遗传 ›› 2024, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (3): 209-218.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.23-248
收稿日期:2023-11-10
修回日期:2023-12-28
出版日期:2024-03-20
发布日期:2024-01-19
通讯作者:
岑山,李晓宇
E-mail:za1632649341@163.com;shancen@hotmail.com;xiaoyulik@hotmail.com
作者简介:张傲,硕士研究生,专业方向:LINE-1与肿瘤维持机制的研究。E-mail: za1632649341@163.com
基金资助:
Ao Zhang( ), Shan Cen(
), Shan Cen( ), Xiaoyu Li(
), Xiaoyu Li( )
)
Received:2023-11-10
Revised:2023-12-28
Published:2024-03-20
Online:2024-01-19
Contact:
Shan Cen, Xiaoyu Li
E-mail:za1632649341@163.com;shancen@hotmail.com;xiaoyulik@hotmail.com
Supported by:摘要:
长散布元件-1 (long interspersed elements-1,LINE-1)是现今在人类基因组中唯一具有自主转座能力的转座子,其转座会引起细胞基因组结构和功能的改变,是导致多种严重疾病的重要因素。在转座过程中,LINE-1 mRNA是转座中间体的核心,宿主细胞对其进行相关修饰直接影响转座。N6-腺苷甲基化修饰(m6A)是真核细胞RNA上最丰富且动态可逆的表观遗传修饰。目前发现m6A修饰也存在于LINE-1 mRNA上,参与LINE-1整个生命周期的调控,影响其转座和基因组中LINE-1相邻基因的表达,进而影响基因组稳定性、细胞自我更新与分化潜能,在人类发育和疾病中具有重要作用。本文介绍了LINE-1 m6A修饰的位置、功能以及相关机制,并总结了LINE-1的m6A修饰对其转座调控的研究进展,以期为相关疾病发生发展的机制研究和治疗提供新的思路。
张傲, 岑山, 李晓宇. N6-腺苷甲基化修饰及其对LINE-1的调控机制[J]. 遗传, 2024, 46(3): 209-218.
Ao Zhang, Shan Cen, Xiaoyu Li. N6-adenosine methylation and the regulatory mechanism on LINE-1[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2024, 46(3): 209-218.
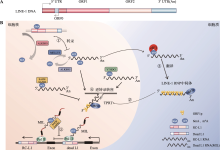
图2
m6A修饰对LINE-1的影响 A:LINE-1的结构。LINE-1由开放阅读框ORF0、ORF1、ORF2和非编码区5′ UTR、3′ UTR构成,5′ UTR 有两个启动子,是双向的:正义启动子活性可转录 ORF1、ORF2,反义启动子(ASP)能够启动与LINE-1方向相反的转录物转录。B:m6A修饰酶影响LINE-1复制周期模式图。①LINE-1 DNA可能富集6mA甲基化修饰,抑制mRNA转录;②LINE-1 mRNA与ORF1p、ORF2p结合生成LINE-1 RNP复合物,入核后进行“TPRT”生成cDNA,插入宿主基因组;③在细胞质中,翻译起始因子eIF3与m6A特异性相互作用,提高翻译水平;④METTL3、YTHDC1促进LINE-1逆转座,ALKBH5、SAFB/SAFB2抑制LINE-1逆转座;⑤SAFB/SAFB2可纠正MILs对重要宿主基因的转录阻断。"

| [1] |
Lander ES, Linton LM, Birren B, Nusbaum C, Zody MC, Baldwin J, Devon K, Dewar K, Doyle M, FitzHugh W, Funke R, Gage D, Harris K, Heaford A, Howland J, Kann L, Lehoczky J, LeVine R, McEwan P, McKernan K, Meldrim J, Mesirov JP, Miranda C, Morris W, Naylor J, Raymond C, Rosetti M, Santos R, Sheridan A, Sougnez C, Stange-Thomann Y, Stojanovic N, Subramanian A, Wyman D, Rogers J, Sulston J, Ainscough R, Beck S, Bentley D, Burton J, Clee C, Carter N, Coulson A, Deadman R, Deloukas P, Dunham A, Dunham I, Durbin R, French L, Grafham D, Gregory S, Hubbard T, Humphray S, Hunt A, Jones M, Lloyd C, McMurray A, Matthews L, Mercer S, Milne S, Mullikin JC, Mungall A, Plumb R, Ross M, Shownkeen R, Sims S, Waterston RH, Wilson RK, Hillier LW, McPherson JD, Marra MA, Mardis ER, Fulton LA, Chinwalla AT, Pepin KH, Gish WR, Chissoe SL, Wendl MC, Delehaunty KD, Miner TL, Delehaunty A, Kramer JB, Cook LL, Fulton RS, Johnson DL, Minx PJ, Clifton SW, Hawkins T, Branscomb E, Predki P, Richardson P, Wenning S, Slezak T, Doggett N, Cheng JF, Olsen A, Lucas S, Elkin C, Uberbacher E, Frazier M, Gibbs RA, Muzny DM, Scherer SE, Bouck JB, Sodergren EJ, Worley KC, Rives CM, Gorrell JH, Metzker ML, Naylor SL, Kucherlapati RS, Nelson DL, Weinstock GM, Sakaki Y, Fujiyama A, Hattori M, Yada T, Toyoda A, Itoh T, Kawagoe C, Watanabe H, Totoki Y, Taylor T, Weissenbach J, Heilig R, Saurin W, Artiguenave F, Brottier P, Bruls T, Pelletier E, Robert C, Wincker P, Smith DR, Doucette-Stamm L, Rubenfield M, Weinstock K, Lee HM, Dubois J, Rosenthal A, Platzer M, Nyakatura G, Taudien S, Rump A, Yang H, Yu J, Wang J, Huang G, Gu J, Hood L, Rowen L, Madan A, Qin S, Davis RW, Federspiel NA, Abola AP, Proctor MJ, Myers RM, Schmutz J, Dickson M, Grimwood J, Cox DR, Olson MV, Kaul R, Raymond C, Shimizu N, Kawasaki K, Minoshima S, Evans GA, Athanasiou M, Schultz R, Roe BA, Chen F, Pan H, Ramser J, Lehrach H, Reinhardt R, McCombie WR, de la Bastide M, Dedhia N, Blöcker H, Hornischer K, Nordsiek G, Agarwala R, Aravind L, Bailey JA, Bateman A, Batzoglou S, Birney E, Bork P, Brown DG, Burge CB, Cerutti L, Chen HC, Church D, Clamp M, Copley RR, Doerks T, Eddy SR, Eichler EE, Furey TS, Galagan J, Gilbert JG, Harmon C, Hayashizaki Y, Haussler D, Hermjakob H, Hokamp K, Jang W, Johnson LS, Jones TA, Kasif S, Kaspryzk A, Kennedy S, Kent WJ, Kitts P, Koonin EV, Korf I, Kulp D, Lancet D, Lowe TM, McLysaght A, Mikkelsen T, Moran JV, Mulder N, Pollara VJ, Ponting CP, Schuler G, Schultz J, Slater G, Smit AF, Stupka E, Szustakowki J, Thierry-Mieg D, Thierry-Mieg J, Wagner L, Wallis J, Wheeler R, Williams A, Wolf YI, Wolfe KH, Yang SP, Yeh RF, Collins F, Guyer MS, Peterson J, Felsenfeld A, Wetterstrand KA, Patrinos A, Morgan MJ, de Jong P, Catanese JJ, Osoegawa K, Shizuya H, Choi S, Chen YJ, Szustakowki J, International Human Genome Sequencing Consortium.. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature, 2001, 409(6822): 860-921.
doi: 10.1038/35057062 |
| [2] |
Belancio VP, Hedges DJ, Deininger P. Mammalian non-LTR retrotransposons: for better or worse, in sickness and in health. Genome Res, 2008, 18(3): 343-358.
doi: 10.1101/gr.5558208 pmid: 18256243 |
| [3] |
Goodier JL, Kazazian HH. Retrotransposons revisited: the restraint and rehabilitation of parasites. Cell, 2008, 135(1): 23-35.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.09.022 pmid: 18854152 |
| [4] |
Babushok DV, Kazazian HH. Progress in understanding the biology of the human mutagen LINE-1. Hum Mutat, 2007, 28(6): 527-539.
doi: 10.1002/humu.20486 pmid: 17309057 |
| [5] |
Zhang X, Zhang R, Yu JP. New understanding of the relevant role of LINE-1 retrotransposition in human disease and immune modulation. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2020, 8: 657.
doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00657 pmid: 32850797 |
| [6] |
Jachowicz JW, Bing XY, Pontabry J, Bošković A, Rando OJ, Torres-Padilla ME. LINE-1 activation after fertilization regulates global chromatin accessibility in the early mouse embryo. Nat Genet, 2017, 49(10): 1502-1510.
doi: 10.1038/ng.3945 pmid: 28846101 |
| [7] | Mao Y, Li XY. Advances in the study of LINE-1 retrotransposition in nervous system. China Med Her, 2019, 16(5): 27-29, 46. |
| 毛洋, 李晓宇. 神经系统中LINE-1转座的研究进展. 中国医药导报, 2019, 16(5): 27-29, 46. | |
| [8] |
Ponomaryova AA, Rykova EY, Gervas PA, Cherdyntseva NV, Mamedov IZ, Azhikina TL. Aberrant methylation of LINE-1 transposable elements: a search for cancer biomarkers. Cells, 2020, 9(9): 2017.
doi: 10.3390/cells9092017 |
| [9] |
Burns KH. Our conflict with transposable elements and its implications for human disease. Annu Rev Pathol, 2020, 15: 51-70.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-pathmechdis-012419-032633 pmid: 31977294 |
| [10] |
Gorbunova V, Seluanov A, Mita P, McKerrow W, Fenyö D, Boeke JD, Linker SB, Gage FH, Kreiling JA, Petrashen AP, Woodham TA, Taylor JR, Helfand SL, Sedivy JM. The role of retrotransposable elements in ageing and age- associated diseases. Nature, 2021, 596(7870): 43-53.
doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03542-y |
| [11] | Liu Q, Wang JH, Li XY, Cen S. The connection between LINE-1 retrotransposition and human tumorigenesis. Hereditas(Beijing), 2016, 38(2): 93-102. |
| 刘茜, 王瑾晖, 李晓宇, 岑山. 逆转录转座子LINE-1与肿瘤的发生和发展. 遗传, 2016, 38(2): 93-102. | |
| [12] |
Ostertag EM, Goodier JL, Zhang Y, Kazazian HH. SVA elements are nonautonomous retrotransposons that cause disease in humans. Am J Hum Genet, 2003, 73(6): 1444-1451.
doi: 10.1086/380207 pmid: 14628287 |
| [13] |
Jones PA. Functions of DNA methylation: islands, start sites, gene bodies and beyond. Nat Rev Genet, 2012, 13(7): 484-492.
doi: 10.1038/nrg3230 pmid: 22641018 |
| [14] |
Fukuda K, Shinkai Y. SETDB1-mediated silencing of retroelements. Viruses, 2020, 12(6): 596.
doi: 10.3390/v12060596 |
| [15] |
Hamdorf M, Idica A, Zisoulis DG, Gamelin L, Martin C, Sanders KJ, Pedersen IM. miR-128 represses L1 retrotransposition by binding directly to L1 RNA. Nat Struct Mol Biol, 2015, 22(10): 824-831.
doi: 10.1038/nsmb.3090 pmid: 26367248 |
| [16] |
De Fazio S, Bartonicek N, Di Giacomo M, Abreu-Goodger C, Sankar A, Funaya C, Antony C, Moreira PN, Enright AJ, O’Carroll D. The endonuclease activity of Mili fuels piRNA amplification that silences LINE1 elements. Nature, 2011, 480(7376): 259-263.
doi: 10.1038/nature10547 |
| [17] |
Choi J, Hwang SY, Ahn K. Interplay between RNASEH2 and MOV10 controls LINE-1 retrotransposition. Nucleic Acids Res, 2018, 46(4): 1912-1926.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1312 pmid: 29315404 |
| [18] |
Goodier JL. Restricting retrotransposons: a review. Mob DNA, 2016, 7: 16.
doi: 10.1186/s13100-016-0070-z |
| [19] |
Hu SQ, Li J, Xu FW, Mei S, Le Duff Y, Yin LJ, Pang XJ, Cen S, Jin Q, Liang C, Guo F. SAMHD1 inhibits LINE-1 retrotransposition by promoting stress granule formation. PLoS Genet, 2015, 11(7): e1005367.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005367 |
| [20] | Dunn DB, Smith JD.Occurrence of a new base in the deoxyribonucleic acid of a strain of Bacterium coli. Nature, 1955, 175(4451): 336-337. |
| [21] | Littlefield JW, Dunn DB. Natural occurrence of thymine and three methylated adenine bases in several ribonucleic acids. Nature, 1958, 181(4604): 254-255. |
| [22] |
Adler M, Weissmann B, Gutman AB. Occurrence of methylated purine bases in yeast ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem, 1958, 230(2): 717-723.
pmid: 13525389 |
| [23] |
Desrosiers R, Friderici K, Rottman F. Identification of methylated nucleosides in messenger RNA from Novikoff hepatoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1974, 71(10): 3971-3975.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.3971 pmid: 4372599 |
| [24] |
Sun T, Wu RY, Ming L. The role of m6A RNA methylation in cancer. Biomed Pharmacother, 2019, 112: 108613.
doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108613 |
| [25] |
Shi HL, Wei JB, He C. Where, when, and how: context- dependent functions of RNA methylation writers, readers, and erasers. Mol Cell, 2019, 74(4): 640-650.
doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.04.025 |
| [26] | Xiao W, Adhikari S, Dahal U, Chen YS, Hao YJ, Sun BF, Sun HY, Li A, Ping XL, Lai WY, Wang X, Ma HL, Huang CM, Yang Y, Huang N, Jiang GB, Wang HL, Zhou Q, Wang XJ, Zhao YL, Yang YG.Nuclear m6A reader YTHDC1 regulates mRNA splicing. Mol Cell, 2016, 61(4): 507-519. |
| [27] |
Bartosovic M, Molares HC, Gregorova P, Hrossova D, Kudla G, Vanacova S. N6-methyladenosine demethylase FTO targets pre-mRNAs and regulates alternative splicing and 3′-end processing. Nucleic Acids Res, 2017, 45(19): 11356-11370.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx778 pmid: 28977517 |
| [28] |
Roundtree IA, Luo GZ, Zhang ZJ, Wang X, Zhou T, Cui YQ, Sha JH, Huang XX, Guerrero L, Xie P, He E, Shen B, He C. YTHDC1 mediates nuclear export of N6- methyladenosine methylated mRNAs. eLife, 2017, 6: e31311.
doi: 10.7554/eLife.31311 |
| [29] |
Wang X, Lu ZK, Gomez A, Hon GC, Yue YN, Han DL, Fu Y, Parisien M, Dai Q, Jia GF, Ren B, Pan T, He C. N6-methyladenosine-dependent regulation of messenger RNA stability. Nature, 2014, 505(7481): 117-120.
doi: 10.1038/nature12730 |
| [30] |
Yang Y, Hsu PJ, Chen YS, Yang YG. Dynamic transcriptomic m6A decoration: writers, erasers, readers and functions in RNA metabolism. Cell Res, 2018, 28(6): 616-624.
doi: 10.1038/s41422-018-0040-8 |
| [31] |
Wang X, Zhao BS, Roundtree IA, Lu ZK, Han DL, Ma HH, Weng XC, Chen K, Shi HL, He C. N6-methyladenosine modulates messenger RNA translation efficiency. Cell, 2015, 161(6): 1388-1399.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.05.014 |
| [32] |
Shi HL, Wang X, Lu ZK, Zhao BS, Ma HH, Hsu PJ, Liu C, He C. YTHDF3 facilitates translation and decay of N6-methyladenosine-modified RNA. Cell Res, 2017, 27(3): 315-328.
doi: 10.1038/cr.2017.15 |
| [33] |
Meyer KD, Patil DP, Zhou J, Zinoviev A, Skabkin MA, Elemento O, Pestova TV, Qian SB, Jaffrey SR. 5′ UTR m6A promotes cap-independent translation. Cell, 2015, 163(4): 999-1010.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.10.012 pmid: 26593424 |
| [34] |
Boulias K, Greer EL. Biological roles of adenine methylation in RNA. Nat Rev Genet, 2023, 24(3): 143-160.
doi: 10.1038/s41576-022-00534-0 |
| [35] |
McGraw S, Vigneault C, Sirard MA. Temporal expression of factors involved in chromatin remodeling and in gene regulation during early bovine in vitro embryo development. Reproduction, 2007, 133(3): 597-608.
doi: 10.1530/REP-06-0251 pmid: 17379654 |
| [36] |
Deng JH, Chen XH, Chen AD, Zheng XC. m6A RNA methylation in brain injury and neurodegenerative disease. Front Neurol, 2022, 13: 995747.
doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.995747 |
| [37] |
Xu ZJ, Lv BB, Qin Y, Zhang B. Emerging roles and mechanism of m6A methylation in cardiometabolic diseases. Cells, 2022, 11(7): 1101.
doi: 10.3390/cells11071101 |
| [38] |
Wilkinson E, Cui YH, He YY. Context-dependent roles of RNA modifications in stress responses and diseases. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(4): 1949.
doi: 10.3390/ijms22041949 |
| [39] |
Deng LJ, Deng WQ, Fan SR, Chen MF, Qi M, Lyu WY, Qi Q, Tiwari AK, Chen JX, Zhang DM, Chen ZS. m6A modification: recent advances, anticancer targeted drug discovery and beyond. Mol Cancer, 2022, 21(1): 52.
doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01510-2 |
| [40] |
Loh D, Reiter RJ. Melatonin: regulation of viral phase separation and epitranscriptomics in post-acute sequelae of COVID-19. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(15): 8122.
doi: 10.3390/ijms23158122 |
| [41] |
Pan YT, Ma P, Liu Y, Li W, Shu YQ. Multiple functions of m6A RNA methylation in cancer. J Hematol Oncol, 2018, 11(1): 48.
doi: 10.1186/s13045-018-0590-8 |
| [42] |
An YY, Duan H. The role of m6A RNA methylation in cancer metabolism. Mol Cancer, 2022, 21(1): 14.
doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01500-4 pmid: 35022030 |
| [43] |
Zhu FY, Yang TR, Yao MF, Shen T, Fang CY. HNRNPA2B1, as a m6A reader, promotes tumorigenesis and metastasis of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Front Oncol, 2021, 11: 716921.
doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.716921 |
| [44] |
Dmitriev SE, Andreev DE, Terenin IM, Olovnikov IA, Prassolov VS, Merrick WC, Shatsky IN. Efficient translation initiation directed by the 900-nucleotide-long and GC-rich 5′ untranslated region of the human retrotransposon LINE-1 mRNA is strictly cap dependent rather than internal ribosome entry site mediated. Mol Cell Biol, 2007, 27(13): 4685-4697.
pmid: 17470553 |
| [45] |
Hwang SY, Jung H, Mun S, Lee S, Park K, Baek SC, Moon HC, Kim H, Kim B, Choi Y, Go YH, Tang WXF, Choi J, Choi JK, Cha HJ, Park HY, Liang P, Kim VN, Han K, Ahn K. L1 retrotransposons exploit RNA m6A modification as an evolutionary driving force. Nat Commun, 2021, 12(1): 880.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21197-1 |
| [46] |
Xiong F, Wang RY, Lee JH, Li SL, Chen SF, Liao ZA, Hasani LA, Nguyen PT, Zhu XY, Krakowiak J, Lee DF, Han L, Tsai KL, Liu Y, Li WB. RNA m6A modification orchestrates a LINE-1-host interaction that facilitates retrotransposition and contributes to long gene vulnerability. Cell Res, 2021, 31(8): 861-885.
doi: 10.1038/s41422-021-00515-8 pmid: 34108665 |
| [47] |
Billon V, Cristofari G. Nascent RNA m6A modification at the heart of the gene-retrotransposon conflict. Cell Res, 2021, 31(8): 829-831.
doi: 10.1038/s41422-021-00518-5 |
| [48] |
Niehrs C, Luke B. Regulatory R-loops as facilitators of gene expression and genome stability. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2020, 21(3): 167-178.
doi: 10.1038/s41580-019-0206-3 |
| [49] |
Mita P, Wudzinska A, Sun XJ, Andrade J, Nayak S, Kahler DJ, Badri S, LaCava J, Ueberheide B, Yun CY, Fenyö D, Boeke JD. LINE-1 protein localization and functional dynamics during the cell cycle. eLife, 2018, 7: e30058.
doi: 10.7554/eLife.30058 |
| [50] |
Abakir A, Giles TC, Cristini A, Foster JM, Dai N, Starczak M, Rubio-Roldan A, Li MM, Eleftheriou M, Crutchley J, Flatt L, Young L, Gaffney DJ, Denning C, Dalhus B, Emes RD, Gackowski D, Corrêa IR, Garcia-Perez JL, Klungland A, Gromak N, Ruzov A. N6-methyladenosine regulates the stability of RNA:DNA hybrids in human cells. Nat Genet, 2020, 52(1): 48-55.
doi: 10.1038/s41588-019-0549-x |
| [51] |
Skourti-Stathaki K, Proudfoot NJ. A double-edged sword: R loops as threats to genome integrity and powerful regulators of gene expression. Genes Dev, 2014, 28(13): 1384-1396.
doi: 10.1101/gad.242990.114 |
| [52] |
García-Muse T, Aguilera A. R loops: from physiological to pathological roles. Cell, 2019, 179(3): 604-618.
doi: S0092-8674(19)31006-2 pmid: 31607512 |
| [53] |
Duda KJ, Ching RW, Jerabek L, Shukeir N, Erikson G, Engist B, Onishi-Seebacher M, Perrera V, Richter F, Mittler G, Fritz K, Helm M, Knuckles P, Bühler M, Jenuwein T. m6A RNA methylation of major satellite repeat transcripts facilitates chromatin association and RNA:DNA hybrid formation in mouse heterochromatin. Nucleic Acids Res, 2021, 49(10): 5568-5587.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab364 |
| [54] |
Kong YM, Cao L, Deikus G, Fan Y, Mead EA, Lai WY, Zhang YZ, Yong R, Sebra R, Wang HL, Zhang XS, Fang G. Critical assessment of DNA adenine methylation in eukaryotes using quantitative deconvolution. Science, 2022, 375(6580): 515-522.
doi: 10.1126/science.abe7489 pmid: 35113693 |
| [55] |
Chen LQ, Zhang Z, Chen HX, Xi JF, Liu XH, Ma DZ, Zhong YH, Ng WH, Chen T, Mak DW, Chen Q, Chen YQ, Luo GZ. High-precision mapping reveals rare N6- deoxyadenosine methylation in the mammalian genome. Cell Discov, 2022, 8(1): 138.
doi: 10.1038/s41421-022-00484-1 pmid: 36575183 |
| [56] |
Wu TP, Wang T, Seetin MG, Lai YQ, Zhu SJ, Lin KX, Liu YF, Byrum SD, Mackintosh SG, Zhong M, Tackett A, Wang GL, Hon LS, Fang G, Swenberg JA, Xiao AZ. DNA methylation on N6-adenine in mammalian embryonic stem cells. Nature, 2016, 532(7599): 329-333.
doi: 10.1038/nature17640 |
| [57] |
Bailey JA, Carrel L, Chakravarti A, Eichler EE. Molecular evidence for a relationship between LINE-1 elements and X chromosome inactivation: the Lyon repeat hypothesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2000, 97(12): 6634-6639.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.12.6634 pmid: 10841562 |
| [58] |
Liu J, Dou XY, Chen CY, Chen C, Liu C, Xu MM, Zhao SQ, Shen B, Gao YW, Han DL, He C. N6-methyladenosine of chromosome-associated regulatory RNA regulates chromatin state and transcription. Science, 2020, 367(6477): 580-586.
doi: 10.1126/science.aay6018 pmid: 31949099 |
| [59] |
Liu JD, Gao MW, He JP, Wu KX, Lin SY, Jin LM, Chen YP, Liu H, Shi JJ, Wang XW, Chang L, Lin YY, Zhao YL, Zhang XF, Zhang M, Luo GZ, Wu GM, Pei DQ, Wang J, Bao XC, Chen JK. The RNA m6A reader YTHDC1 silences retrotransposons and guards ES cell identity. Nature, 2021, 591(7849): 322-326.
doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03313-9 |
| [60] |
Selmi T, Lanzuolo C. Driving chromatin organisation through N6-methyladenosine modification of RNA: what do we know and what lies ahead? Genes (Basel), 2022, 13(2): 340.
doi: 10.3390/genes13020340 |
| [61] |
Percharde M, Lin CJ, Yin YF, Guan J, Peixoto GA, Bulut-Karslioglu A, Biechele S, Huang B, Shen XH, Ramalho-Santos M. A LINE1-Nucleolin partnership regulates early development and ESC identity. Cell, 2018, 174(2): 391-405.e19.
doi: S0092-8674(18)30655-X pmid: 29937225 |
| [62] |
Chen C, Liu WQ, Guo JY, Liu YY, Liu XL, Liu J, Dou XY, Le RR, Huang YX, Li C, Yang LY, Kou XC, Zhao YH, Wu Y, Chen JY, Wang H, Shen B, Gao YW, Gao SR. Nuclear m6A reader YTHDC1 regulates the scaffold function of LINE1 RNA in mouse ESCs and early embryos. Protein Cell, 2021, 12(6): 455-474.
doi: 10.1007/s13238-021-00837-8 |
| [63] | Sommerkamp P. Substrates of the m6A demethylase FTO: FTO-LINE1 RNA axis regulates chromatin state in mESCs. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2022, 7(1): 212. |
| [64] |
Wei JB, Yu XB, Yang L, Liu XL, Gao BY, Huang BX, Dou XY, Liu J, Zou ZY, Cui XL, Zhang LS, Zhao XS, Liu QZ, He PC, Sepich-Poore C, Zhong N, Liu WQ, Li YH, Kou XC, Zhao YH, Wu Y, Cheng XJ, Chen C, An YM, Dong XY, Wang HY, Shu Q, Hao ZY, Duan T, He YY, Li XK, Gao SR, Gao YW, He C. FTO mediates LINE1 m6A demethylation and chromatin regulation in mESCs and mouse development. Science, 2022, 376(6596): 968-973.
doi: 10.1126/science.abe9582 |
| [65] |
Li Y, Xia LJ, Tan KF, Ye XD, Zuo ZX, Li MC, Xiao R, Wang ZH, Liu XN, Deng MQ, Cui JR, Yang MT, Luo QZ, Liu S, Cao X, Zhu HR, Liu TQ, Hu JX, Shi JF, Xiao S, Xia LX. N6-methyladenosine co-transcriptionally directs the demethylation of histone H3K9me2. Nat Genet, 2020, 52(9): 870-877.
doi: 10.1038/s41588-020-0677-3 |
| [66] |
Chelmicki T, Roger E, Teissandier A, Dura M, Bonneville L, Rucli S, Dossin F, Fouassier C, Lameiras S, Bourc’his D. m6A RNA methylation regulates the fate of endogenous retroviruses. Nature, 2021, 591(7849): 312-316.
doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-03135-1 |
| [67] |
Rodic N. LINE-1 activity and regulation in cancer. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed), 2018, 23(9): 1680-1686.
doi: 10.2741/4666 pmid: 29293456 |
| [68] |
Gu ZM, Liu YX, Zhang Y, Cao H, Lyu JH, Wang X, Wylie A, Newkirk SJ, Jones AE, Lee M, Botten GA, Deng M, Dickerson KE, Zhang CC, An WF, Abrams JM, Xu J. Silencing of LINE-1 retrotransposons is a selective dependency of myeloid leukemia. Nat Genet, 2021, 53(5): 672-682.
doi: 10.1038/s41588-021-00829-8 pmid: 33833453 |
| [1] | 刘羽诚, 申妍婷, 田志喜. 大豆泛基因组研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2024, 46(3): 183-198. |
| [2] | 廉小平, 黄光福, 张玉娇, 张静, 胡凤益, 张石来. 长雄野生稻有利基因的发掘与利用[J]. 遗传, 2023, 45(9): 765-780. |
| [3] | 时文睿, 渠鸿竹, 方向东. 痛风的多组学研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2023, 45(8): 643-657. |
| [4] | 马钧, 樊安平, 王武生, 张金川, 江晓军, 马瑞军, 贾社强, 刘飞, 雷初朝, 黄永震. 全基因组重测序解析秦川牛保种群遗传多样性和遗传结构[J]. 遗传, 2023, 45(7): 602-616. |
| [5] | 高智慧, 黄佳新, 罗昊玉, 徐海冬, 娄明, 宁博林, 邢晓旭, 牟芳, 李辉, 王宁. 鸡NRG4基因组及转录本结构分析[J]. 遗传, 2023, 45(5): 447-458. |
| [6] | 王舜泽, 江丰, 朱东丽, 杨铁林, 郭燕. Hi-C技术在三维基因组学和疾病致病机理研究中的应用[J]. 遗传, 2023, 45(4): 279-294. |
| [7] | 徐丹同, 王祎菲, 蔡佳丽, 龚文滔, 潘向春, 田雨晗, 沈箐鹏, 李加琪, 袁晓龙. 利用人类全基因组亚硫酸氢盐测序数据检测CNVs的研究[J]. 遗传, 2023, 45(4): 324-340. |
| [8] | 陈栋, 王书杰, 赵真坚, 姬祥, 申琦, 余杨, 崔晟頔, 王俊戈, 陈子旸, 王金勇, 郭宗义, 吴平先, 唐国庆. 基于机器学习的猪生长性状基因组预测[J]. 遗传, 2023, 45(10): 922-932. |
| [9] | 陈荟玉, 赵素文. 噬菌体Z基因组生物合成通路的研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2023, 45(10): 887-903. |
| [10] | 夏凯, 刘芳美, 陈雨晴, 陈珊珊, 黄春莹, 赵学群, 沙如意, 黄俊. 基于比较基因组学的解脂亚罗酵母CA20高产赤藓糖醇机理及进化分析[J]. 遗传, 2023, 45(10): 904-921. |
| [11] | 陈秀丽, 黄海燕, 吴强. 靶向敲除β-珠蛋白基因座控制区增强子HS2对K562细胞转录组的影响[J]. 遗传, 2022, 44(9): 783-797. |
| [12] | 许梦萱, 周明. 植物RNA聚合酶IV调控DNA甲基化和发育的研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2022, 44(7): 567-580. |
| [13] | 平婉菁, 刘逸宸, 付巧妹. 沉积物古DNA探秘灭绝古人类演化[J]. 遗传, 2022, 44(5): 362-369. |
| [14] | 徐纪明, 朱建树, 李梦真, 胡晗, 毛传澡. 侧翼序列获取技术研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2022, 44(4): 313-321. |
| [15] | 刘聪, 冯佳妮, 李玮玮, 朱伟伟, 薛云新, 王岱, 赵西林. 细胞dNTP库的稳态维持与基因组稳定性[J]. 遗传, 2022, 44(2): 96-106. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||

www.chinagene.cn
备案号:京ICP备09063187号-4
总访问:,今日访问:,当前在线:
