch YV, Liew LC, Lister R, Lewsey MG, Whelan J. Extensive transcriptomic and epigenomic remodelling occurs during Arabidopsis thaliana germination. Genome Biol, 2017, 18(1):172.
doi: 10.1186/s13059-017-1302-3 pmid: 28911330 |
| [62] | Long JC, Walker J, She WJ, Aldridge B, Gao HB, Deans S, Vickers M, Feng XQ,. Nurse cell-derived small RNAs define paternal epigenetic inheritance in Arabidopsis. Science, 2021, 373(6550): eabh0556. |
| [63] | Hale CJ, Stonaker JL, Gross SM, Hollick JB. A novel snf2 protein maintains trans-generational regulatory states established by paramutation in maize. PLoS Biol, 2007, 5(10):2156-2165. |
| [64] |
Feng Sh, Jacobsen SE, Reik W. Epigenetic reprogramming in plant and animal development. Science, 2010, 330(6004):622-627.
doi: 10.1126/science.1190614 |
| [65] |
Kawashima T, Berger F. Epigenetic reprogramming in plant sexual reproduction. Nat Rev Genet, 2014, 15(9):613-624.
doi: 10.1038/nrg3685 pmid: 25048170 |
| [66] |
Walker J, Gao HB, Zhang JY, Aldridge B, Vickers M, Higgins JD, Feng XQ. Sexual-lineage-specific DNA methylation regulates meiosis in Arabidopsis. Nat Genet, 2018, 50(1):130-137.
doi: 10.1038/s41588-017-0008-5 pmid: 29255257 |
| [67] |
Fei Y, Nyikó T, Molnar A. Non-perfectly matching small RNAs can induce stable and heritable epigenetic modifications and can be used as molecular markers to trace the origin and fate of silencing RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res, 2021, 49(4):1900-1913.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab023 |
| [68] |
Pikaard CS, Haag JR, Ream T, Wierzbicki AT. Roles of RNA polymerase IV in gene silencing. Trends Plant Sci, 2008, 13(7):390-397.
doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2008.04.008 pmid: 18514566 |
| [69] |
Pontier D, Yahubyan G, vega D, Bulski A, Saez-vasquez J, Hakimi MA, Lerbs-Mache S, Colot V, Lagrange T. Reinforcement of silencing at transposons and highly repeated sequences requires the concerted action of two distinct RNA polymerases IV in Arabidopsis. Gene Dev, 2005, 19(17):2030-2040.
doi: 10.1101/gad.348405 |
| [70] |
Initiative AG. Analysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature, 2000, 408(6814):796-815.
doi: 10.1038/35048692 |
| [71] |
Zhang S, Wu XQ, Xie HT, Zhao SS, Wu JG. Multifaceted roles of RNA polymerase IV in plant growth and development. J Exp Bot, 2020, 71(19):5725-5732.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/eraa346 |
| [72] |
Wang ZX, Butel N, Santos-González J, Borges F, Yi J, Martienssen RA, Martinez G, Köhler C. Polymerase IV plays a crucial role in pollen development in Capsella. Plant Cell, 2020, 32(4):950-966.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.19.00938 |
| [73] |
Grover JW, Kendall T, Baten A, Burgess D, Freeling M, King GJ, Mosher RA. Maternal components of RNA-directed DNA methylation are required for seed development in Brassica rapa. Plant J, 2018, 94(4):575-582.
doi: 10.1111/tpj.13910 |
| [74] | Gouil Q, Baulcombe DC. DNA Methylation signatures of the plant chromomethyl transferases. PLoS Genet, 2016, 12(12): e1006526. |
| [75] |
Zhang C, Wei Y, Xu L, Wu KC, Yang L, Shi CN, Yang GY, Chen D, Yu FF, Xie Q, Ding SW, Wu JG. A Bunyavirus-inducible ubiquitin ligase targets RNA polymerase IV for degradation during viral pathogenesis in rice. Mol Plant, 2020, 13(6):836-850.
doi: S1674-2052(20)30040-X pmid: 32087369 |
| [76] |
Parkinson SE, Gross SM, Hollick JB. Maize sex determination and abaxial leaf fates are canalized by a factor that maintains repressed epigenetic states. Dev Biol, 2007, 308(2):462-473.
pmid: 17612519 |
| [77] |
Forestan C, Farinati S, Aiese Cigliano R, Lunardon A, Sanseverino W, Varotto S. Maize RNA Pol IV affects the expression of genes with nearby TE insertions and has a genome-wide repressive impact on transcription. BMC Plant Biol, 2017, 17(1):161.
doi: 10.1186/s12870-017-1108-1 |
| [78] |
Hollick JB, Kermicle JL, Parkinson SE. Rmr6 maintains meiotic inheritance of paramutant states in Zea mays. Genetics, 2005, 171(2):725-740.
pmid: 16020780 |
| [79] |
Erhard KF Jr, Stonaker JL, Parkinson SE, Lim JP, Hale CJ, Hollick JB. RNA polymerase IV functions in paramutation in Zea mays. Science, 2009, 323(5918):1201-1205.
doi: 10.1126/science.1164508 pmid: 19251626 |
| [80] |
Hollick JB. Paramutation and related phenomena in diverse species. Nat Rev Genet, 2017, 18(1):5-23.
doi: 10.1038/nrg.2016.115 pmid: 27748375 |
| [81] |
Wang LL, Zheng KZ, Zeng LJ, Xu DC, Zhu TX, Yin YM, Zhan HD, Wu YF, Yang DL. Reinforcement of CHH methylation through RNA-directed DNA methylation ensures sexual reproduction in rice. Plant Physiol, 2022, 188(2):1189-1209.
doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiab531 |
| [82] |
Wei LY, Gu LF, Song XW, Cui XK, Lu ZK, Zhou M, Wang LL, Hu FY, Zhai JX, Meyers BC, Cao XF. Dicer-like 3 produces transposable element-associated 24-nt siRNAs that control agricultural traits in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2014, 111(10):3877-3882.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1318131111 |
| [83] |
Deng YW, Zhai KR, Xie Z, Yang DY, Zhu XD, Liu JZ, Wang X, Qin P, Yang YZ, Zhang GM, Li Q, Zhang JF, Wu SQ, Milazzo J, Mao B, Wang E, Xie H, Tharreau D, He ZH. Epigenetic regulation of antagonistic receptors confers rice blast resistance with yield balance. Science, 2017, 355(6328):962-965.
doi: 10.1126/science.aai8898 |
| [84] | Zheng KZ, Wang LL, Zeng LJ, Xu DC, Guo ZX, Gao XQ, Yang DL. The effect of RNA polymerase V on 24-nt siRNA accumulation depends on DNA methylation contexts and histone modifications in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2021, 118(30): e2100709118. |
| [85] |
Moritoh S, Eun C, Ono A, Asao H, Okano Y, Yamaguchi K, Shimatani Z, Koizumi A, Terada R. Targeted disruption of an orthologue of DOMAINS REARRANGED METHYLASE 2, OsDRM2, impairs the growth of rice plants by abnormal DNA methylation. Plant J, 2012, 71(1):85-98.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2012.04974.x |
| [86] | Ghoshal B, Picard CL, Vong B, Feng SH, Jacobsen SE. CRISPR-based targeting of DNA methylation in Arabidopsis thaliana by a bacterial CG-specific DNA methyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2021, 118(23): e2125016118. |
| [87] |
Papikian A, Liu WL, Gallego-Bartolomé J, Jacobsen SE. Site-specific manipulation of Arabidopsis loci using CRISPR-Cas9 SunTag systems. Nat Commun, 2019, 10(1):729.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-08736-7 pmid: 30760722 |
| [88] |
Tang SJ, Yang C, Wang D, Deng X, Cao XF, Song XW. Targeted DNA demethylation produces heritable epialleles in rice. Sci China Life Sci, 2022, 65(4):753-756.
doi: 10.1007/s11427-021-1974-7 |
| [1] | 时文睿, 渠鸿竹, 方向东. 痛风的多组学研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2023, 45(8): 643-657. |
| [2] | 金良, 陈语婕, 陈勇军. 发育性和癫痫性脑病遗传学病因及诊疗的研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2023, 45(7): 553-567. |
| [3] | 何山, 赵健, 宋晓峰. N6-甲基腺苷修饰对女性生殖系统功能的影响[J]. 遗传, 2023, 45(6): 472-487. |
| [4] | 李菲菲, 郝燕敏, 崔敏龙, 朴春兰. 金鱼草RADIALIS-like 1基因克隆与功能研究[J]. 遗传, 2023, 45(6): 526-535. |
| [5] | 邢超凡, 王闽涛, 王磊, 申欣. 两侧对称动物左右不对称发生机制研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2023, 45(6): 488-500. |
| [6] | 王文龙, 张春霞. 哺乳动物卵子与早期胚胎中全转录组poly(A)尾研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2023, 45(4): 273-278. |
| [7] | 栾思楠, 刘乐乐, 周佳圆, 努尔阿斯娅·伊马木, 崔敏龙, 朴春兰. 欧洲千里光花发育相关基因SvGLOBOSA功能研究[J]. 遗传, 2022, 44(6): 521-530. |
| [8] | 张元, 赵语婷, 庄乐南, 贺津. 转录中介体复合物在心血管发育和疾病中的转录调控作用[J]. 遗传, 2022, 44(5): 383-397. |
| [9] | 王孟晓, 何淑君. 神经胶质细胞调控黑腹果蝇生理行为研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2022, 44(4): 300-312. |
| [10] | 王梓川, 张嘉祺, 李磊. 哺乳动物早期胚胎发育的体外研究[J]. 遗传, 2022, 44(4): 269-274. |
| [11] | 曲卉, 柳毅, 陈雅文, 汪晖. 环境因素所致印迹基因改变与子代器官发育[J]. 遗传, 2022, 44(2): 107-116. |
| [12] | 吴丹丹, 李荣, 李晓南, 刘倩琦, 窦莉华. 一例ZMPSTE24基因复合杂合突变导致颅骨下颌骨皮肤发育不全B型的诊断和基因检测分析[J]. 遗传, 2022, 44(12): 1167-1174. |
| [13] | 毛轲, 孟子秋, 张永彪. 神经嵴发育调控及颅面部遗传基础研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2022, 44(12): 1089-1102. |
| [14] | 张祉靖, 乔钰, 孙宇晨, 雷蕾. 表观“阅读器”BET蛋白家族对哺乳动物发育和iPSC重编程的调控[J]. 遗传, 2022, 44(1): 36-45. |
| [15] | 杨恒, 逄越, 李庆伟. 七鳃鳗胆道闭锁过程中胆汁酸耐受机制研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2022, 44(1): 59-67. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||

www.chinagene.cn
备案号:京ICP备09063187号-4
总访问:,今日访问:,当前在线:

