遗传 ›› 2025, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (7): 786-796.doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.24-364
刘姣姣1,2( ), 卢心河1,2(
), 卢心河1,2( ), 殷红彦3, 周海龙2(
), 殷红彦3, 周海龙2( ), 李汉增1(
), 李汉增1( ), 徐顺清1(
), 徐顺清1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-12-02
修回日期:2025-01-15
出版日期:2025-07-20
发布日期:2025-03-13
通讯作者:
周海龙,博士,教授,研究方向:海洋环境生物学。E-mail: hlongzhou@163.com;作者简介:刘姣姣,硕士研究生,专业方向:生物与医药(生物信息学)。E-mail: jjiaoliu@hainanu.edu.cn刘姣姣和卢心河并列第一作者。
基金资助:
Jiaojiao Liu1,2( ), Xinhe Lu1,2(
), Xinhe Lu1,2( ), Hongyan Yin3, Hailong Zhou2(
), Hongyan Yin3, Hailong Zhou2( ), Hanzeng Li1(
), Hanzeng Li1( ), Shunqing Xu1(
), Shunqing Xu1( )
)
Received:2024-12-02
Revised:2025-01-15
Published:2025-07-20
Online:2025-03-13
Supported by:摘要:
秀丽线虫(C. elegans)是生物学研究的重要模式生物之一,在自然环境中选择细菌食物来源时表现出明显的偏好,然而食物选择这一与进化优势息息相关的生理现象背后的机制并不完全清楚。乙酸钙不动杆菌(Acinetobacter calcoaceticus,Ac)是一种广泛分布于潮湿环境中的革兰氏阴性杆菌。本研究通过比较秀丽线虫在两种细菌食源下的食物偏好性、咽泵频率、体脂含量、寿命长短以及基因表达差异,揭示了秀丽线虫摄食Ac引起脂质代谢变化以及摄食偏好行为,并利用转录组学方法分析了秀丽线虫摄食大肠杆菌OP50和Ac后的基因表达差异,为理解秀丽线虫与微生物互作机制提供了新的视角。
刘姣姣, 卢心河, 殷红彦, 周海龙, 李汉增, 徐顺清. 基于转录组学分析秀丽线虫对乙酸钙不动杆菌的摄食偏好行为[J]. 遗传, 2025, 47(7): 786-796.
Jiaojiao Liu, Xinhe Lu, Hongyan Yin, Hailong Zhou, Hanzeng Li, Shunqing Xu. Analysis of food preference behavior of C. elegans to Acinetobacter calcoaceticus based on transcriptomics[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2025, 47(7): 786-796.
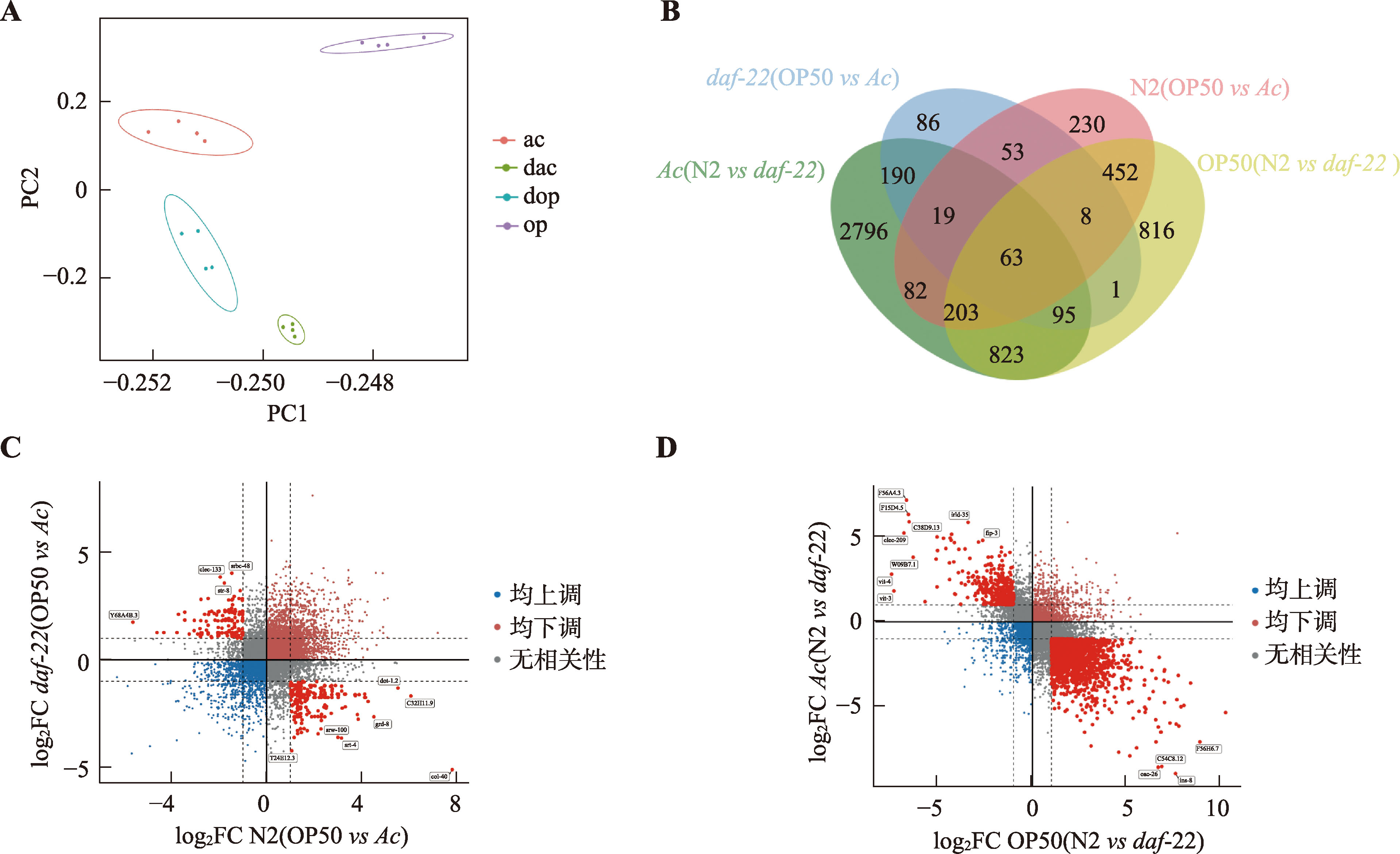
图3
差异基因表达筛选结果 A:4组样本主成分分析图。ac:N2秀丽线虫摄食Ac;dac:daf-22突变型秀丽线虫摄食Ac;dop:daf-22突变型秀丽线虫摄食OP50;op:N2秀丽线虫摄食OP50;B:4组样本韦恩图。N2(OP50 vs Ac):摄食OP50和Ac的两种N2秀丽线虫之间比较;daf-22(OP50 vs Ac):摄食OP50和Ac的两种daf-22突变型秀丽线虫之间比较;OP50(N2 vs daf-22):摄食OP50的N2和daf-22突变型两种秀丽线虫之间比较;Ac(N2 vs daf-22):摄食Ac的N2和daf-22突变型两种秀丽线虫之间比较;C:摄食OP50和Ac的两种N2秀丽线虫与摄食OP50和Ac的两种daf-22突变型秀丽线虫的变化趋势基因图;D:摄食OP50的N2和daf-22突变型两种秀丽线虫与摄食Ac的N2和daf-22突变型两种秀丽线虫的变化趋势基因图。"
| [1] |
Zečić A, Dhondt I, Braeckman BP. The nutritional requirements of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genes Nutr, 2019, 14: 15.
pmid: 31080524 |
| [2] |
Zhang JY, Holdorf AD, Walhout AJ. C. elegans and its bacterial diet as a model for systems-level understanding of host-microbiota interactions. Curr Opin Biotechnol, 2017, 46: 74-80.
pmid: 28189107 |
| [3] |
Schulenburg H, Félix MA. The natural biotic environment of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics, 2017, 206(1): 55-86.
pmid: 28476862 |
| [4] |
Abada EA, Sung H, Dwivedi M, Park BJ, Lee SK, Ahnn J. C. elegans behavior of preference choice on bacterial food. Mol Cells, 2009, 28(3): 209-213.
pmid: 19756391 |
| [5] |
Freyth K, Janowitz T, Nunes F, Voss M, Heinick A, Bertaux J, Scheu S, Paul RJ. Reproductive fitness and dietary choice behavior of the genetic model organism Caenorhabditis elegans under semi-natural conditions. Mol Cells, 2010, 30(4): 347-353.
pmid: 20821059 |
| [6] |
Kim DH, Flavell SW. Host-microbe interactions and the behavior of Caenorhabditis elegans. J Neurogenet, 2020, 34(3-4): 500-509.
pmid: 32781873 |
| [7] |
Shtonda BB, Avery L. Dietary choice behavior in Caenorhabditis elegans. J Exp Biol, 2006, 209(Pt 1): 89-102.
pmid: 16354781 |
| [8] |
Zhang Y, Lu H, Bargmann CI. Pathogenic bacteria induce aversive olfactory learning in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature, 2005, 438(7065): 179-184.
pmid: 16281027 |
| [9] |
Haçariz O, Viau C, Karimian F, Xia JG. The symbiotic relationship between Caenorhabditis elegans and members of its microbiome contributes to worm fitness and lifespan extension. BMC Genomics, 2021, 22(1): 364.
pmid: 34011272 |
| [10] |
Midha A, Schlosser J, Hartmann S. Reciprocal interactions between nematodes and their microbial environments. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2017, 7: 144.
pmid: 28497029 |
| [11] |
Benoit T, Sajjad D, Cloutier M, Lapen DR, Craiovan E, Sykes EME, Kumar A, Khan IUH. Acinetobacter calcoaceticus-baumannii complex prevalence, spatial- temporal distribution, and contamination sources in Canadian aquatic environments. Microbiol Spectr, 2024, 12(10): e0150924.
pmid: 39240108 |
| [12] | Yuan WQ. Clinical distribution and drug resistance of 417 strains of Acinetobacter calcoaceticus. Chin Pract Med, 2013, 8(16): 154-155. |
| 袁文清. 417株醋酸钙不动杆菌的临床分布及耐药性研究. 中国实用医药, 2013, 8(16): 154-155. | |
| [13] | Li Y, Wang XY, Luo H, Yang MD, Li J, Li LF, Zhao JP, Bi J, Chen B, Wang RG. Application of Caenorhabditis elegans in pathogenicity evaluation of Acinetobacter calcoaceticus. J Environ Health, 2020, 37(3): 228-232. |
| 李煜, 王雪岩, 罗环, 杨梦迪, 梁婧, 李隆飞, 赵金萍, 毕洁, 陈斌, 王如刚. 秀丽隐杆线虫在乙酸钙不动杆菌致病性评价中的应用. 环境与健康杂志, 2020, 37(3): 228-232. | |
| [14] |
Butcher RA, Ragains JR, Li WQ, Ruvkun G, Clardy J, Mak HY. Biosynthesis of the Caenorhabditis elegans dauer pheromone. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2009, 106(6): 1875-1879.
pmid: 19174521 |
| [15] |
Lee D, Fox BW, Palomino DF, Panda O, Tenjo FJ, Koury EJ, Evans KS, Stevens L, Rodrigues PR, Kolodziej AR, Schroeder FC, Andersen EC. Natural genetic variation in the pheromone production of C. elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2023, 120(26): e2221150120.
pmid: 37339205 |
| [16] |
Ren HS, Yin K, Lu XH, Liu JJ, Li DD, Liu ZJ, Zhou HL, Xu SQ, Li HZ. Synergy between nanoplastics and benzo[a]pyrene promotes senescence by aggravating ferroptosis and impairing mitochondria integrity in Caenorhabditis elegans. Sci Total Environ, 2024, 946: 174418.
pmid: 38960162 |
| [17] |
Wan QL, Meng X, Wang CY, Dai WY, Luo ZH, Yin ZN, Ju ZY, Fu XD, Yang J, Ye QS, Zhang ZH, Zhou QH. Histone H3K4me3 modification is a transgenerational epigenetic signal for lipid metabolism in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nat Commun, 2022, 13(1): 768.
pmid: 35140229 |
| [18] |
Guo XL, Zhang HL, Zheng XP, Zhou QJ, Yang Y, Chen XQ, Du AF. Structural and functional characterization of a novel gene, Hc-daf-22, from the strongylid nematode Haemonchus contortus. Parasit Vectors, 2016, 9(1): 422.
pmid: 27472920 |
| [19] |
Yu GC. Thirteen years of clusterProfiler. Innovation (Camb), 2024, 5(6): 100722.
pmid: 39529960 |
| [20] |
Love MI, Huber W, Anders S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol, 2014, 15(12): 550.
pmid: 25516281 |
| [21] |
Xu SB, Hu EQ, Cai YT, Xie ZJ, Luo X, Zhan L, Tang WL, Wang QW, Liu BD, Wang R, Xie WQ, Wu TZ, Xie LW, Yu GC. Using clusterProfiler to characterize multiomics data. Nat Protoc, 2024, 19(11): 3292-3320.
pmid: 39019974 |
| [22] | Ginestet C. ggplot2: C.elegant graphics for data analysis. J R Stat Soc A Stat, 2011, 174(1): 245-246. |
| [23] |
Chan JP, Wright JR, Wong HT, Ardasheva A, Brumbaugh J, McLimans C, Lamendella R. Using bacterial transcriptomics to investigate targets of host-bacterial interactions in Caenorhabditis elegans. Sci Rep, 2019, 9(1): 5545.
pmid: 30944351 |
| [24] |
Li Y, Ding WQ, Li CY, Liu Y. HLH-11 modulates lipid metabolism in response to nutrient availability. Nat Commun, 2020, 11(1): 5959.
pmid: 33235199 |
| [25] |
Zhang YR, Zou XJ, Ding YH, Wang HZ, Wu XY, Liang B. Comparative genomics and functional study of lipid metabolic genes in Caenorhabditis elegans. BMC Genomics, 2013, 14: 164.
pmid: 23496871 |
| [26] |
Yu L, Yan XM, Ye CL, Zhao HY, Chen XY, Hu F, Li HX. Bacterial respiration and growth rates affect the feeding preferences, brood size and lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans. PLoS One, 2015, 10(7): e0134401.
pmid: 26222828 |
| [27] |
Khan F, Jain S, Oloketuyi SF. Bacteria and bacterial products: foe and friends to Caenorhabditis elegans. Microbiol Res, 2018, 215: 102-113.
pmid: 30172296 |
| [28] |
White JQ, Nicholas TJ, Gritton J, Truong L, Davidson ER, Jorgensen EM. The sensory circuitry for sexual attraction in C. elegans males. Curr Biol, 2007, 17(21): 1847-1857.
pmid: 17964166 |
| [29] | Yi JX, Li R, Chen QL, Luo HW, Li DL, Wang F. Bx-Daf-22 in bursaphelenchus xylophilus (Aphelenchida: Aphelenchoididae): cloning and expression. Chin Agric Sci Bull, 2018, 34(30): 71-75. |
| 易家娴, 李仁, 陈俏丽, 罗洪巍, 李丹蕾, 王峰. 松材线虫Bx-Daf-22基因鉴定及表达. 中国农学通报, 2018, 34(30): 71-75. |
| [1] | 陈敏, 韩娜, 缪玉, 强裕俊, 张雯, 刘蓬勃, 刘起勇, 栗冬梅. 物种分化因素影响下的巴尔通体差异转录组分析[J]. 遗传, 2025, 47(3): 366-381. |
| [2] | 韩超飞, 陈灵, 王源秀, 程前, 左胜, 刘华彬, 王程亮. 基于转录组学挖掘与分析NJ9108水稻种子寿命的关键基因[J]. 遗传, 2025, 47(3): 351-365. |
| [3] | 韦恒, 刘天鹏, 何继红, 董孔军, 任瑞玉, 张磊, 李亚伟, 郝子义, 杨天育. 糜子GRF转录因子全基因组鉴定及在茎分生组织中的表达特征[J]. 遗传, 2024, 46(3): 242-255. |
| [4] | 温馨, 梅锦, 钱美玉, 蒋一丹, 王娟, 许士博, 王翠喆, 张君. 基于转录组测序对GULP1下游靶基因筛选及分析[J]. 遗传, 2024, 46(10): 860-870. |
| [5] | 徐晓鹏, 范小英. 单细胞精度的表达数量性状位点研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2024, 46(10): 795-806. |
| [6] | 时文睿, 渠鸿竹, 方向东. 痛风的多组学研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2023, 45(8): 643-657. |
| [7] | 韩熙, 罗富成. 单细胞转录组测序在少突胶质谱系细胞异质性与神经系统疾病中的应用[J]. 遗传, 2023, 45(3): 198-211. |
| [8] | 郭彦, 杨乐乐, 戚华宇. 小鼠雄性生殖干细胞转录组分析揭示成熟精原干细胞特征[J]. 遗传, 2022, 44(7): 591-608. |
| [9] | 骆红波, 曹鹏博, 周钢桥. DNA甲基化驱动的转录表达特征作为肝癌预后预测标志物的价值[J]. 遗传, 2020, 42(8): 775-787. |
| [10] | 石田培,张莉. 全转录组学在畜牧业中的应用[J]. 遗传, 2019, 41(3): 193-205. |
| [11] | 张高华, 于树涛, 王鹤, 王旭达. 高油酸花生发芽期低温胁迫转录组及差异表达基因分析[J]. 遗传, 2019, 41(11): 1050-1059. |
| [12] | 任岚,肖茹丹,张倩,娄晓敏,张昭军,方向东. KLF1和KLF9对K562细胞红系分化的协同调控作用[J]. 遗传, 2018, 40(11): 998-1006. |
| [13] | 杨莹,陈宇晟,孙宝发,杨运桂. RNA甲基化修饰调控和规律[J]. 遗传, 2018, 40(11): 964-976. |
| [14] | 刘亚军,张峰,刘宏德,孙啸. 下一代测序技术在干细胞转录调控研究中的应用[J]. 遗传, 2017, 39(8): 717-725. |
| [15] | 叶仲杰,刘启鹏,岑山,李晓宇. LINE-1编码的逆转录酶在肿瘤形成过程中的作用[J]. 遗传, 2017, 39(5): 368-376. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||

www.chinagene.cn
备案号:京ICP备09063187号-4
总访问:,今日访问:,当前在线:
