遗传 ›› 2025, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (11): 1256-1268.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.25-117
收稿日期:2025-04-27
修回日期:2025-06-18
出版日期:2025-11-20
发布日期:2025-07-08
通讯作者:
黄志斌,博士,副教授,研究方向:人类疾病斑马鱼动物模型的建立、造血发育以及调控。E-mail: huangzhb1986@scut.edu.cn作者简介:寇涵婧,本科生,专业方向:生物学。E-mail:965143018@qq.com
基金资助:
Hanjing Kou( ), Zhibin Huang(
), Zhibin Huang( ), Wenqing Zhang(
), Wenqing Zhang( ), Qi Chen(
), Qi Chen( )
)
Received:2025-04-27
Revised:2025-06-18
Published:2025-11-20
Online:2025-07-08
Supported by:摘要:
小胶质细胞作为中枢神经系统的固有免疫细胞,可通过吞噬作用有序地清除坏死神经元、细胞碎片及病原体并维持整个神经系统的稳定。吞噬作用是细胞内一系列蛋白协同调控的动态过程,包括捕获货物形成吞噬体、吞噬体成熟以及溶酶体降解等步骤。其中,吞噬体成熟过程依赖V-ATPase为溶酶体持续提供酸化,而V-ATPase的质子转运效率则主要取决于a亚基。在哺乳动物中,V-ATPase a亚基有4种亚型(a1、a2、a3和a4),斑马鱼(Danio rerio)仅有前3种(a1、a2和a3),且它们所靶向的细胞类型和亚细胞器定位具有显著差异。据报道,V-ATPase a3亚基主要定位于破骨细胞的溶酶体并辅助酸化从而促进骨吸收,本实验室前期的研究结果显示V-ATPase a3亚基同样定位于斑马鱼小胶质细胞的溶酶体,但V-ATPase a3亚基在小胶质细胞发育过程中的作用及其对吞噬体成熟的调控机制尚不明确。本研究利用V-ATPase a3亚基缺陷(tcirg1b−/−)的斑马鱼模型,通过整体原位杂交、免疫荧光、免疫共沉淀和凋亡实验等探究了V-ATPase a3亚基调控小胶质细胞吞噬体成熟的分子机制。结果显示,V-ATPase a3亚基在斑马鱼发育早期即开始表达,a3亚基缺陷会导致小胶质细胞吞噬体异常堆积,细胞胀大且活跃度降低,呈现“消化不良”表型。通过外源性标记晚期吞噬体并进行免疫荧光染色,进一步验证了a3亚基缺陷会引起小胶质细胞的晚期吞噬体和溶酶体融合障碍。随后,免疫共沉淀实验结果表明V-ATPase a3亚基可与晚期吞噬体标记物Rab7蛋白相结合,而rab7敲低实验可重现小胶质细胞“消化不良”表型,以上结果综合提示V-ATPase a3亚基可能通过结合Rab7并促进小胶质细胞的吞噬体顺利降解。综上所述,本研究阐明了V-ATPase a3亚基对小胶质细胞发育的影响以及其调控吞噬体和溶酶体膜融合的分子机制,为进一步理解吞噬体成熟过程提供了数据支持和理论依据。
寇涵婧, 黄志斌, 张文清, 陈琪. V-ATPase a3亚基调控小胶质细胞吞噬体成熟的机制[J]. 遗传, 2025, 47(11): 1256-1268.
Hanjing Kou, Zhibin Huang, Wenqing Zhang, Qi Chen. Effect of V-ATPase a3 subunit on microglial phagosome maturation in zebrafish[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2025, 47(11): 1256-1268.
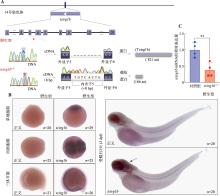
图1
tcirg1b基因突变位点示意图及tcirg1b mRNA表达检测 A:DNA测序结果显示tcirg1b−/−突变体出现A-T单碱基点突变,cDNA测序结果显示tcirg1b−/−突变体出现8 bp额外碱基插入,蛋白预测结果显示tcirg1b−/−突变体仅剩166 aa。B:单细胞期、四细胞期、三体节期和3 dpf的野生型胚胎tcirg1b mRNA反义探针和正义探针整体原位杂交;黑色箭头指示tcirg1b mRNA在3 dpf的斑马鱼头部高表达。C:qRT-PCR检测3 dpf对照组和tcirg1b−/−胚胎中tcirg1b mRNA的相对表达量。共计4次生物学重复,非配对t检验,**P<0.01。"
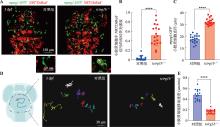
图2
tcirg1b−/−斑马鱼小胶质细胞的吞噬体降解功能及小胶质细胞迁移速度检测 A:3 dpf 对照组和tcirg1b−/−双转基因背景胚胎的活体成像。Tg(mpeg1:GFP)转基因品系标记巨噬细胞(绿色荧光),Tg(NBT:DsRed)转基因品系标记神经元(红色荧光),右下角为白色虚线框的局部放大图(3×),白色箭头所示为小胶质细胞中被吞噬的凋亡神经元,即吞噬体信号。B:3 dpf 对照组和tcirg1b−/−胚胎的小胶质细胞NBT:DsRed阳性信号的相对荧光强度统计。每组斑马鱼n=18,非配对t检验,****P<0.0001。C:3 dpf 对照组和tcirg1b−/−胚胎中mpeg1:GFP阳性小胶质细胞(“人字缝”区域巨噬细胞)的直径统计结果。统计数值为胚胎样本中随机7个小胶质细胞直径的平均值,每个随机小胶质细胞直径=(最长直径+最短直径)/2。每组斑马鱼n=18,非配对t检验,****P<0.0001。D:3 dpf 对照组和tcirg1b−/−胚胎中Tg(mpeg1:GFP)标记的小胶质细胞运动轨迹,由ImageJ 软件MTrackJ模块绘制。每组斑马鱼n=16,图示为其中一次胚胎样本中随机7个小胶质细胞的运动轨迹。E:3 dpf 对照组和tcirg1b−/−胚胎中Tg(mpeg1:GFP)标记的小胶质细胞移动速度统计。每组斑马鱼样本数n=16,非配对t检验,****P<0.0001,每条斑马鱼随机挑选7个小胶质细胞获取移动速度并取平均值作为一次样本。"
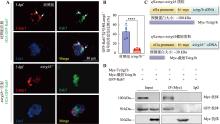
图3
V-ATPase a3亚基与Rab7的互作及其对吞噬体成熟的调控 A:对单细胞期的对照组或tcirg1b−/−胚胎注射H2A:GFP-Rab7质粒,并于3 dpf收样进行免疫荧光染色,检测GFP-Rab7阳性信号和Lamp1阳性信号在Lcp1阳性小胶质细胞中的共定位比例。白色箭头所示为双阳性的共定位信号,比例数据由软件Imaris 9.0.1输出。B:在Lcp1阳性小胶质细胞中,GFP-Rab7阳性信号和Lamp1阳性信号的共定位比例统计结果。每个统计点为胚胎样本中随机7个小胶质细胞共定位比例的平均值;每组斑马鱼样本数n=6,非配对t检验,****P<0.0001。C:过表达载体构建示意图。D:免疫共沉淀(Co-IP)检测V-ATPase a3亚基与Rab7的相互作用。从同时含有GFP-Rab7和Myc-Tcirg1b(或Myc-截短Tcirg1b)的3 dpf野生型胚胎中提取总蛋白,用于Co-IP实验。Myc抗体用于检测Tcirg1b和截短的Tcirg1b蛋白,GFP抗体用于检测Rab7。"

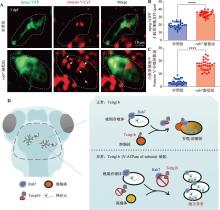
图4
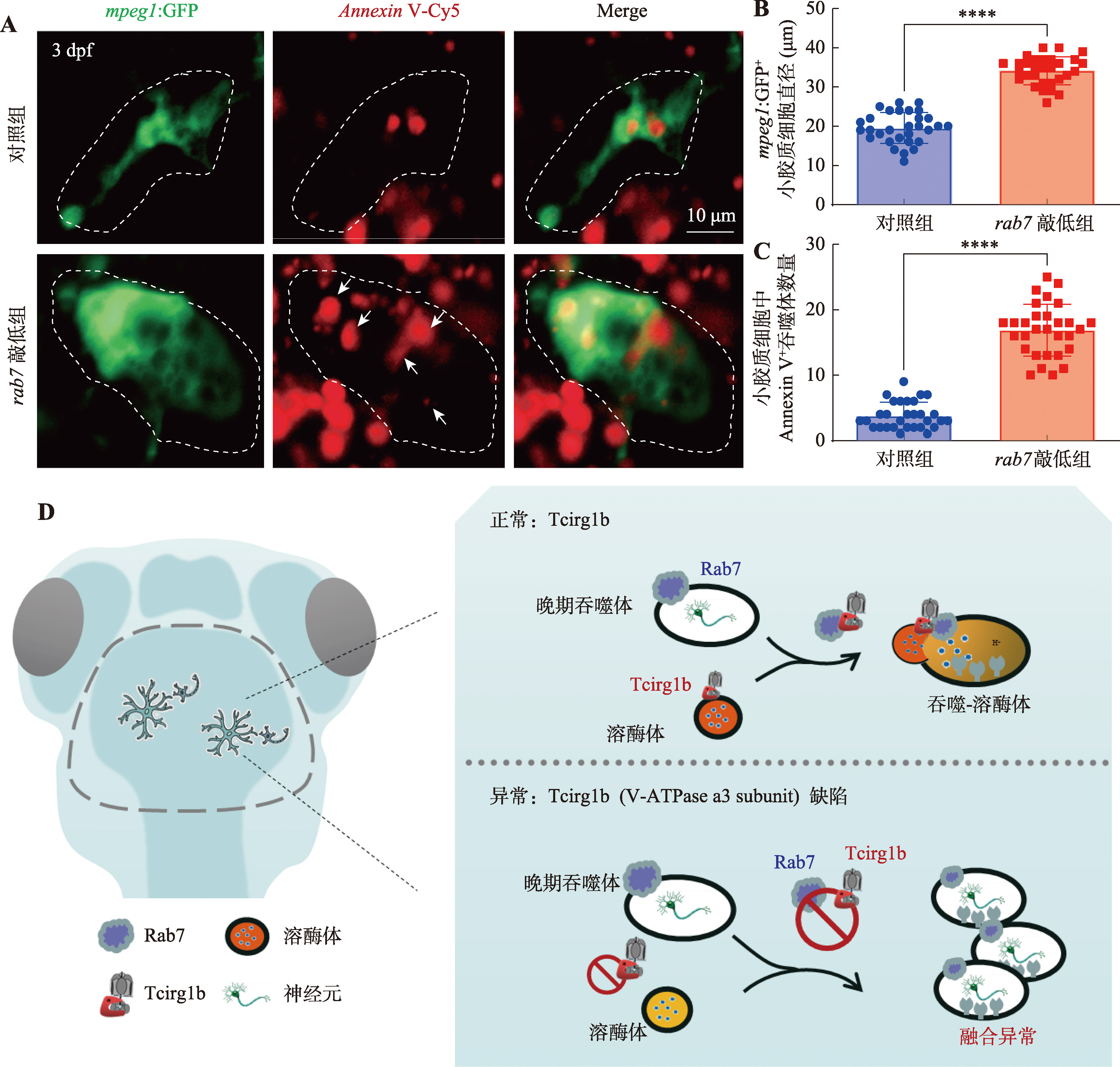
斑马鱼rab7敲低对小胶质细胞吞噬体成熟的影响 A:3 dpf对照组和rab7敲低组mpeg1:GFP 阳性信号标记小胶质细胞荧光成像及Annexin V-Cy5凋亡检测。白色箭头所示为Annexin V-Cy5标记的凋亡信号聚集在rab7敲低的小胶质细胞。B:3 dpf对照组和rab7敲低组mpeg1:GFP阳性小胶质细胞的直径统计结果。每组斑马鱼样本数n=10条,每条斑马鱼随机取3个小胶质细胞,每个随机小胶质细胞直径=(最长直径+最短直径)/2。非配对t检验,****P< 0.0001。C:3 dpf对照组和rab7敲低组小胶质细胞中Annexin V-Cy5阳性信号的数量统计。每组斑马鱼样本数n=10条,每条斑马鱼随机取3个小胶质细胞。非配对t检验,****P<0.0001。D:V-ATPase a3亚基参与调控吞噬体成熟机制示意图。"
| [1] |
Prinz M, Jung S, Priller J. Microglia biology: one century of evolving concepts. Cell, 2019, 179(2): 292-311.
pmid: 31585077 |
| [2] |
Savage JC, Carrier M, Tremblay MÈ. Morphology of microglia across contexts of health and disease. Methods Mol Biol, 2019, 2034: 13-26.
pmid: 31392674 |
| [3] |
Wang HY, Ye JR, Peng Y, Ma WY, Chen HD, Sun HS, Feng ZP, He WB, Li G, Chu SF, Zhang Z, Chen NH. CKLF induces microglial activation via triggering defective mitophagy and mitochondrial dysfunction. Autophagy, 2024, 20(3): 590-613.
pmid: 37908119 |
| [4] |
Lukens JR, Eyo UB. Microglia and neurodevelopmental disorders. Annu Rev Neurosci, 2022, 45: 425-445.
pmid: 37908119 |
| [5] |
Merighi S, Nigro M, Travagli A, Gessi S. Microglia and Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(21): 12990.
pmid: 36361780 |
| [6] |
Au NPB, Ma CHE. Neuroinflammation, microglia and implications for retinal ganglion cell survival and axon regeneration in traumatic optic neuropathy. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 860070.
pmid: 35309305 |
| [7] |
Vidal-Itriago A, Radford RAW, Aramideh JA, Maurel C, Scherer NM, Don EK, Lee A, Chung RS, Graeber MB, Morsch M. Microglia morphophysiological diversity and its implications for the CNS. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 997786.
pmid: 36341385 |
| [8] |
Xu TT, Liu C, Deng SY, Gan L, Zhang ZJ, Yang GY, Tian HL, Tang YH. The roles of microglia and astrocytes in myelin phagocytosis in the central nervous system. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab, 2023, 43(3): 325-340.
pmid: 36324281 |
| [9] |
Quick JD, Silva C, Wong JH, Lim KL, Reynolds R, Barron AM, Zeng JL, Lo CH. Lysosomal acidification dysfunction in microglia: an emerging pathogenic mechanism of neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. J Neuroinflammation, 2023, 20(1): 185.
pmid: 37543564 |
| [10] |
Harry GJ. Microglia during development and aging. Pharmacol Ther, 2013, 139(3): 313-326.
pmid: 23644076 |
| [11] |
Borst K, Dumas AA, Prinz M. Microglia: immune and non-immune functions. Immunity, 2021, 54(10): 2194-2208.
pmid: 34644556 |
| [12] |
Levin R, Grinstein S, Canton J. The life cycle of phagosomes: formation, maturation, and resolution. Immunol Rev, 2016, 273(1): 156-179.
pmid: 27558334 |
| [13] |
Samie M, Wang X, ZHANG XL, Goschka A, Li XR, Cheng XP, Gregg E, Azar M, Zhuo Y, Garrity AG, Gao Q, Slaugenhaupt S, Pickel J, Zolov SN, Weisman LS, Lenk GM, Titus S, Bryant-Genevier M, Southall N, Juan M, Ferrer M, Xu HX. A TRP channel in the lysosome regulates large particle phagocytosis via focal exocytosis. Dev Cell, 2013, 26(5): 511-524.
pmid: 23993788 |
| [14] |
Bajno L, Peng XR, Schreiber AD, Moore HP, Trimble WS, Grinstein S. Focal exocytosis of VAMP3-containing vesicles at sites of phagosome formation. J Cell Biol, 2000, 149(3): 697-706.
pmid: 10791982 |
| [15] |
Jaumouillé V, Grinstein S. Receptor mobility, the cytoskeleton, and particle binding during phagocytosis. Curr Opin Cell Biol, 2011, 23(1): 22-29.
pmid: 21074980 |
| [16] |
Fountain A, Inpanathan S, Alves P, Verdawala MB, Botelho RJ. Phagosome maturation in macrophages: eat, digest, adapt, and repeat. Adv Biol Regul, 2021, 82: 100832.
pmid: 34717137 |
| [17] |
Norris A, Grant BD. Endosomal microdomains: formation and function. Curr Opin Cell Biol, 2020, 65: 86-95.
pmid: 32247230 |
| [18] |
Li GP, Marlin MC. Rab family of GTPases. Methods Mol Biol, 2015, 1298: 1-15.
pmid: 25800828 |
| [19] |
Stenmark H, Olkkonen VM. The Rab GTPase family. Genome Biol, 2001, 2(5): REVIEWS3007.
pmid: 11387043 |
| [20] |
Vieira OV, Bucci C, Harrison RE, Trimble WS, Lanzetti L, Gruenberg J, Schreiber AD, Stahl PD, Grinstein S. Modulation of Rab5 and Rab7 recruitment to phagosomes by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Mol Cell Biol, 2003, 23(7): 2501-2514.
pmid: 12640132 |
| [21] |
Roberts RL, Barbieri MA, Ullrich J, Stahl PD. Dynamics of rab5 activation in endocytosis and phagocytosis. J Leukoc Biol, 2000, 68(5): 627-632.
pmid: 11073100 |
| [22] |
Langemeyer L, Fröhlich F, Ungermann C. Rab GTPase function in endosome and lysosome biogenesis. Trends Cell Biol, 2018, 28(11): 957-970.
pmid: 30025982 |
| [23] |
van der kant R, Fish A, Janssen L, Janssen H, Krom S, Ho N, Brummelkamp T, Carette J, Rocha N, Neefjes J. Late endosomal transport and tethering are coupled processes controlled by RILP and the cholesterol sensor ORP1L. J Cell Sci, 2013, 126(Pt 15): 3462-3474.
pmid: 23729732 |
| [24] |
Vieira OV, Botelho RJ, Grinstein S. Phagosome maturation: aging gracefully. Biochem J, 2002, 366(Pt 3): 689-704.
pmid: 12061891 |
| [25] |
Pols MS ten Brink C, Gosavi P, Oorschot V, Klumperman J. The HOPS proteins hVps41 and hVps39 are required for homotypic and heterotypic late endosome fusion. Traffic, 2013, 14(2): 219-232.
pmid: 23167963 |
| [26] |
Yang CL, Wang XC. Lysosome biogenesis: regulation and functions. J Cell Biol, 2021, 220(6): e202102001.
pmid: 33950241 |
| [27] |
Futai M, Sun-Wada GH, Wada Y, Matsumoto N, Nakanishi-Matsui M. Vacuolar-type ATPase: a proton pump to lysosomal trafficking. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci, 2019, 95(6): 261-277.
pmid: 31189779 |
| [28] |
Fillingame RH, Dmitriev OY. Structural model of the transmembrane Fo rotary sector of H+-transporting ATP synthase derived by solution NMR and intersubunit cross-linking in situ. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2002, 1565(2): 232-245.
pmid: 31189779 |
| [29] |
Kawasaki-Nishi S, Nishi T, Forgac M. Arg-735 of the 100-kDa subunit a of the yeast V-ATPase is essential for proton translocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2001, 98(22): 12397-12402.
pmid: 11592980 |
| [30] |
Chen Q, Kou HJ, Demy DL, Liu W, Li JC, Wen ZL, Herbomel P, Huang ZB, Zhang WQ, Xu J. The different roles of V-ATPase a subunits in phagocytosis/endocytosis and autophagy. Autophagy, 2024, 20(10): 2297-2313.
pmid: 38873931 |
| [31] |
Nyman JKE, Väänänen HK. A rationale for osteoclast selectivity of inhibiting the lysosomal V-ATPase a3 isoform. Calcif Tissue Int, 2010, 87(3): 273-283.
pmid: 20596699 |
| [32] |
Sobacchi C, Frattini A, Orchard P, Porras O, Tezcan I, Andolina M, Babul-Hirji R, Baric I, Canham N, Chitayat D, Dupuis-Girod S, Ellis I, Etzioni A, Fasth A, Fisher A, Gerritsen B, Gulino V, Horwitz E, Klamroth V, Lanino E, Mirolo M, Musio A, Matthijs G, Nonomaya S, Notarangelo LD, Ochs HD, Furga AS, Valiaho J, van Hove JL, Vihinen M, Vujic D, Vezzoni P, Villa A. The mutational spectrum of human malignant autosomal recessive osteopetrosis. Hum Mol Genet, 2001, 10(17): 1767-1773.
pmid: 11532986 |
| [33] |
Kawamura N, Tabata H, Sun-Wada GH, Wada Y. Optic nerve compression and retinal degeneration in Tcirg1 mutant mice lacking the vacuolar-type H+-ATPase a3 subunit. PLoS One, 2010, 5(8): e12086.
pmid: 20711468 |
| [34] |
Yu T, Guo WL, Tian Y, Xu J, Chen JH, Li L, Wen ZL. Distinct regulatory networks control the development of macrophages of different origins in zebrafish. Blood, 2017, 129(4): 509-519.
pmid: 27940477 |
| [35] |
Peri F, Nüsslein-Volhard C. Live imaging of neuronal degradation by microglia reveals a role for v0-ATPase a1 in phagosomal fusion in vivo. Cell, 2008, 133(5): 916-927.
pmid: 18510934 |
| [36] | Westerfield M. The zebrafish book: a guide for the laboratory use of zebrafish (Danio rerio). 4th ed. University of Oregon Press, Eugene, OR, 1995. |
| [37] |
Chitramuthu BP, Bennett HPJ. High resolution whole mount in situ hybridization within zebrafish embryos to study gene expression and function. J Vis Exp, 2013, (80): e50644.
pmid: 24192694 |
| [38] | Hong JX, Xu SE, Zhang WQ, Liu W. The interaction of Pu.1 and cMyb in zebrafish neutrophil development. Hereditas(Beijing), 2024, 46(4): 319-332. |
| 洪佳馨, 徐颂恩, 张文清, 刘伟. Pu. 1和cMyb在斑马鱼中性粒细胞发育中的相互作用. 遗传, 2024, 46(4): 319-332. | |
| [39] | Lu JA, Huang CY, Lin ZY, Tang Z, Ma N, Huang ZB. The role of the cd99l2 gene on leukocyte interstitial migration in zebrafish. Hereditas(Beijing), 2022, 44(9): 789-809. |
| 卢荆澳, 黄春燕, 林芷茵, 唐政, 马宁, 黄志斌. cd99l2基因调控斑马鱼白细胞组织间的迁移机制. 遗传, 2022, 44(9): 798-809. | |
| [40] |
Huang ZH, Yang XJ, Qin X, Chen KM, Liu W, Xu J, Li JC, Zhang WQ, Huang ZB. Localized production of LECT2 by orthotopic histiocytes during inflammation. J Genet Genomics, 2024, 51(12): 1517-1520.
pmid: 39369817 |
| [41] |
Nayak D, Roth TL, Mcgavern DB. Microglia development and function. Annu Rev Immunol, 2014, 32: 367-402.
pmid: 24471431 |
| [42] |
Jin W, Dai YM, Li FN, Zhu L, Huang ZB, Liu W, Li JC, Zhang MJ, Du JL, Zhang WQ, Wen ZL. Dysregulation of microglial function contributes to neuronal impairment in mcoln1a-deficient zebrafish. iScience, 2019, 13: 391-401.
pmid: 30897512 |
| [1] | 高云海, 邓家杰, 肖霄, 潘鲁湲, 何牡丹, 张蕴斌. 斑马鱼ppp6r3调控性腺分化和配子发生的作用研究[J]. 遗传, 2025, 47(9): 1023-1031. |
| [2] | 林杰豪, 杨童舒, 张文清, 刘伟. Lyl1不同转录本在斑马鱼原始造血中的作用[J]. 遗传, 2025, 47(5): 573-588. |
| [3] | 刘吉祥, 赖思婷, 白晶, 徐进. Il34拯救甲硝唑导致的斑马鱼中枢神经系统轴突再生障碍[J]. 遗传, 2024, 46(6): 478-489. |
| [4] | 洪佳馨, 徐颂恩, 张文清, 刘伟. Pu.1和cMyb在斑马鱼中性粒细胞发育中的相互作用[J]. 遗传, 2024, 46(4): 319-332. |
| [5] | 孙飘, 李颖, 刘帆, 王璐. TPI缺乏症斑马鱼模型的构建及分析[J]. 遗传, 2024, 46(3): 232-241. |
| [6] | 杨晓君, 黄振瀚, 刘伟, 张文清, 黄志斌. CD209同源基因在斑马鱼中的鉴定及功能表征[J]. 遗传, 2024, 46(11): 947-957. |
| [7] | 李凯伦, 卢荆奥, 陈小辉, 张文清, 刘伟. 尿囊素促进破骨细胞缺陷斑马鱼骨折修复[J]. 遗传, 2023, 45(4): 341-353. |
| [8] | 商晓康, 张思萌, 倪军军. 组织蛋白酶B参与脑衰老及阿尔兹海默症发生发展研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2023, 45(3): 212-220. |
| [9] | 卢荆澳, 黄春燕, 林芷茵, 唐政, 马宁, 黄志斌. cd99l2基因调控斑马鱼白细胞组织间的迁移机制[J]. 遗传, 2022, 44(9): 798-809. |
| [10] | 郑鹏飞, 谢海波, 朱盼盼, 赵呈天. 斑马鱼神经底板处神经元的分布及特征[J]. 遗传, 2022, 44(6): 510-520. |
| [11] | 张婷婷, 刘峰. 斑马鱼蛋白酪氨酸硫酸化修饰的检测方法研究[J]. 遗传, 2022, 44(2): 178-186. |
| [12] | 贾婷婷, 雷蕾, 吴歆媛, 蔡顺有, 陈艺璇, 薛钰. 二甲双胍对斑马鱼骨骼发育及损伤修复的机制研究[J]. 遗传, 2022, 44(1): 68-79. |
| [13] | 郭佳妮, 刘帆, 王璐. 斑马鱼血液疾病模型及应用[J]. 遗传, 2020, 42(8): 725-738. |
| [14] | 熊凤,谢训卫,潘鲁媛,李阔宇,柳力月,张昀,李玲璐,孙永华. 国家斑马鱼资源中心的资源、技术和服务建设[J]. 遗传, 2018, 40(8): 683-692. |
| [15] | 许璟瑾, 张文娟, 王静怡, 姚丽云, 潘裕添, 欧一新, 薛钰, . 金线莲抑制斑马鱼黑色素形成的活性组分筛选及机理研究[J]. 遗传, 2017, 39(12): 1178-1187. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||

www.chinagene.cn
备案号:京ICP备09063187号-4
总访问:,今日访问:,当前在线:
